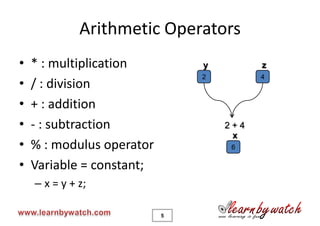
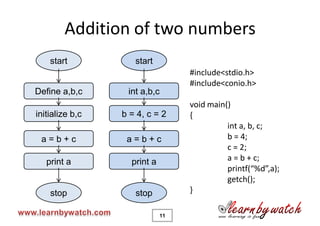
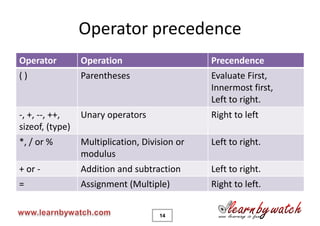
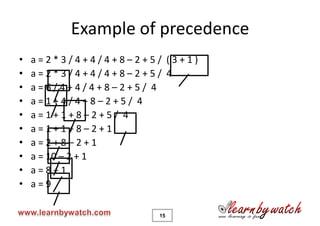
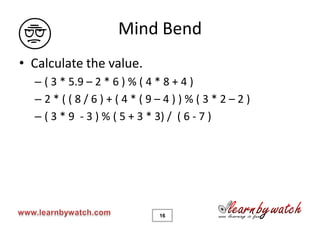
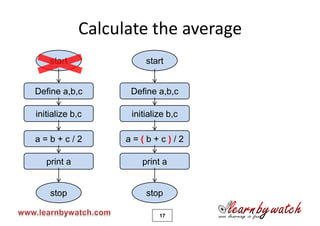
This document provides an introduction to the C programming language by Yogendra Pal. It discusses basic C concepts like data types, arithmetic operators, assignment operators, unary operators, operator precedence, and provides examples of simple programs to add two numbers, calculate the average of two numbers, and convert between kilometers and meters. The document encourages the reader to solve practice problems and quizzes on the provided website and to email the author with any questions.