The document explains the processes of diffusion and osmosis, including their definitions and mechanisms, using examples from a gummi bear lab and dialysis bag experiments. It discusses the effects of different water concentrations on cells in hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic environments, detailing processes such as plasmolysis and turgor pressure. Additionally, it covers the concepts of passive and active transport of molecules across semi-permeable membranes.

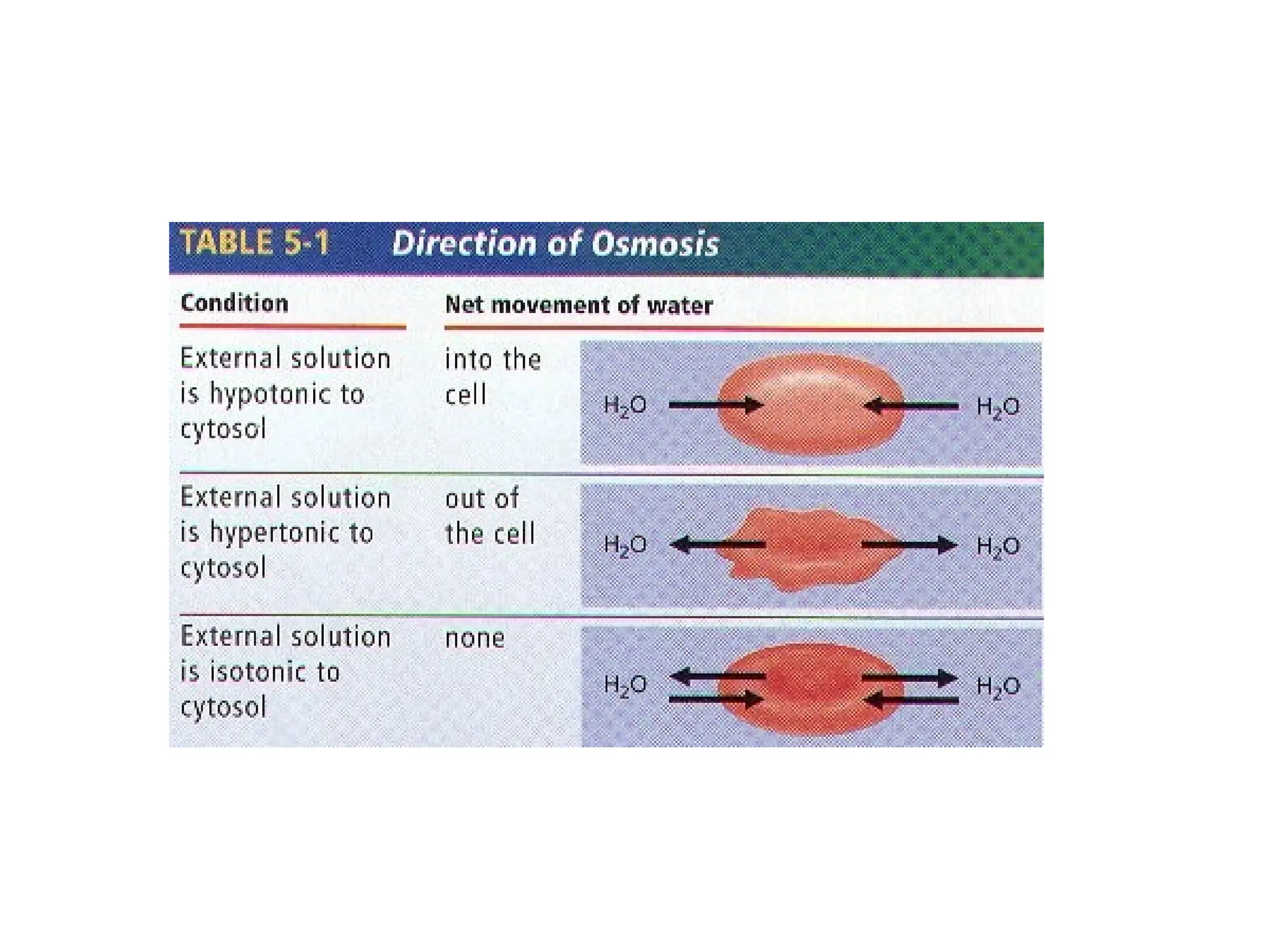
![Osmosis
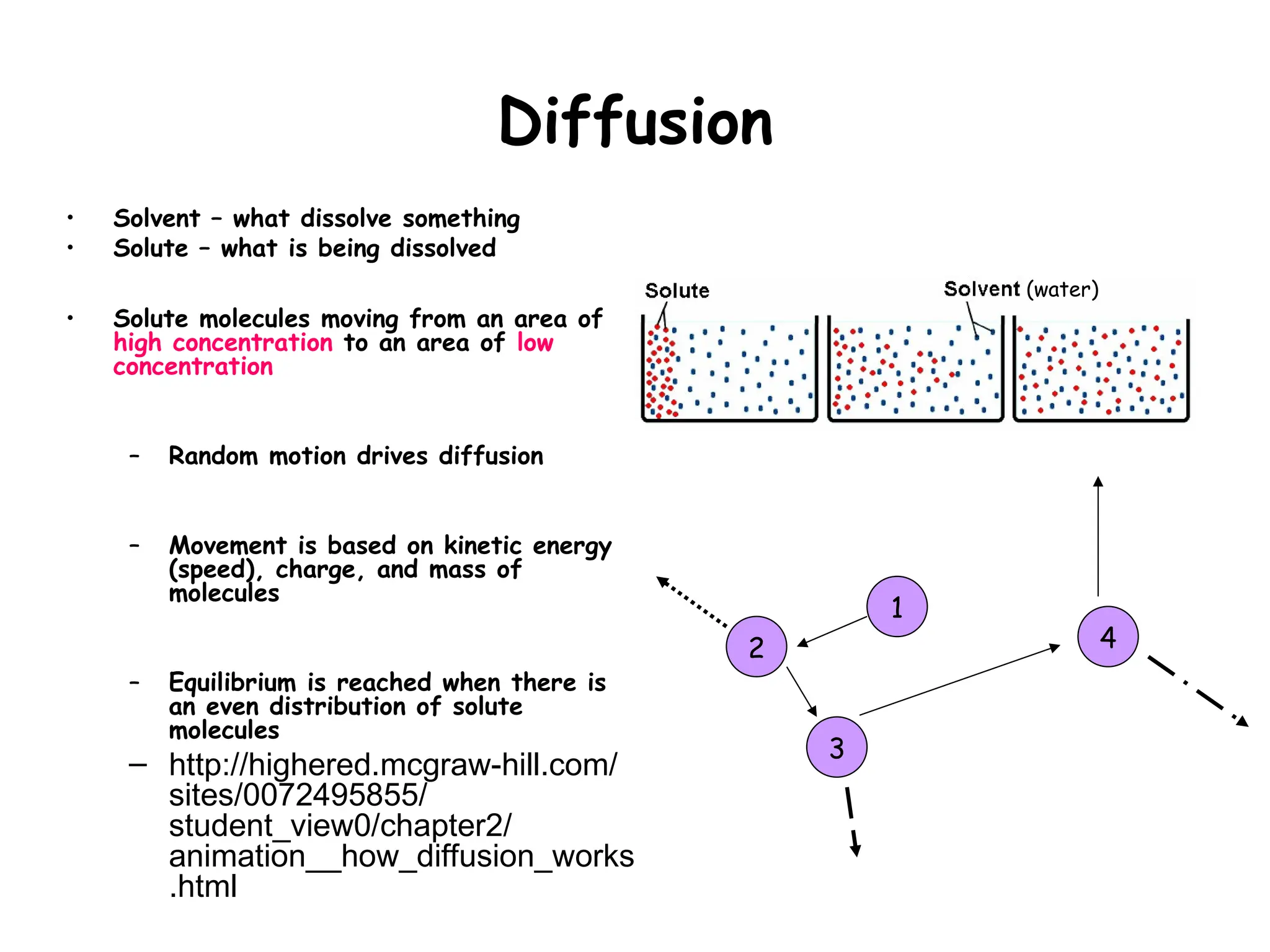
• Diffusion of water through a semi-
permeable membrane
– Semi-permeable: permeable to
solvents (WATER), but not to
large molecules
– High [water] to low [water]
• Dissolved molecules (i.e. glucose,
starch) are called solutes
• REMEMBER:
Water = solvent
Glucose, Starch = solutes
http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/
chapter2/animation__how_osmosis_works.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diffusion-and-osmosis-241201124736-be53680f/75/diffusion-and-osmosis-a-simple-introduction-ppt-4-2048.jpg)
![Effect of Water on Cells
• Hypertonic Environment
– High [solute], low [water]
– The cell will shrink
– Plasmolysis – cell death
Hypotonic Environment
– High [water], low [solute]
– Plants – turgor pressure – plant
like this!!
– Animals – cytolysis – cell
bursting
• Isotonic Environment
– [water] = [solute]
Isotonic
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
Part 3 pg. 85](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diffusion-and-osmosis-241201124736-be53680f/75/diffusion-and-osmosis-a-simple-introduction-ppt-5-2048.jpg)