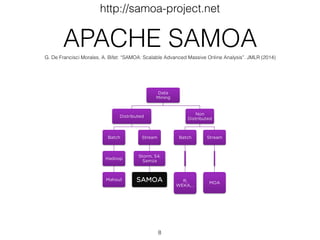
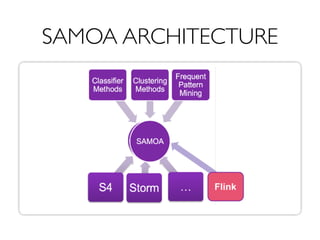
The document is a presentation on artificial intelligence (AI) and data stream mining by Albert Bifet, covering various aspects such as the definition of AI, its challenges, and machine learning for data streams. It discusses the importance of real-time analytics, characteristics of AI systems, and the need for adaptive models that can learn from changing data streams. Additionally, it introduces open-source tools like MOA and SAMOA for online learning from data streams and highlights the significance of the Internet of Things (IoT).












![Approximation Algorithms
• General idea, good for streaming algorithms
• Small error ε with high probability 1-δ
• True hypothesis H, and learned hypothesis Ĥ
• Pr[ |H - Ĥ| < ε|H| ] > 1-δ
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-imt-tpt-180316205917/85/Artificial-intelligence-and-data-stream-mining-20-320.jpg)