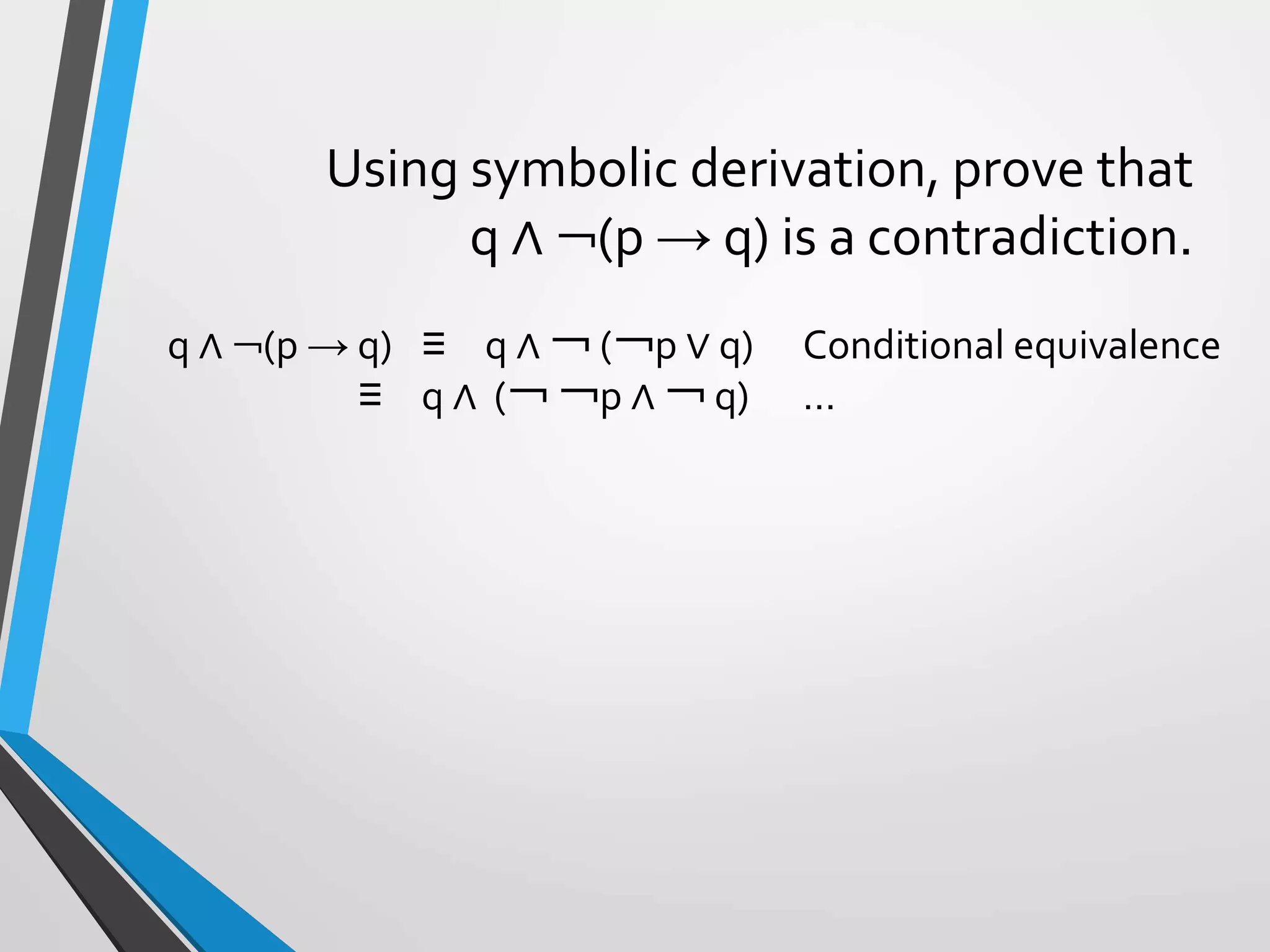
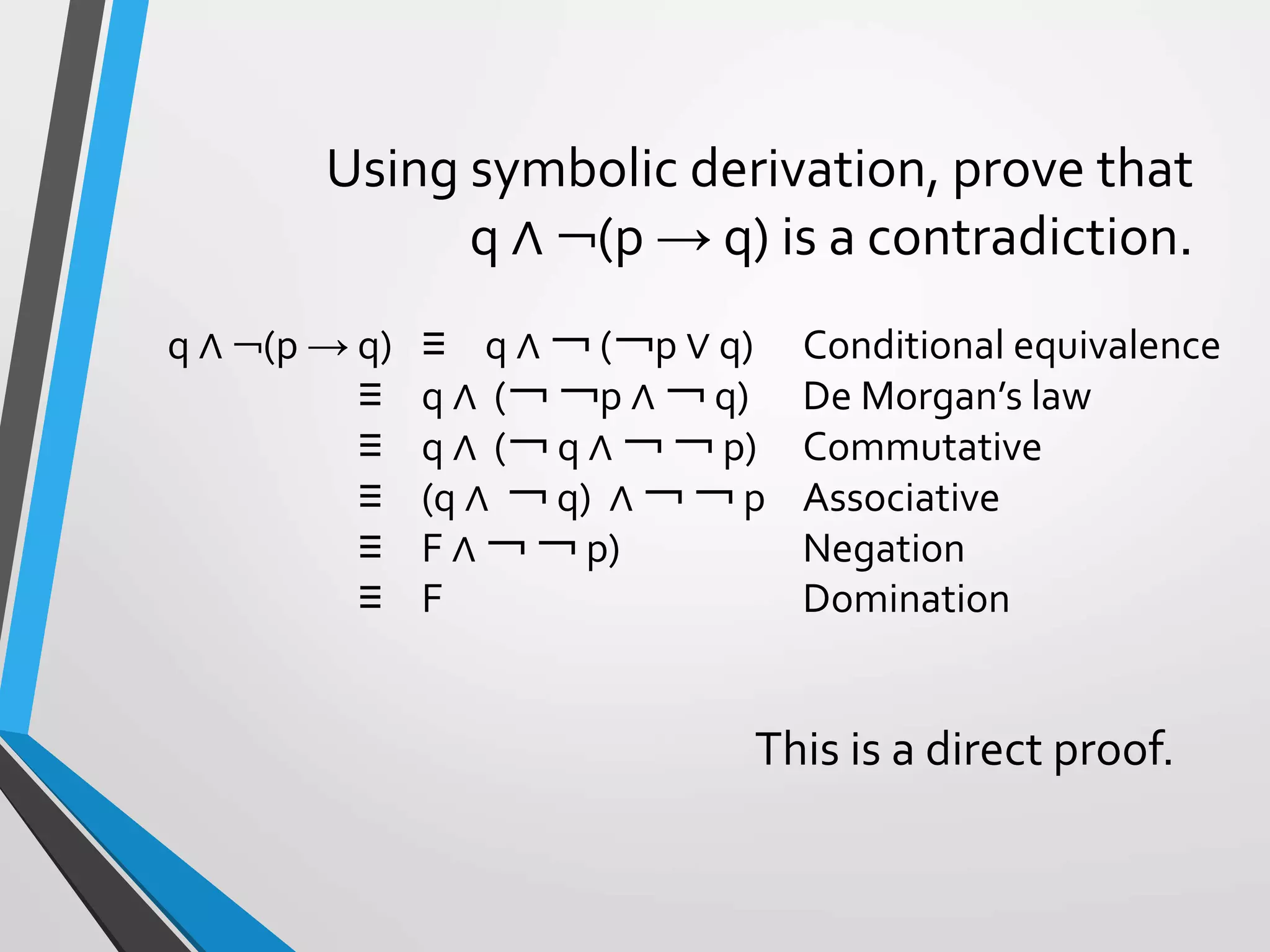
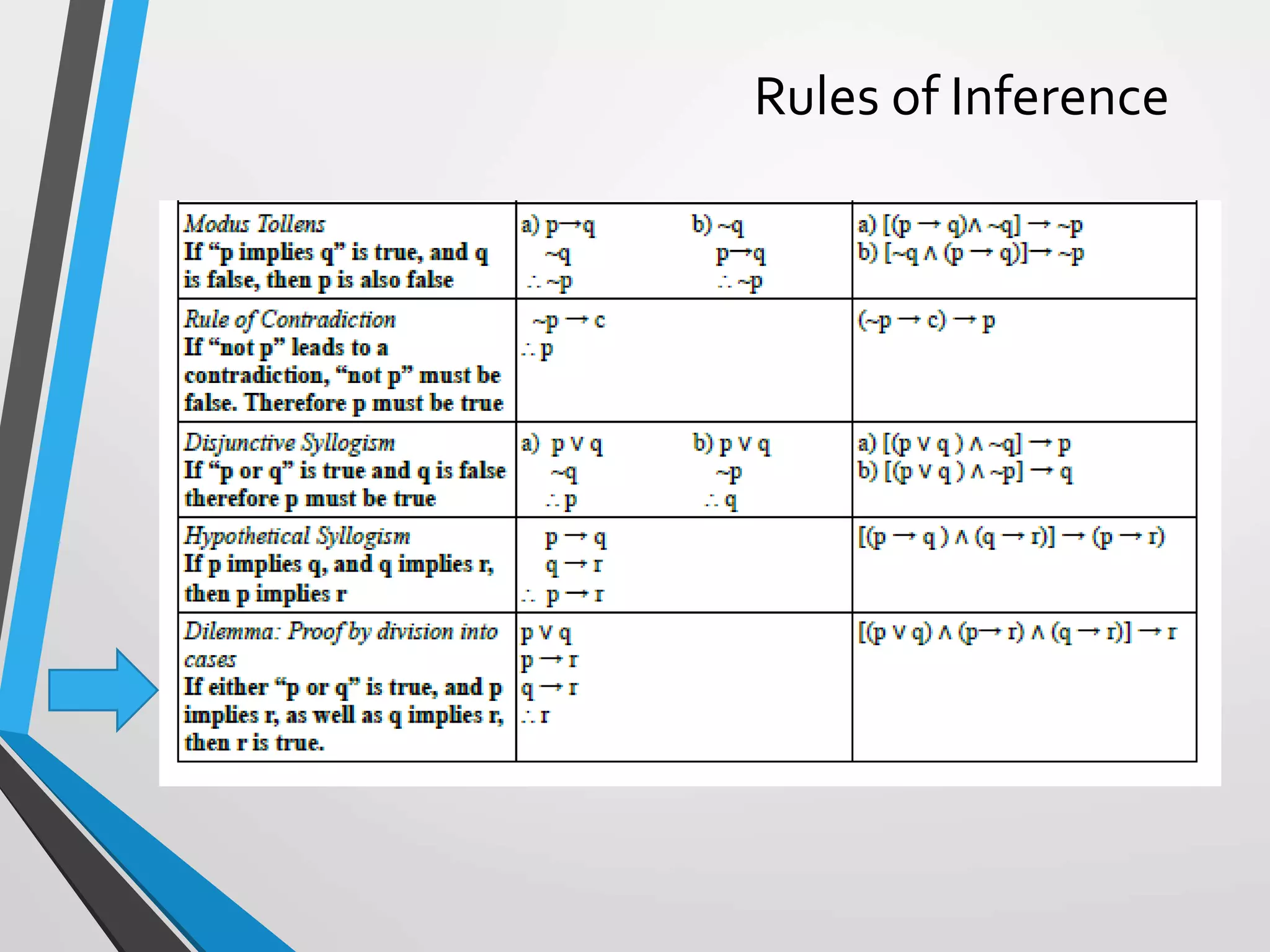
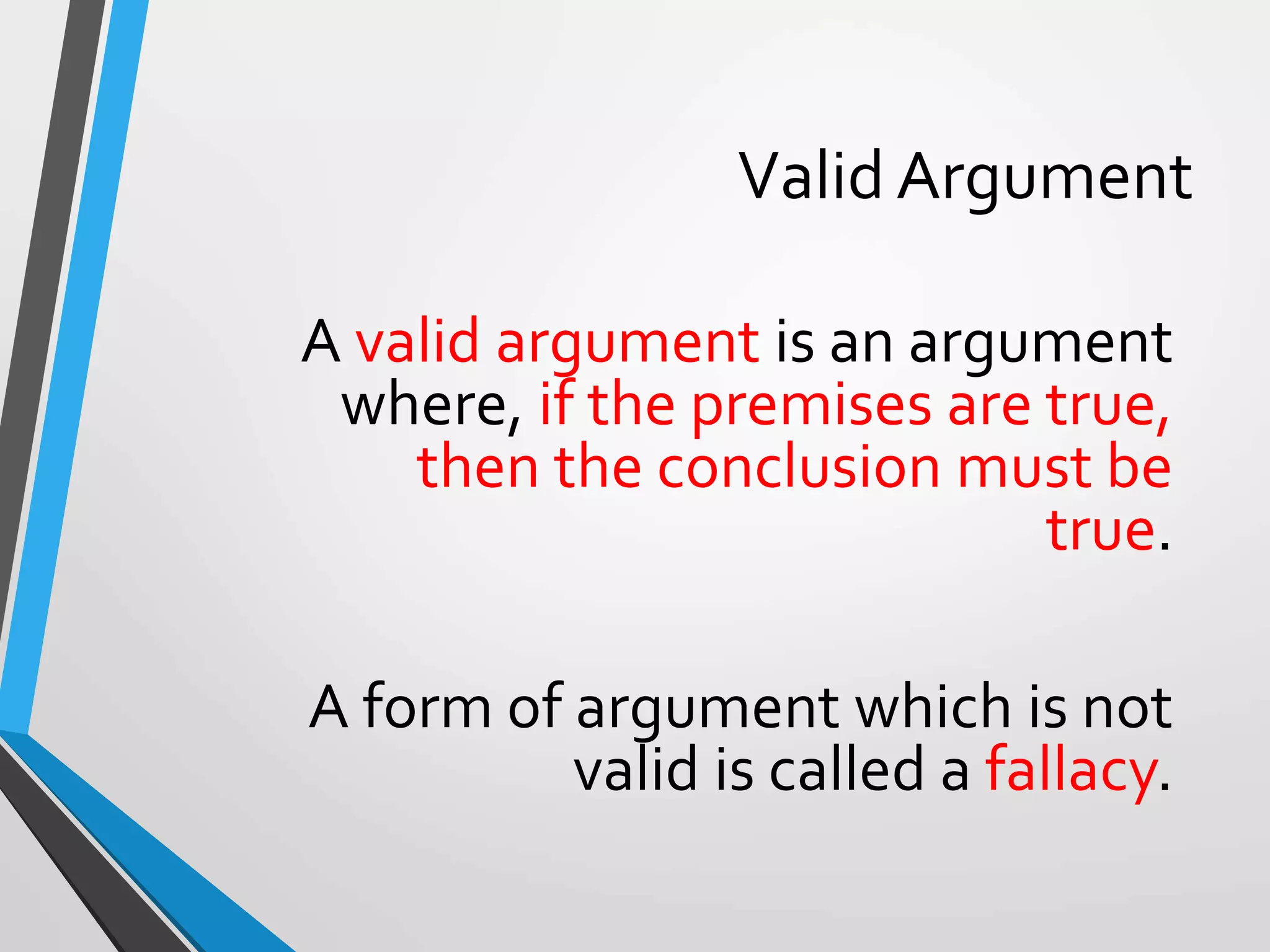
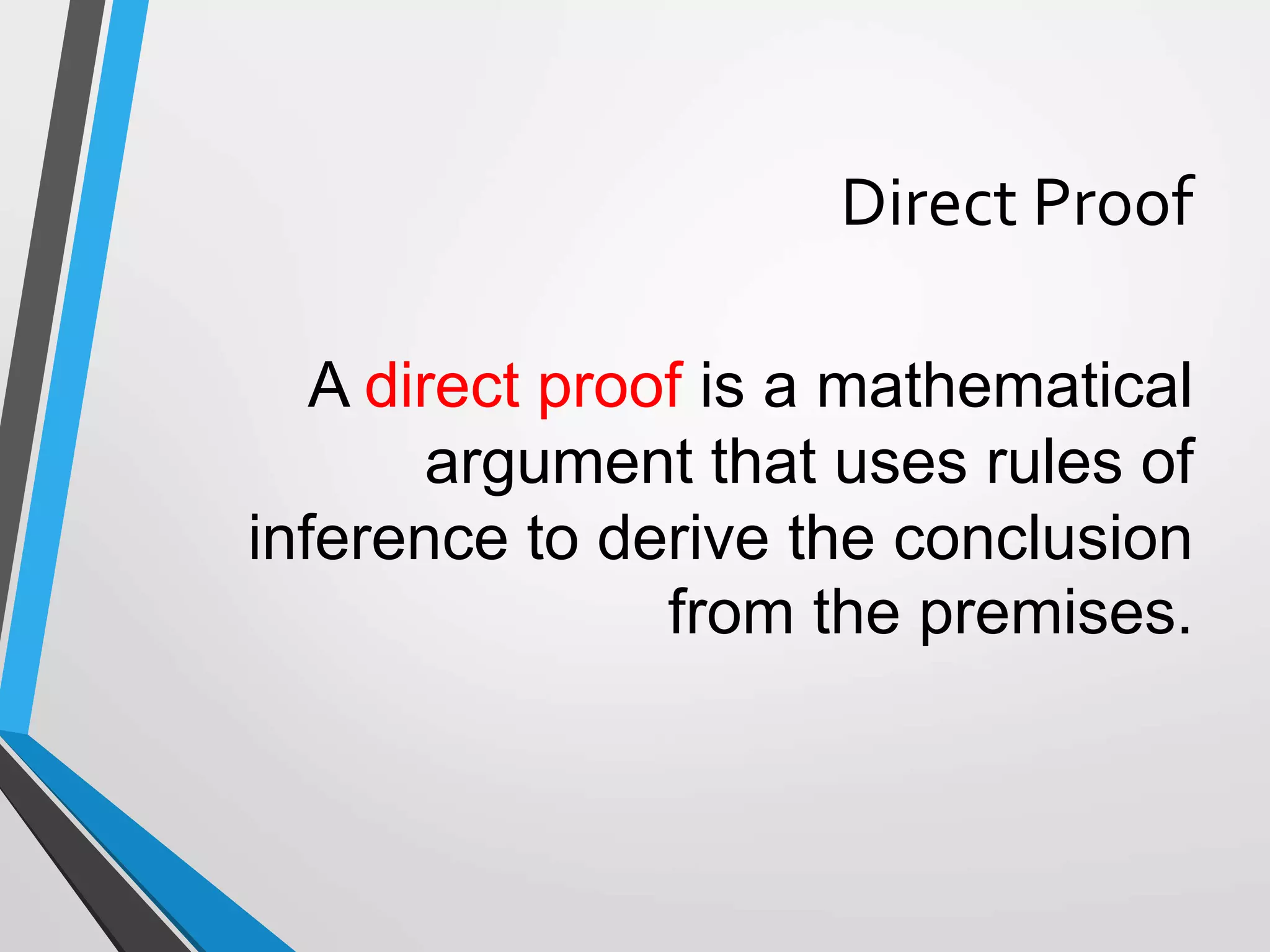
The document discusses arguments and methods of proof in discrete mathematics. It begins by defining an argument as a series of propositions that build to a conclusion. An argument is valid if the conclusion necessarily follows from true premises. The document then provides examples of valid and invalid argument forms. It introduces truth tables to assess validity and identifies common valid argument forms like modus ponens and modus tollens. The document also discusses direct proofs, proof by cases, and other proof techniques in discrete mathematics.





![Symbolically, we have…
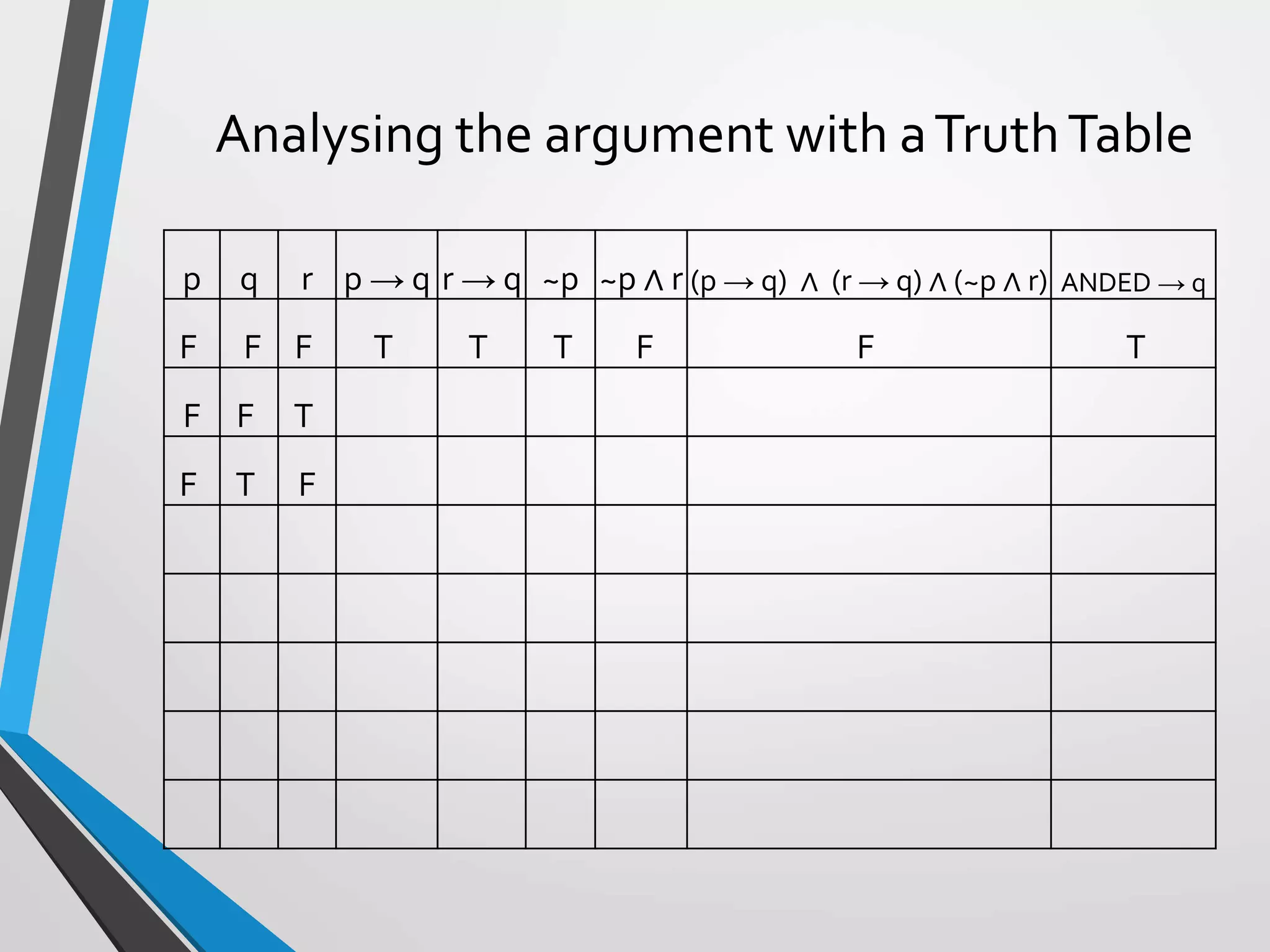
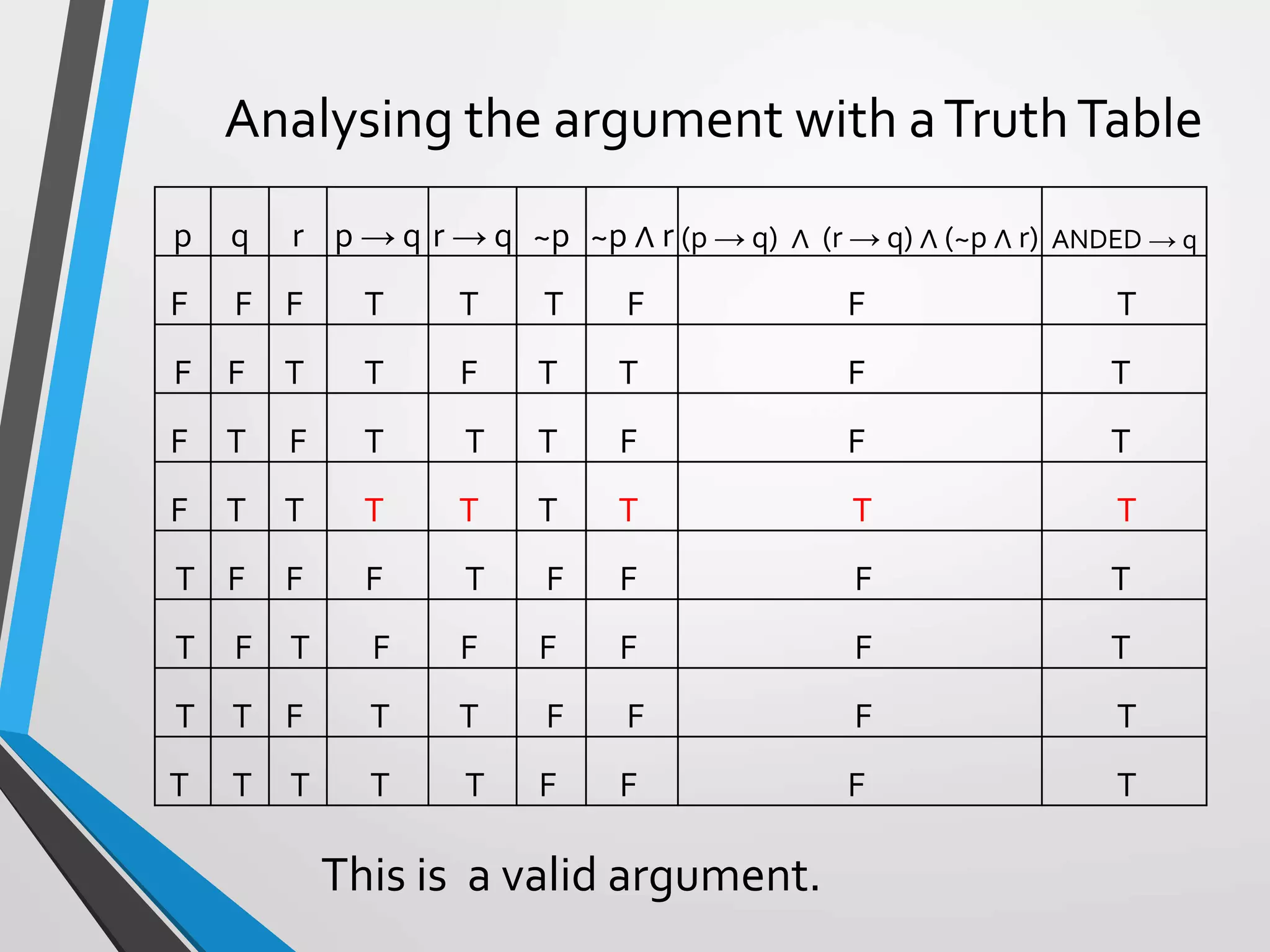
• Premises
• If p [there is cream], then q [I will drink coffee].
• If r [there is a donut], then q [I will drink coffee],
• ~p [There is no cream] and r [there is a donut].
• Conclusion
• q [I will drink coffee].
and the argument format is:
p → q
r → q
~p ∧ r
--------
q
p: there is cream
q: I will drink coffee
r: there is a donut](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-7-2048.jpg)



![Argument form…
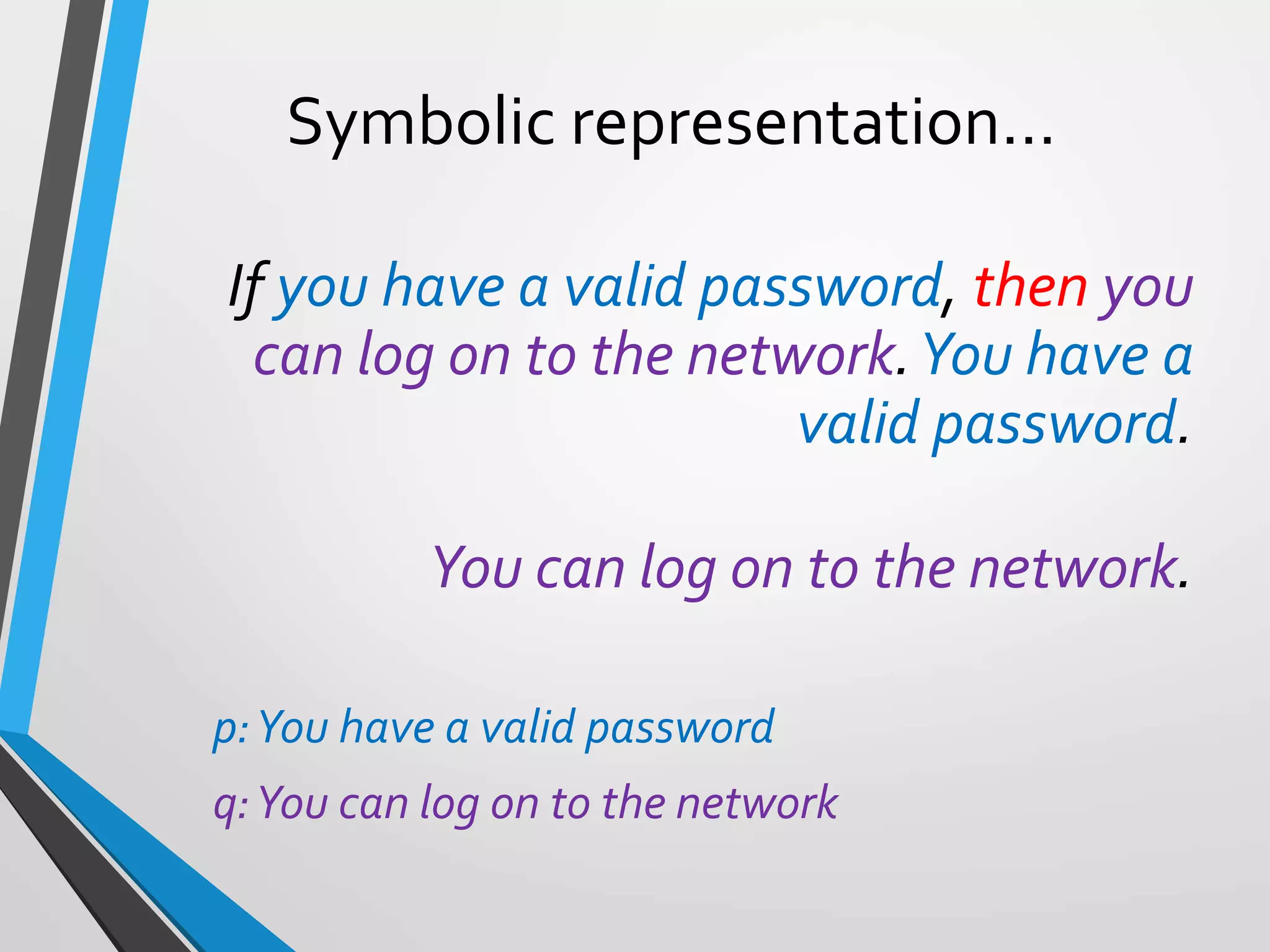
If you have a valid password, then you can log on to the
network.You have a valid password.
You can log on to the network.
p:You have a valid password
q:You can log on to the network
Argument form
p → q
P
--------
q
We can write the argument as: [p ∧ (p → q) ] → q](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-15-2048.jpg)
![Assessing validity of [p ∧ (p → q)] → q
p q p → q p ∧ (p → q) [p ∧ (p → q)] → q
F F T F T
F T T F T
T F F F T
T T T T T
The last row is where p =T and p → q =T and the argument implication is
T and so the argument is valid. It is a tautology so it is valid anyway.
•This argument form is called modus
ponens and is a valid argument.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-16-2048.jpg)



![Assessing validity of [p ∧ (p → q)] → q
p q p → q p ∧ (p → q) [p ∧ (p → q)] → q
F F T F T
F T T F T
T F F F T
T T T T T
•It is a valid argument. Do you recognise
the argument form?
*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-20-2048.jpg)
![Assessing validity of [p ∧ (p → q)] → q
p q p → q p ∧ (p → q) [p ∧ (p → q)] → q
F F T F T
F T T F T
T F F F T
T T T T T
• It is a valid argument. Do you recognise the
argument form?
• Remember we had called this modus ponens.
• We need to be able to recall the argument form as
we can simply quote that to determine whether
an argument is valid or not.
*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-21-2048.jpg)


![Argument form…
¬qYou can’t log on to the network.
If p:you have a valid password, then q you can log on
to the network.
¬p You do not have a current password.
p → q
¬ q
----------
¬ p
We can write this in shorthand as: [(p → q) ∧ ¬ q] → ¬ p](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-24-2048.jpg)
![Assessing the argument form using a truth table
p q p → q ¬p ¬q (p → q) ∧ ¬q [(p → q) ∧ ¬q] → ¬p
F F
F T
T F
T T](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-25-2048.jpg)
![Is it a valid argument?
p q p → q ¬p ¬q (p → q) ∧ ¬q [(p → q) ∧ ¬q] → ¬p
F F T T T T T
F T T T F F T
T F F F T F T
T T T F F F T
*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-26-2048.jpg)
![Is it a valid argument?
It is a valid argument.This
argument f0rm is called
modus tollens.
p q p → q ¬p ¬q (p → q) ∧ ¬q [(p → q) ∧ ¬q] → ¬p
F F T T T T T
F T T T F F T
T F F F T F T
T T T F F F T](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-27-2048.jpg)

![Assign Logical variables
If p [Mr. Scott is still with us], then
q [the power will come on].
q [The power comes on].
Therefore, p [Mr. Scott is still with us].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-29-2048.jpg)
![Argument form
If p [Mr. Scott is still
with us], then q [the
power will come on]. q
[The power comes on].
Therefore, p [Mr. Scott
is still with us].
p → q
q
----------
p
This is a case of affirming the consequent
of a conditional and concluding that the
antecedent is true.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-30-2048.jpg)
![Assessing validity of [(p → q) ∧ q ] → p
p q p → q (p → q) ∧ q [(p → q) ∧ q]→ p
F F T F T
F T T T F
T F F F T
T T T T T
•Is this a valid argument?
*
*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-31-2048.jpg)
![Argument form
If p [Mr. Scott is still
with us], then q [the
power will come on]. q
[The power comes on].
Therefore, p [Mr. Scott
is still with us].
p → q
q
----------
p
This is a case of affirming the consequent of a
conditional and concluding that the antecedent is
true, The argument form is [(p → q) ∧ q] → p but
this is NOT a valid argument.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-32-2048.jpg)

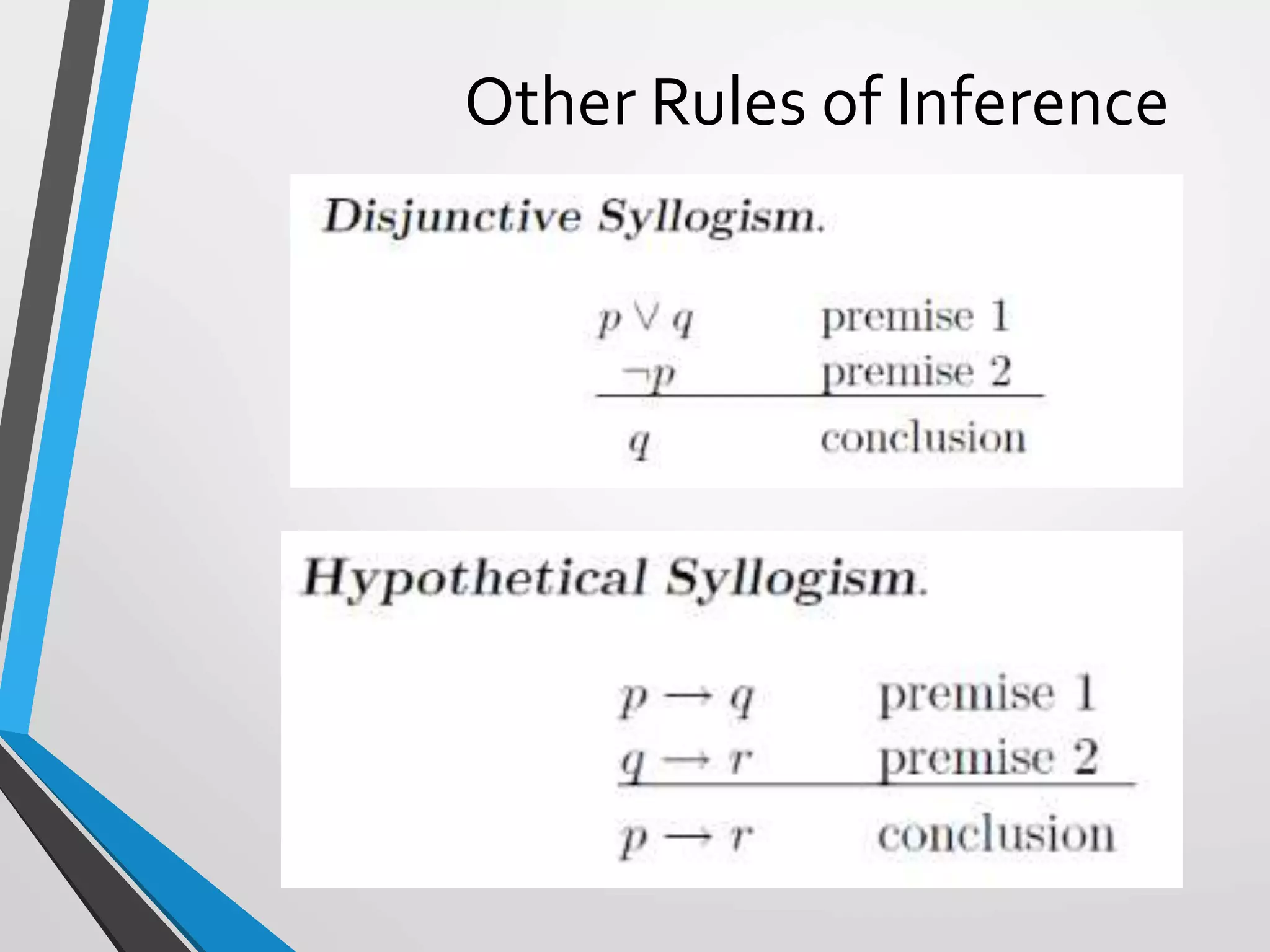
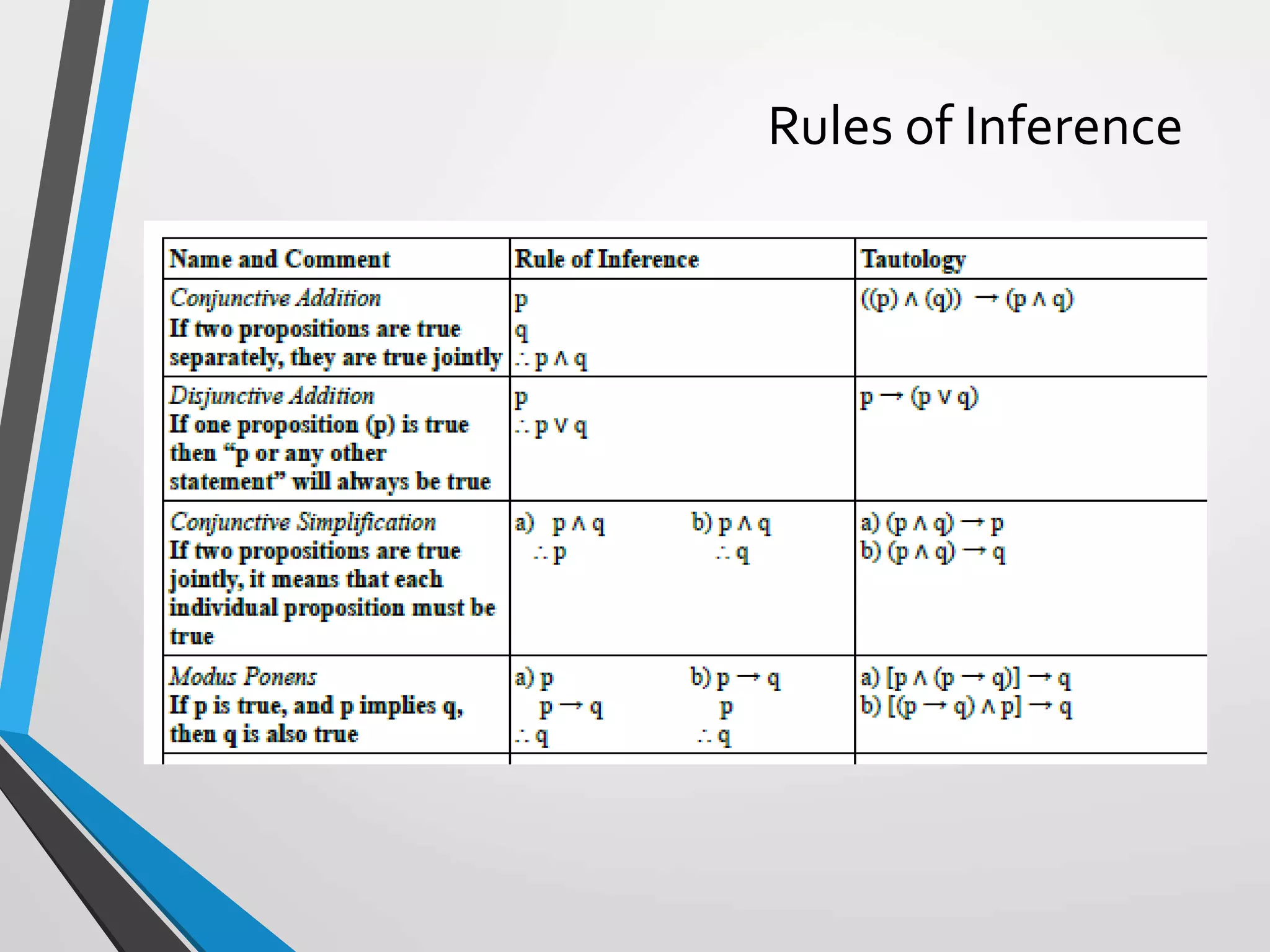
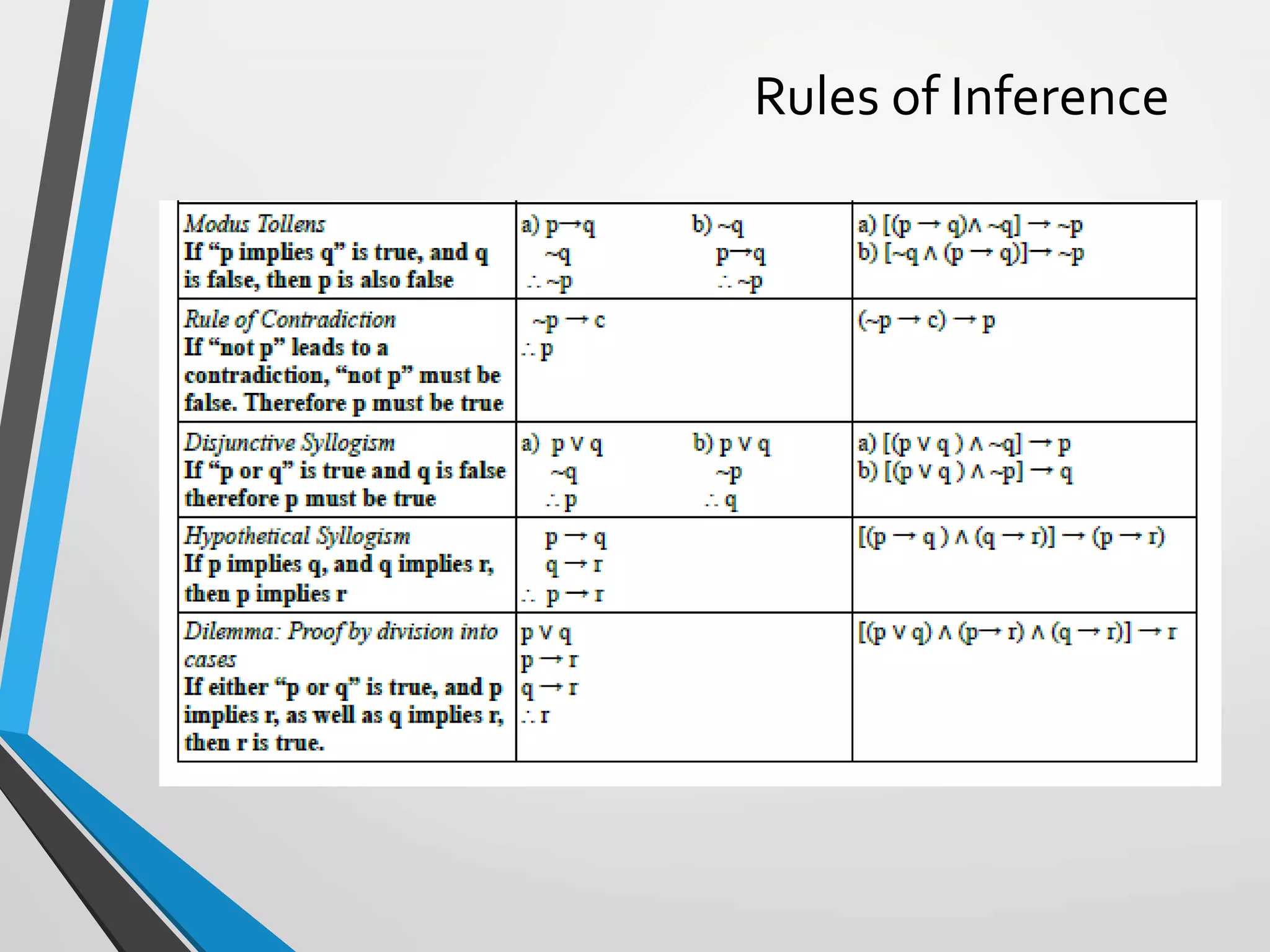








![RTP: (p ∨ q) ∧ ¬p → q
p ∨ q Premise 1
≡ ¬q → p Implication
¬p Premise 2
So we have, (¬q → p) ∧ ¬p
Recall: [(p → q) ∧ ¬ q] → ¬ p so applying this
inference rule, we have [(¬q → p) ∧ ¬p] → ¬ ¬q](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/argumentsandmethodsofproof-200306230546/75/Arguments-and-methods-of-proof-46-2048.jpg)