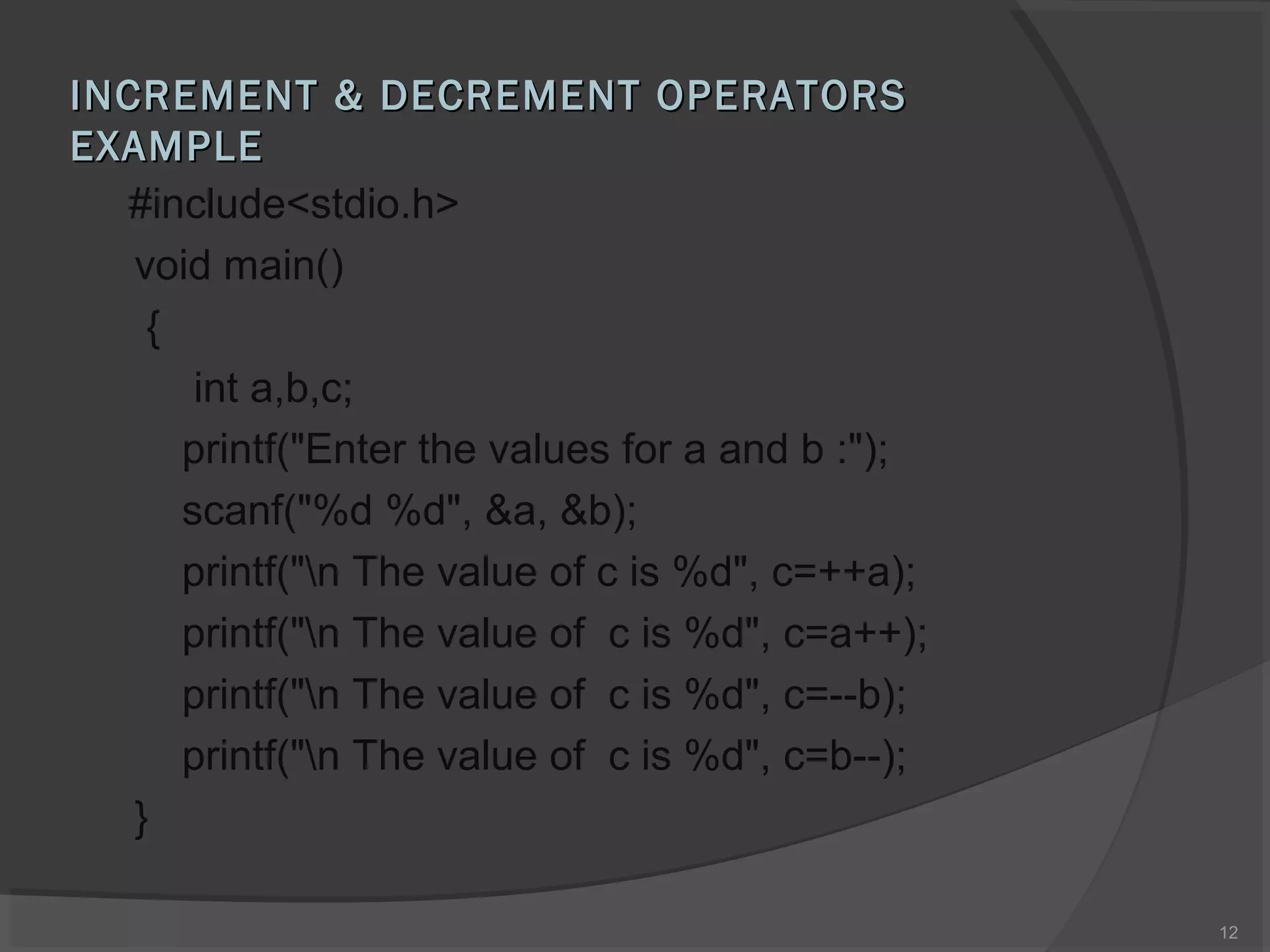
This document discusses different types of operators in C programming language. It describes arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, increment/decrement, conditional, bitwise and special operators. For each type of operator, it provides the syntax, examples of use, and meaning or purpose. The key types of operators covered are arithmetic (for math operations), relational (for comparisons), logical (for conditional logic), and assignment (for assigning values). Examples are provided to demonstrate how each operator is used in C code.