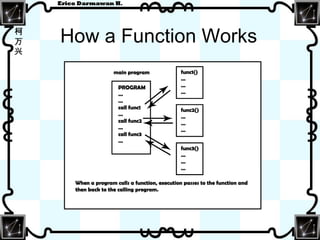
A function is a named, independent section of code that performs a specific task and optionally returns a value. The key components of a function are the function header, return type, name, parameters, body, local variables, statements, and returning a value. Recursion refers to a function calling itself directly or indirectly. Exercises include creating programs that use functions to calculate the average of integers, display text a given number of times, calculate the factorial of a number recursively and non-recursively.





![Writing a Function The function components: The Function Header [Line 12] The Function Return Type The Function Name The Parameter List The Function Body [Lines 18-19] Local Variables [Line 15] Function Statements [Lines 18] Returning a Value [Lines 19]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functions-procedures-7-1233232816482839-1/85/Functions-Procedures-7-7-320.jpg)


