Embed presentation



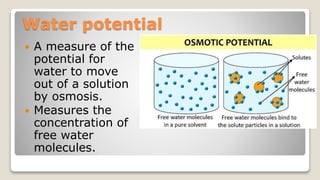

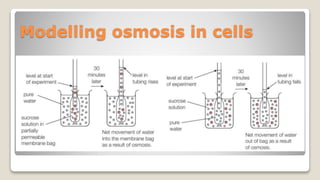

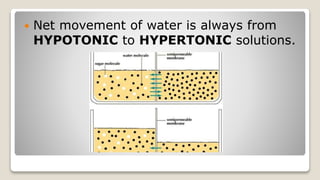
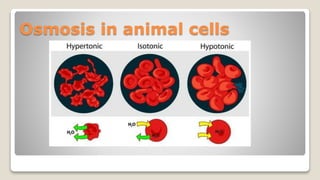
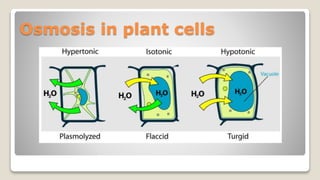
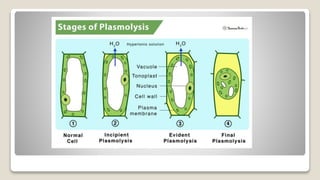
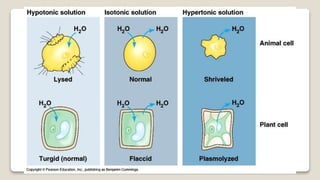

Osmosis is defined as the net movement of free water molecules through a partially permeable membrane down a water potential gradient. It occurs when a cell is placed in a solution with a different osmotic concentration - the concentration of solutes that affect water movement. If the solution has a lower osmotic concentration than the cell (hypotonic), water will move into the cell. If it has a higher concentration (hypertonic), water will move out. Net water movement is always from the hypotonic to the hypertonic solution.











