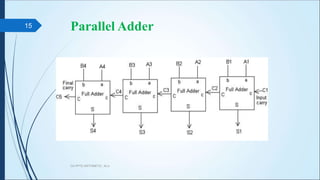
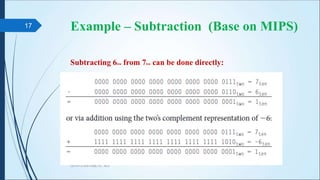
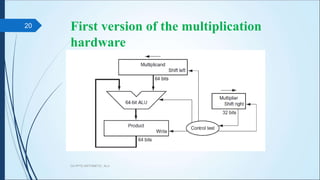
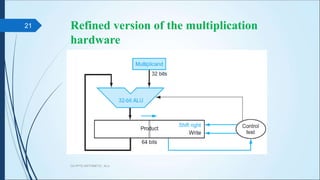
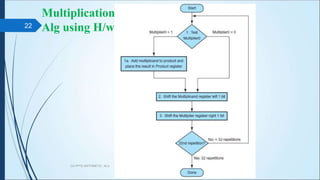
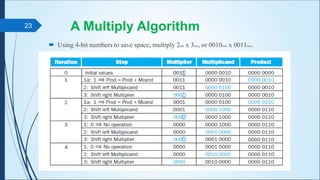
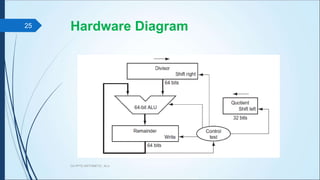
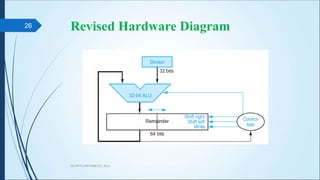
The document discusses arithmetic operations in computer architecture. It describes how the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) performs operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division on fixed-point and floating-point numbers. It explains different representations for integers like signed magnitude, one's complement and two's complement. Addition and subtraction are implemented using half adders, full adders and parallel adders. Multiplication is done by shifting and adding and division uses a repeated subtraction approach. Hardware designs for performing these operations are also presented.














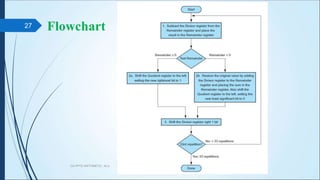
![Example: Using a 4 bit version of the Algorithm
Divide 710 by 210 [0000 0111(2) by 0010(2)]
CA PPT5 ARITHMETIC, ALU
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticlogicunit-230419071115-84c352c7/85/ARITHMETIC-LOGIC-UNIT-ppt-28-320.jpg)