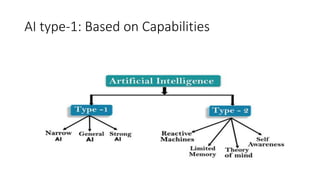
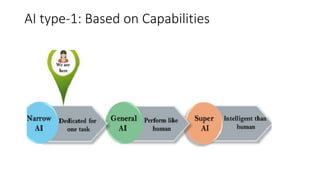
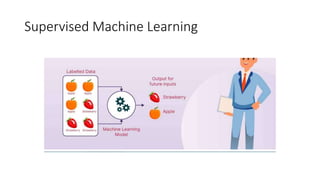
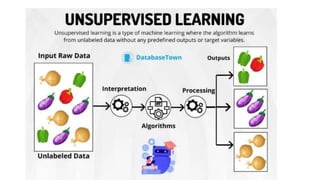
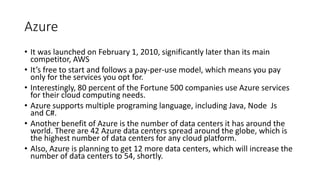
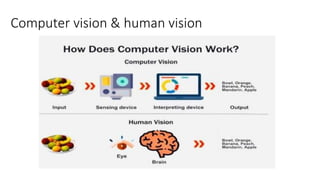
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, describing their capabilities and different types such as narrow AI, general AI, and super AI. It covers various machine learning techniques, including supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning, as well as applications in cloud computing, anomaly detection, and computer vision. Additionally, it highlights Microsoft's Azure platform, which facilitates the development and deployment of AI and machine learning solutions.