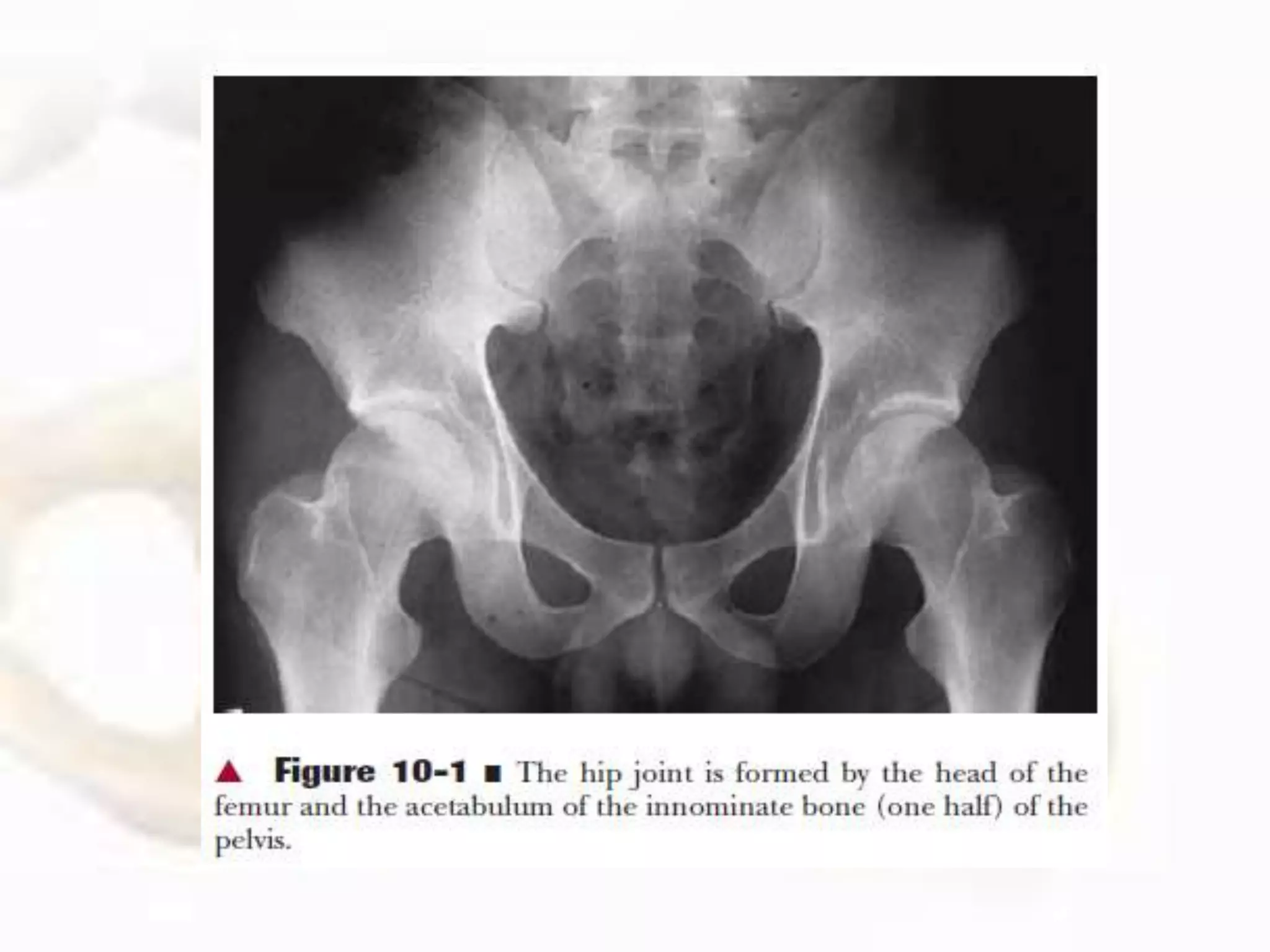
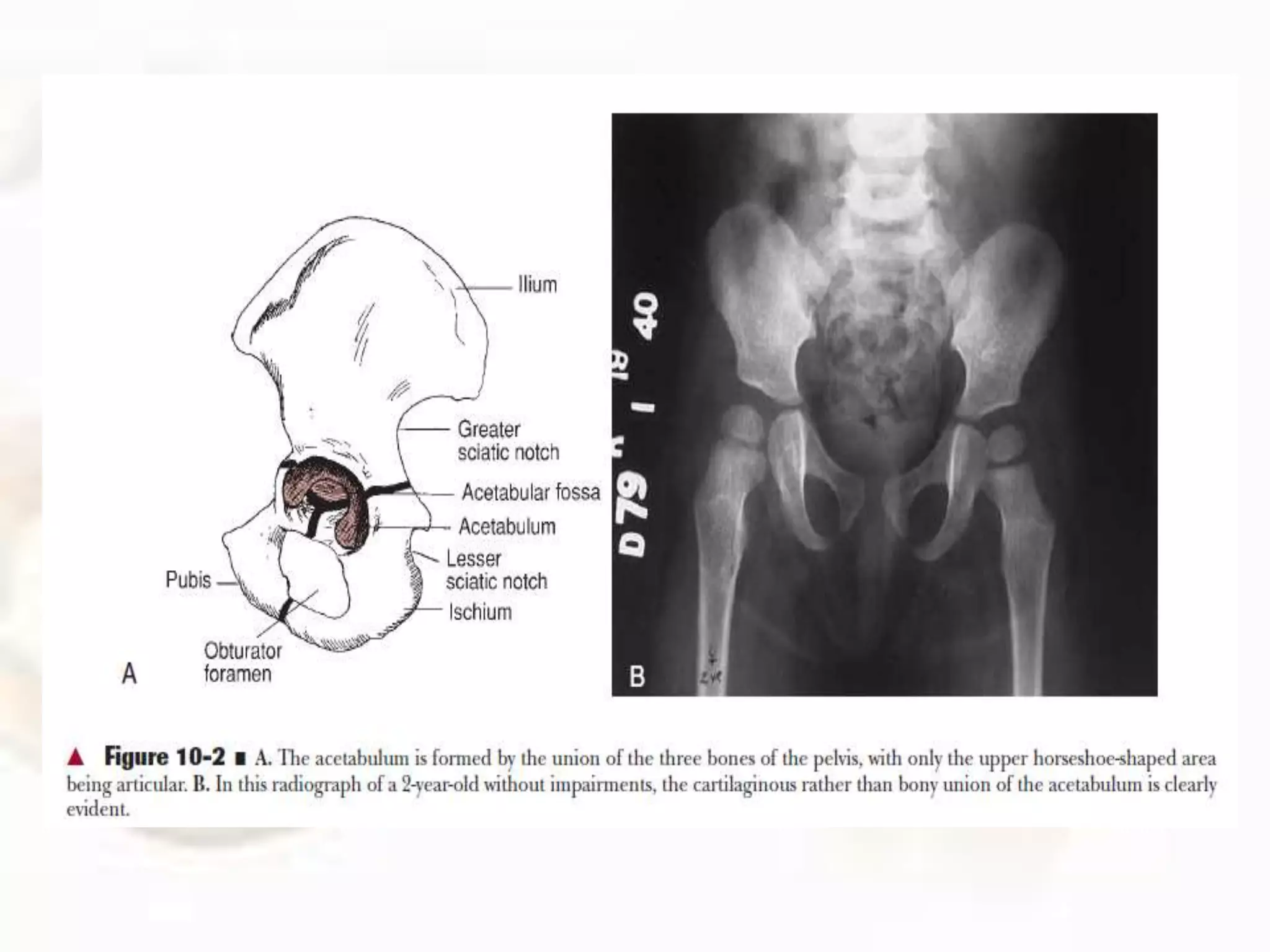
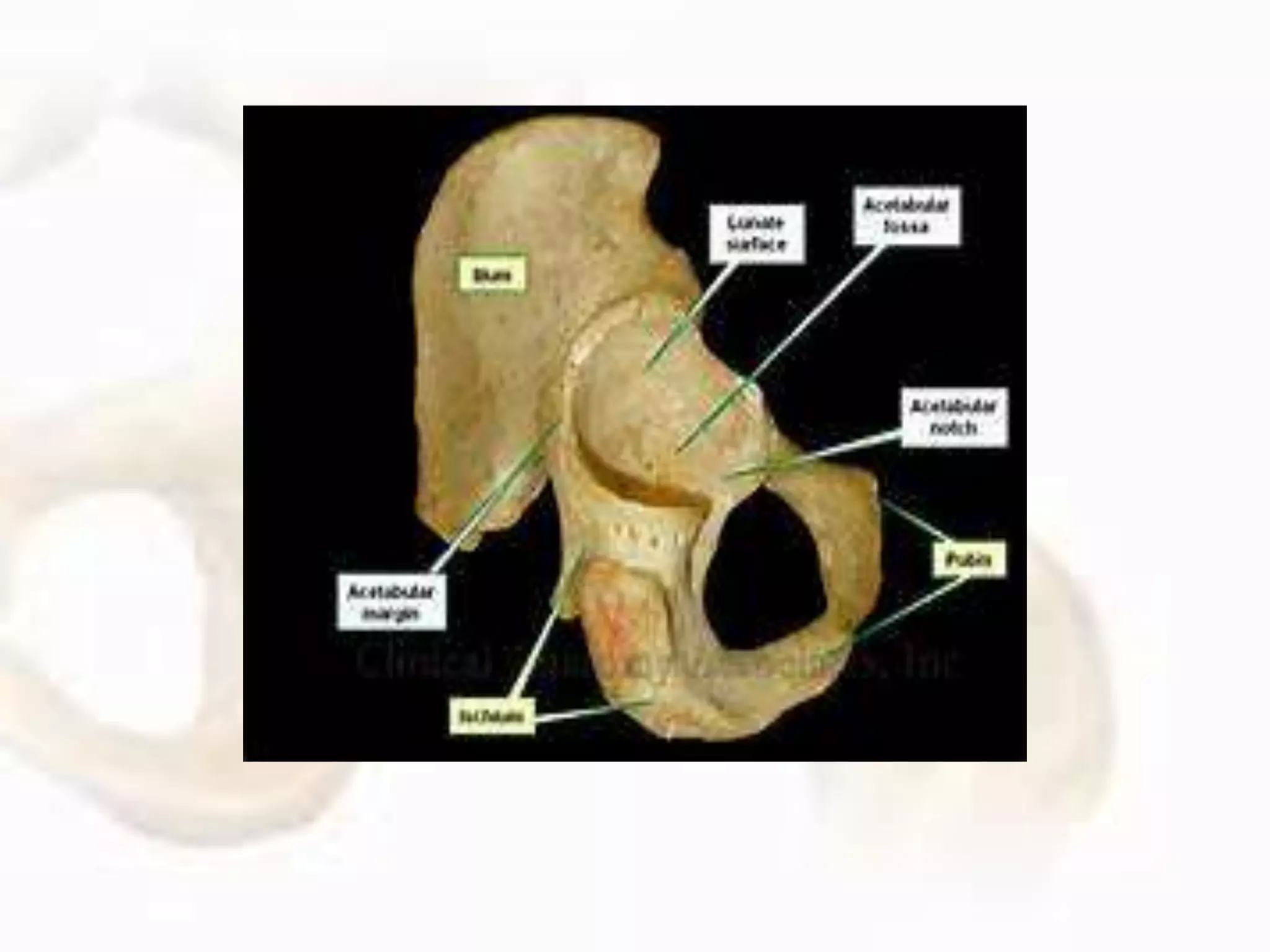
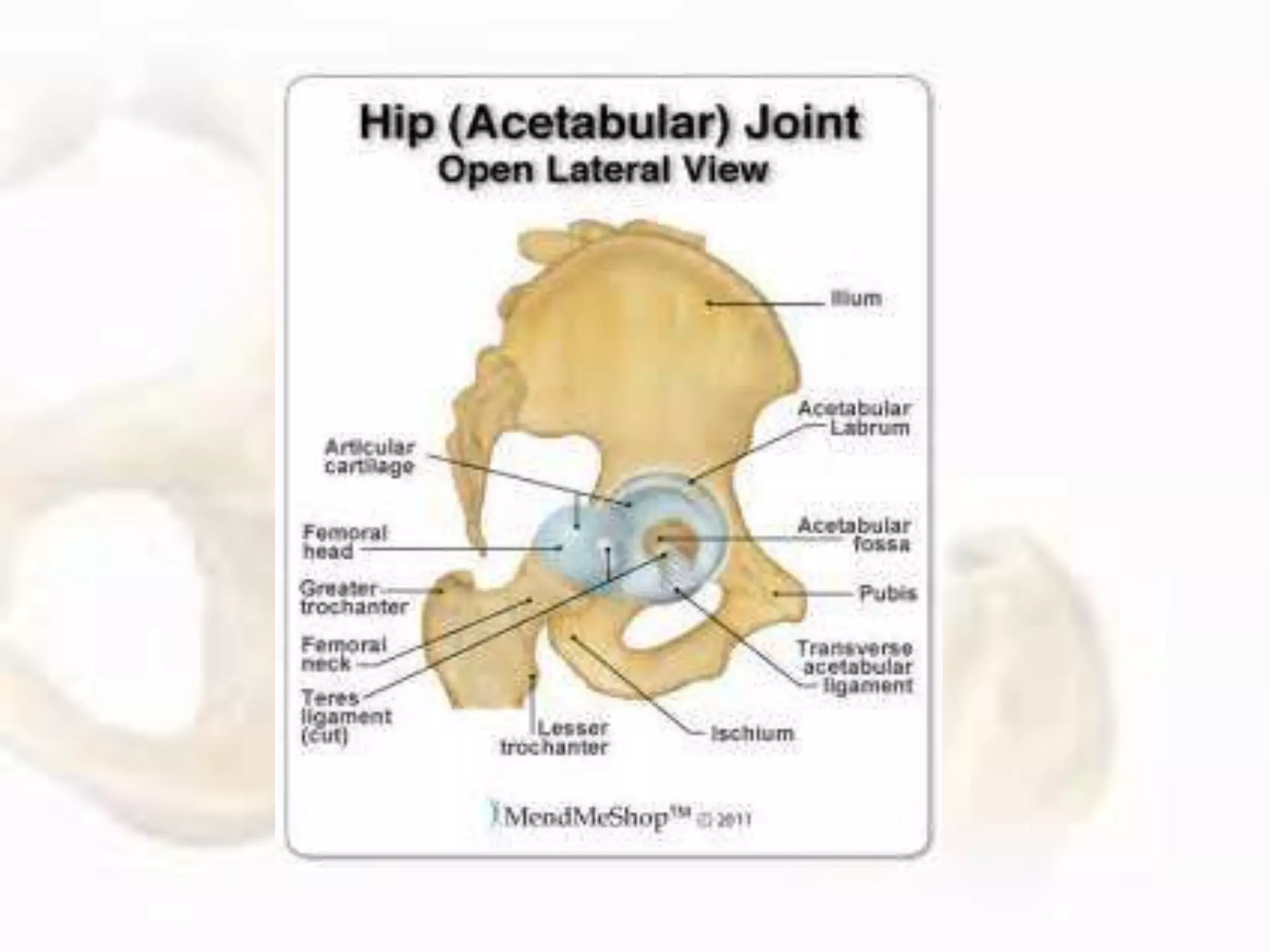
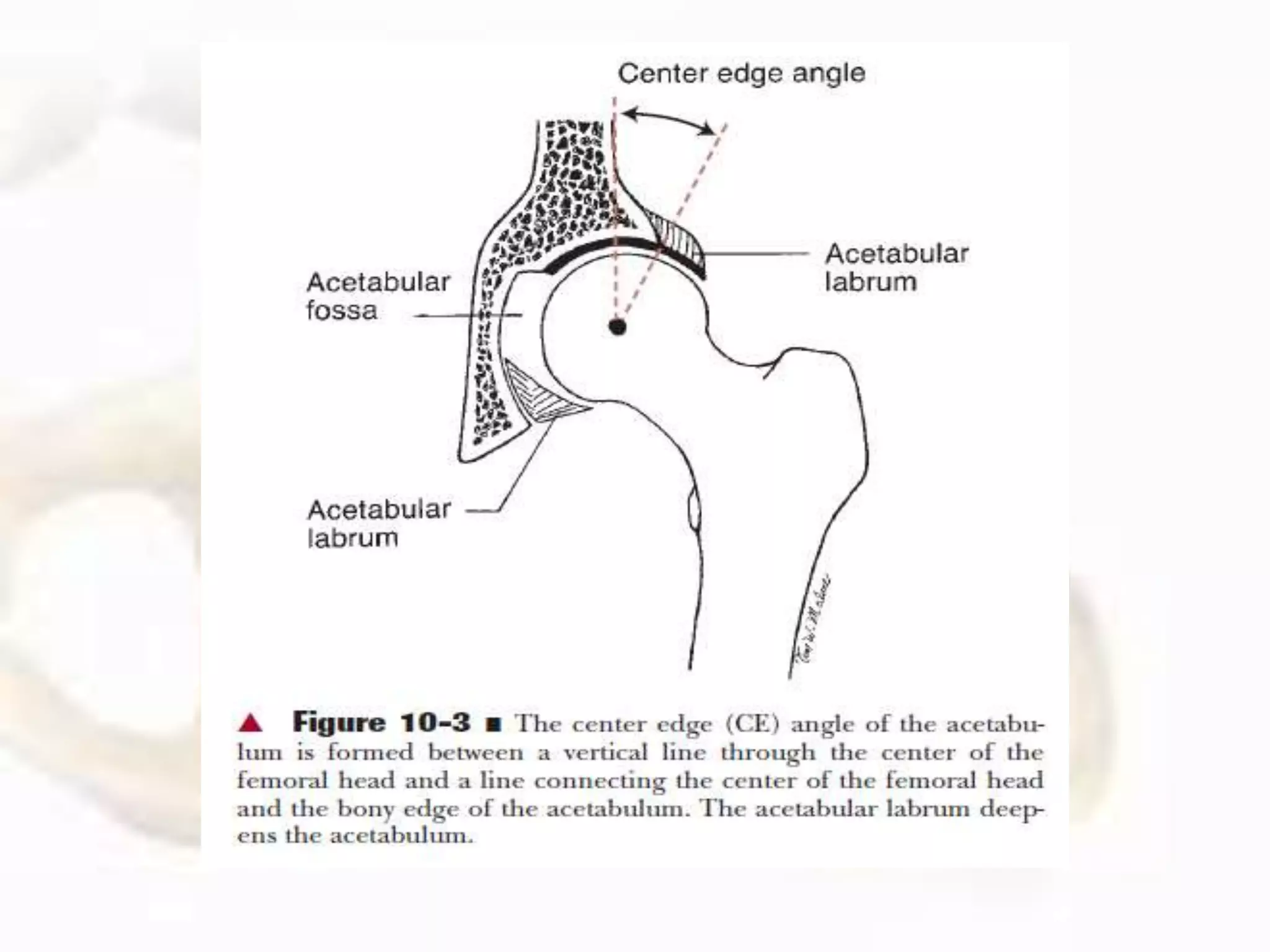
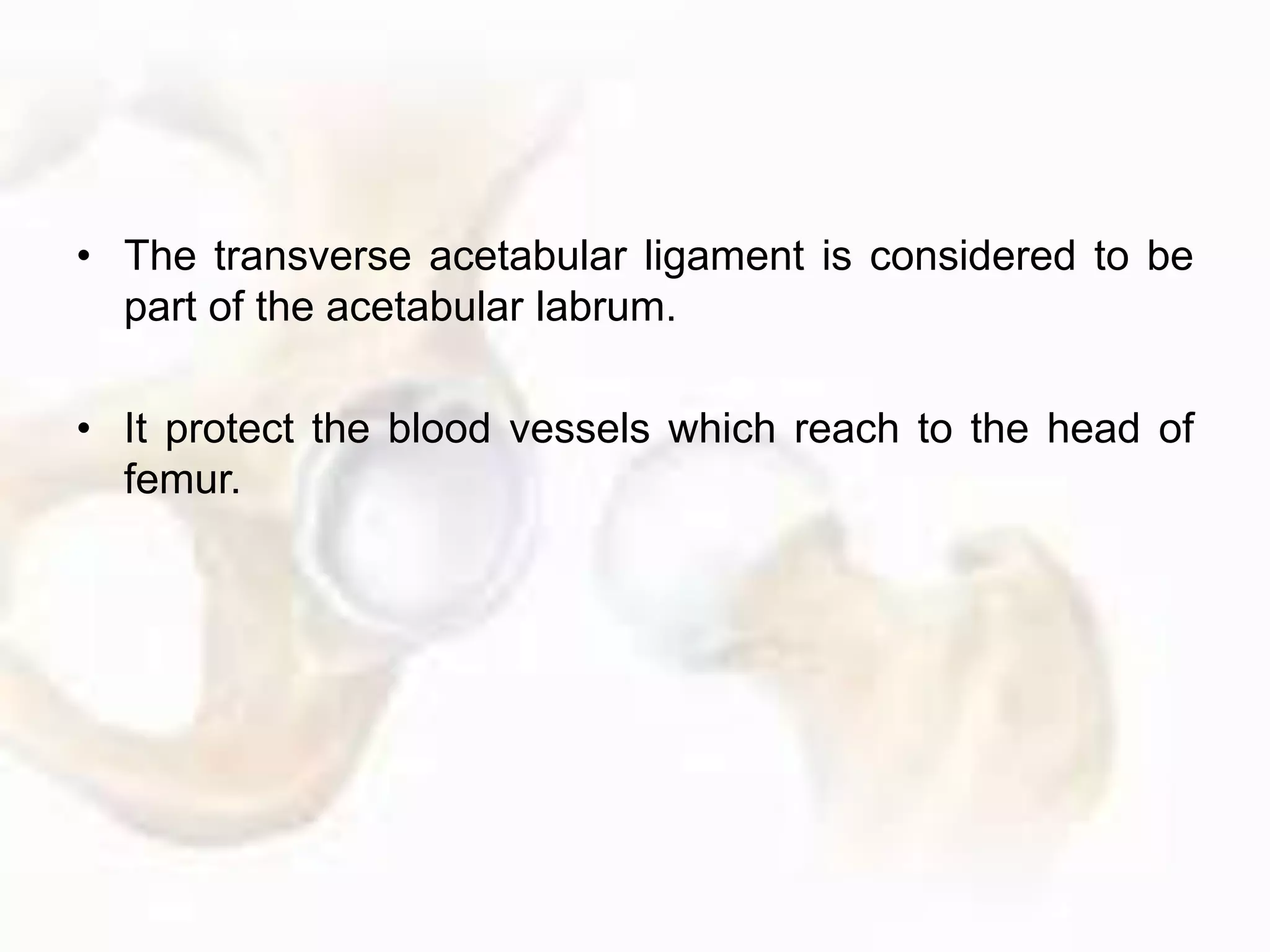
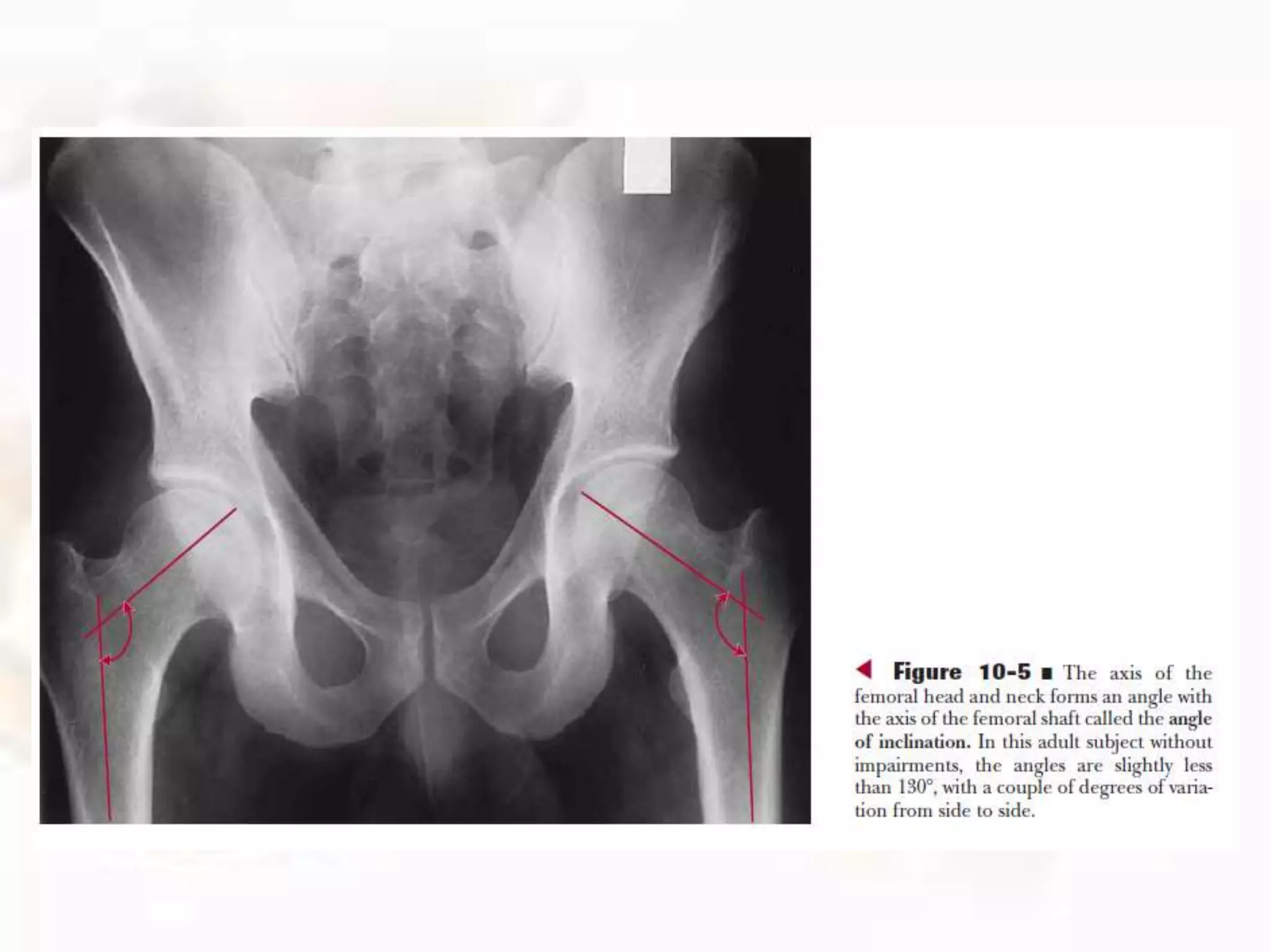
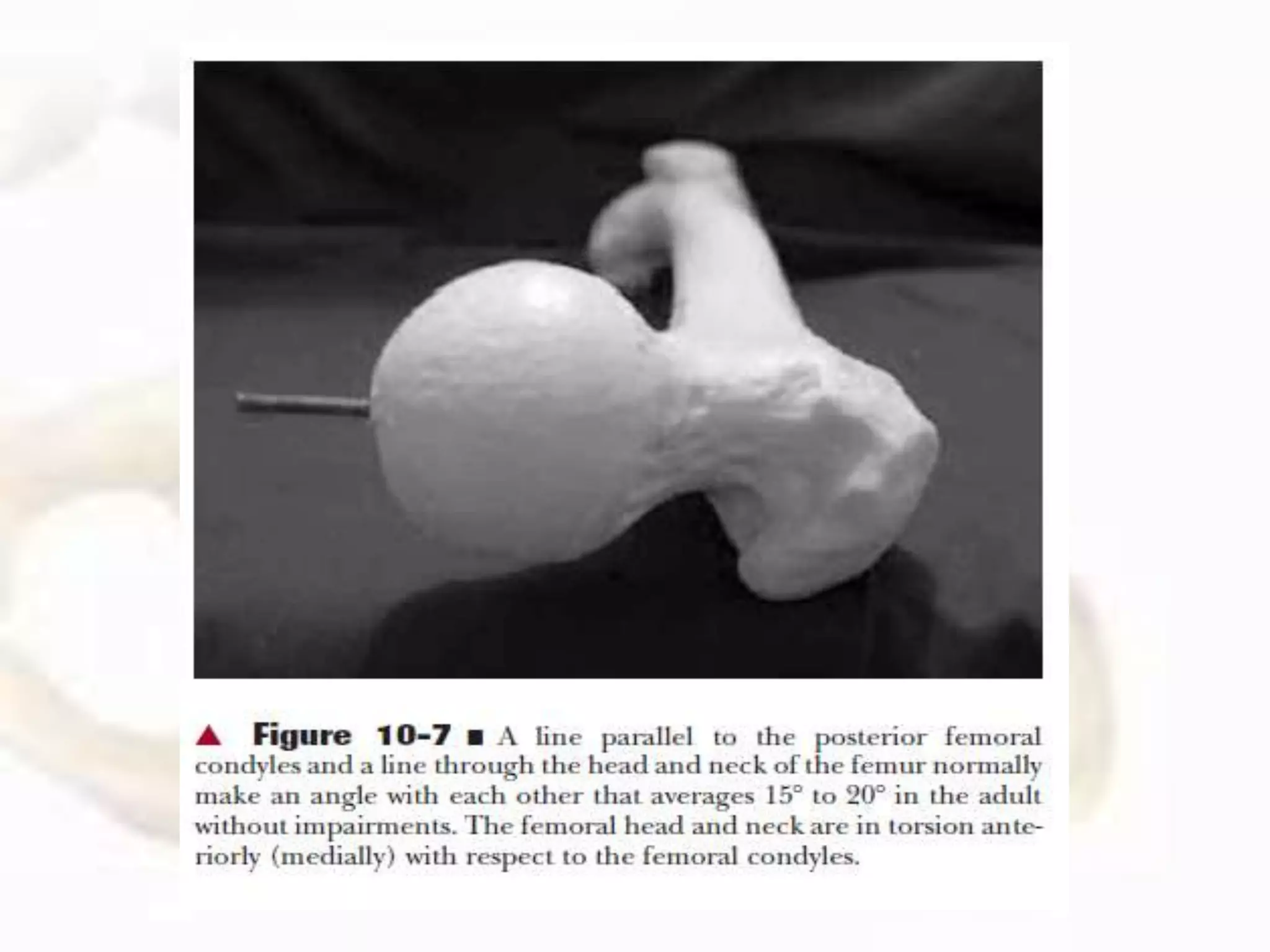
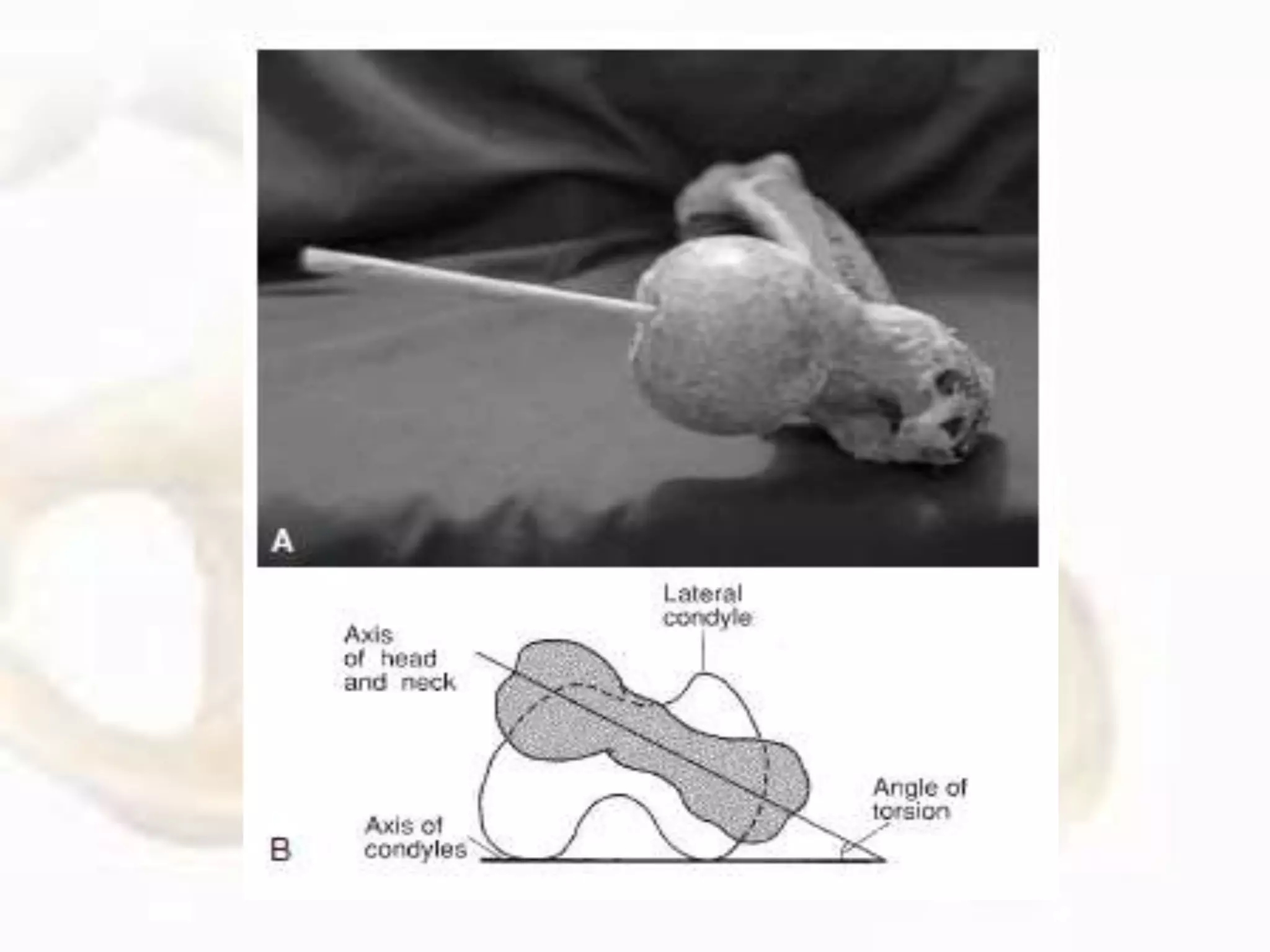
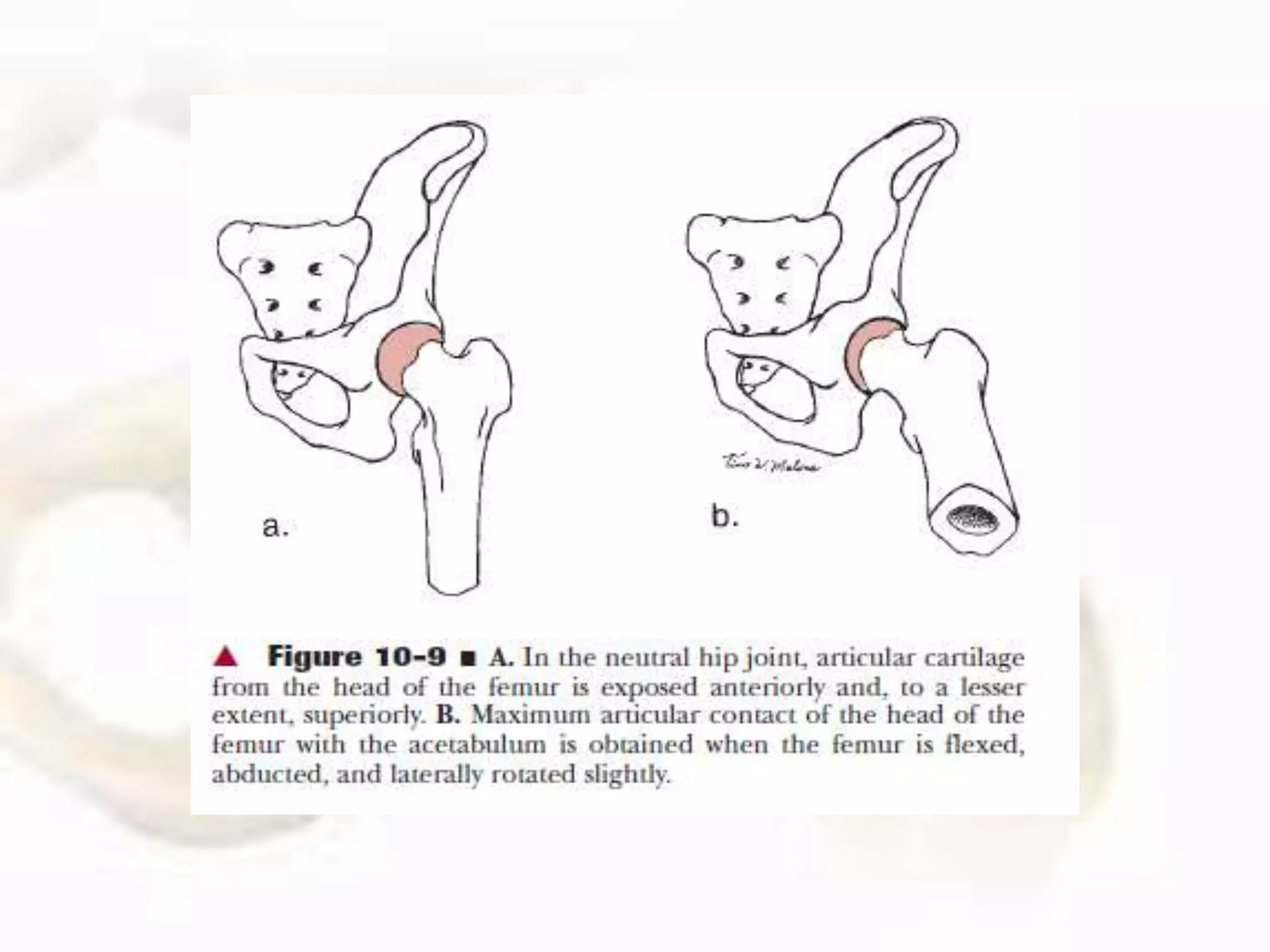
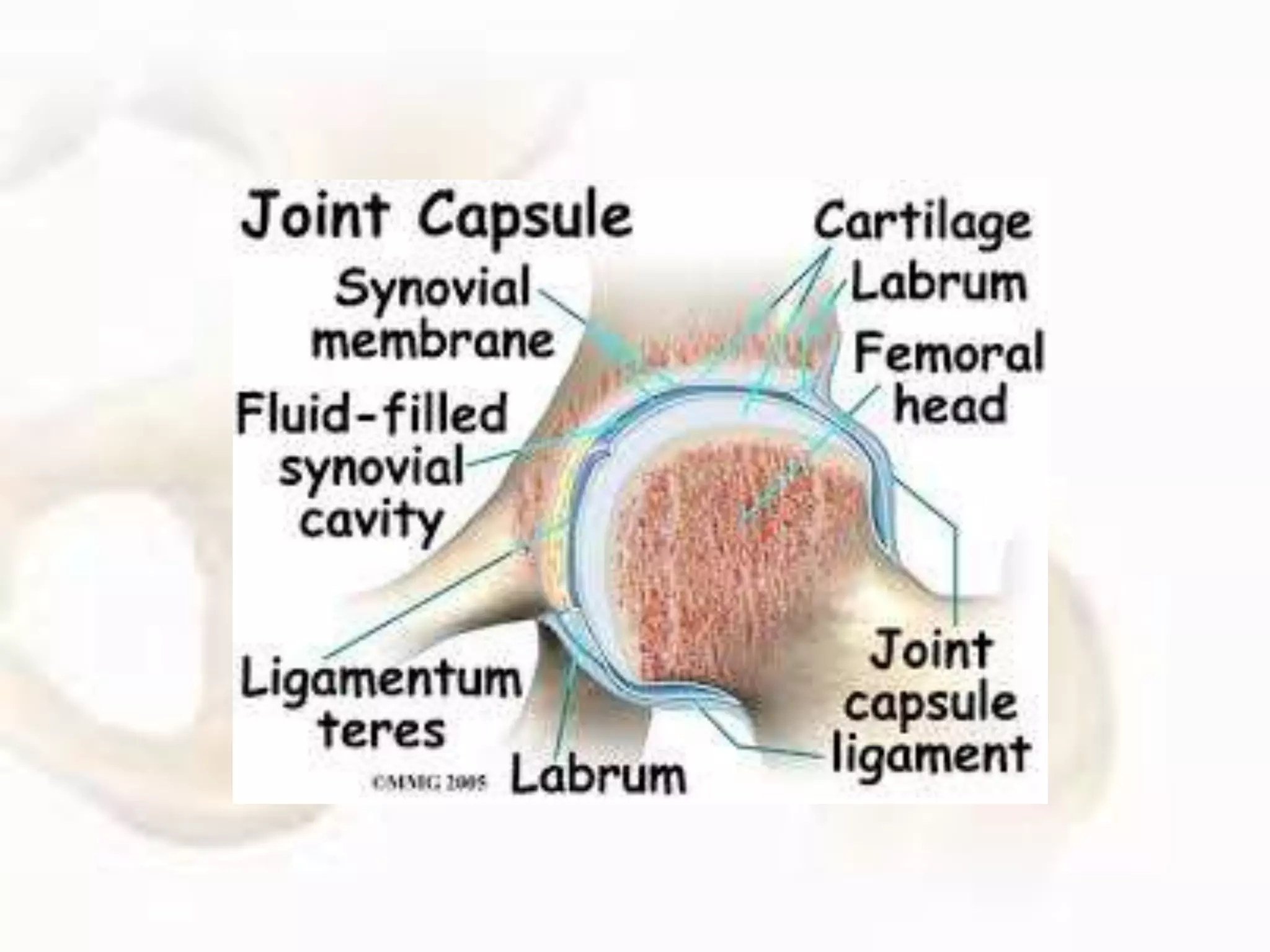
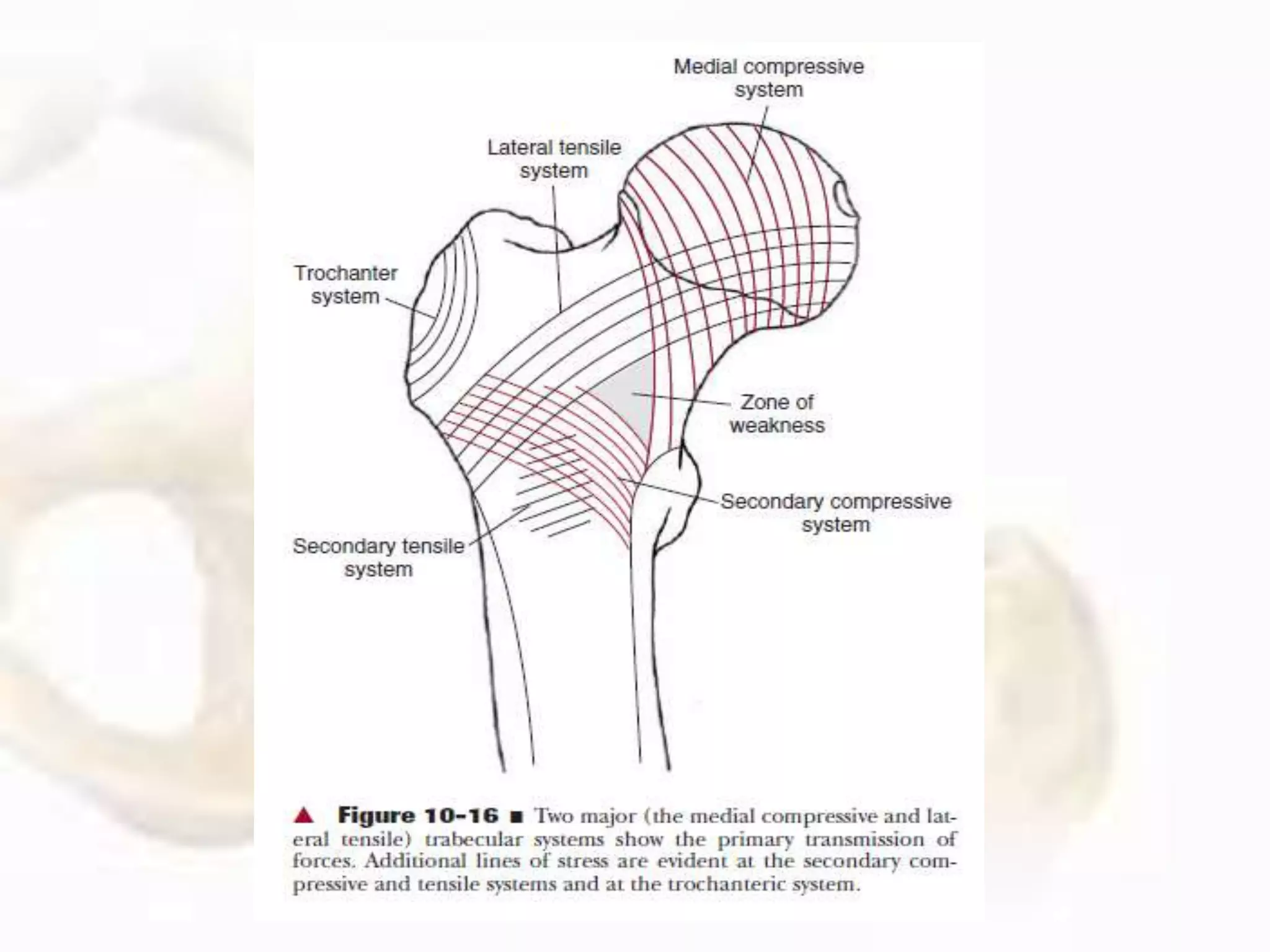
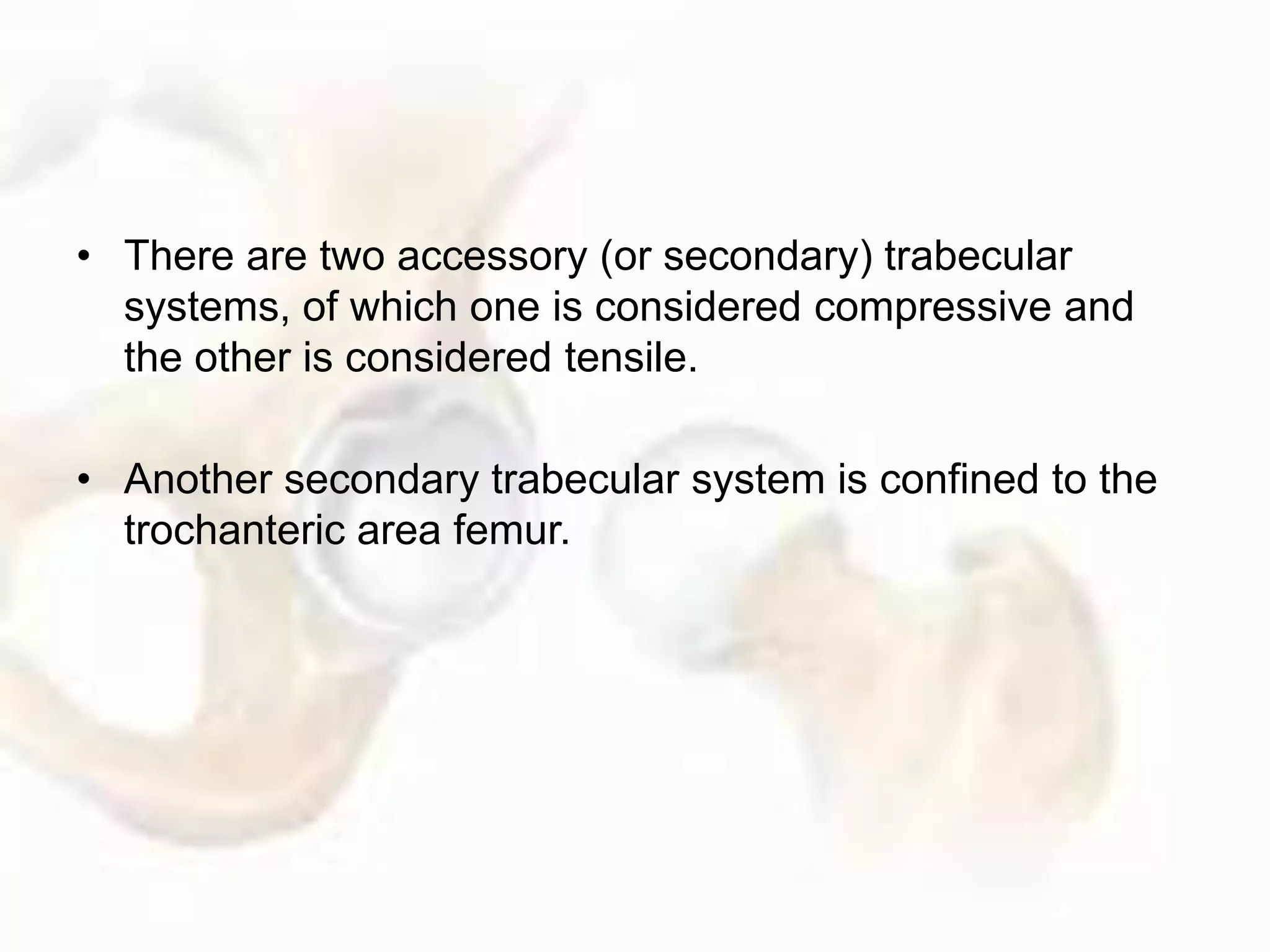
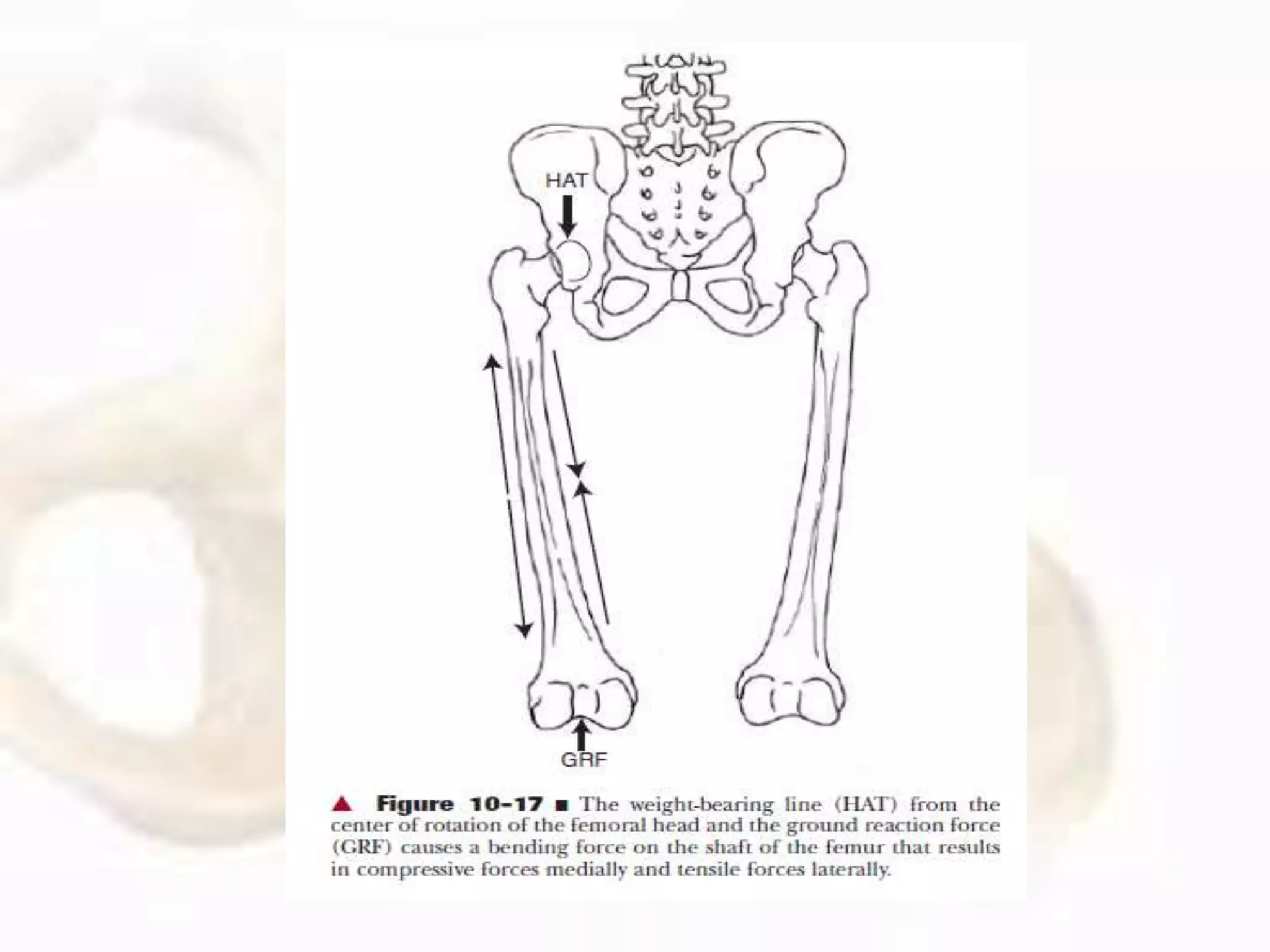
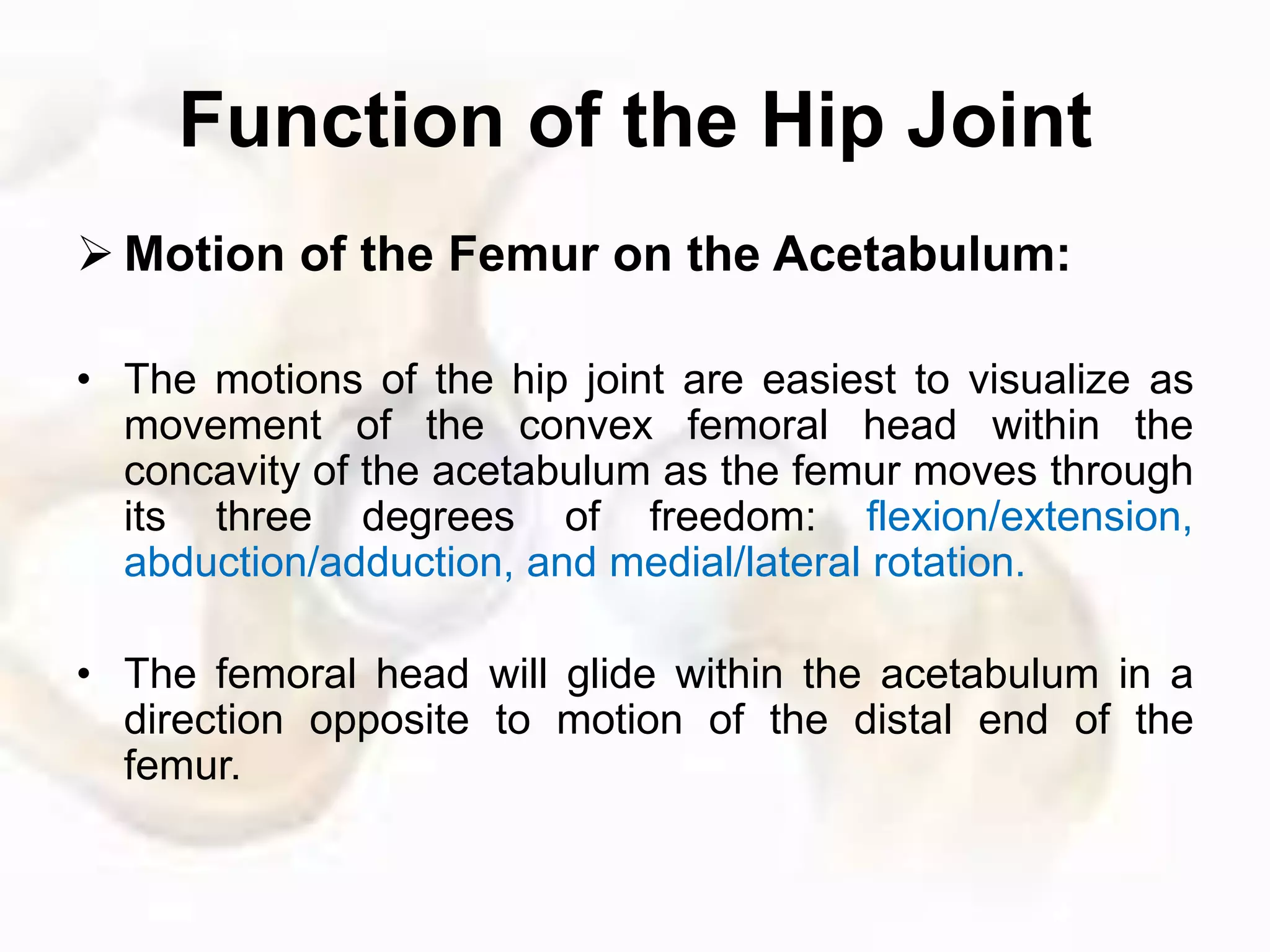
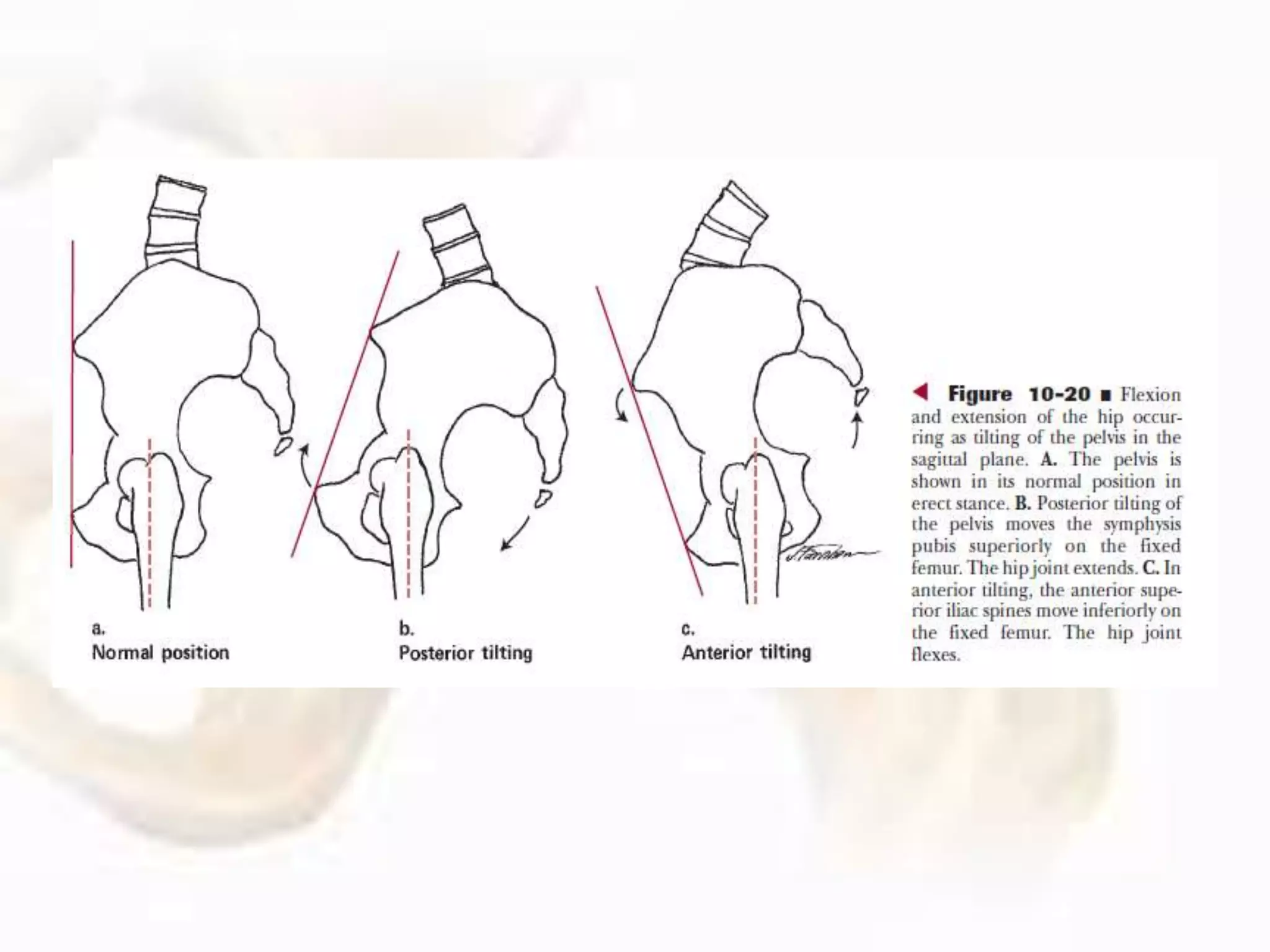
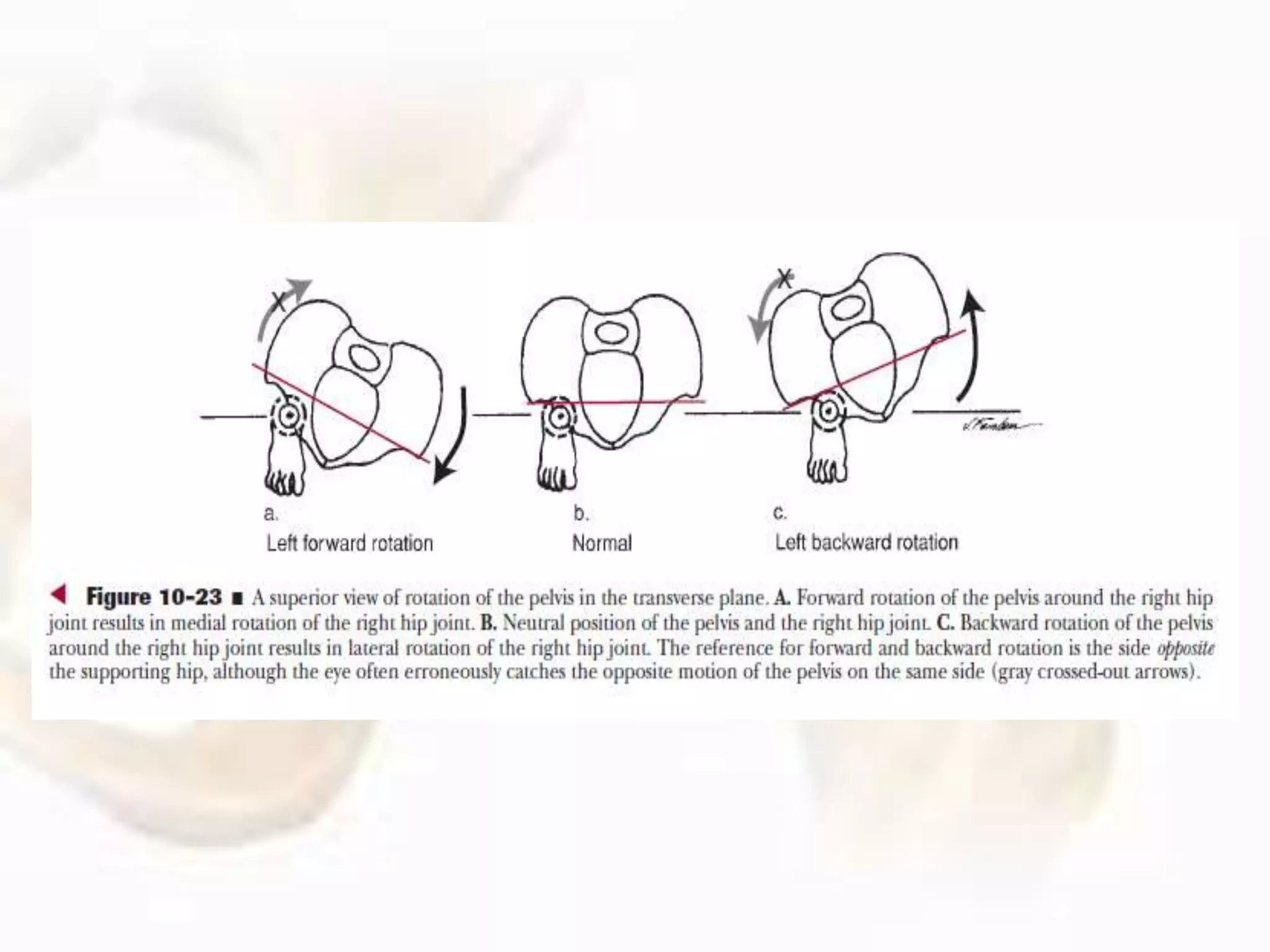
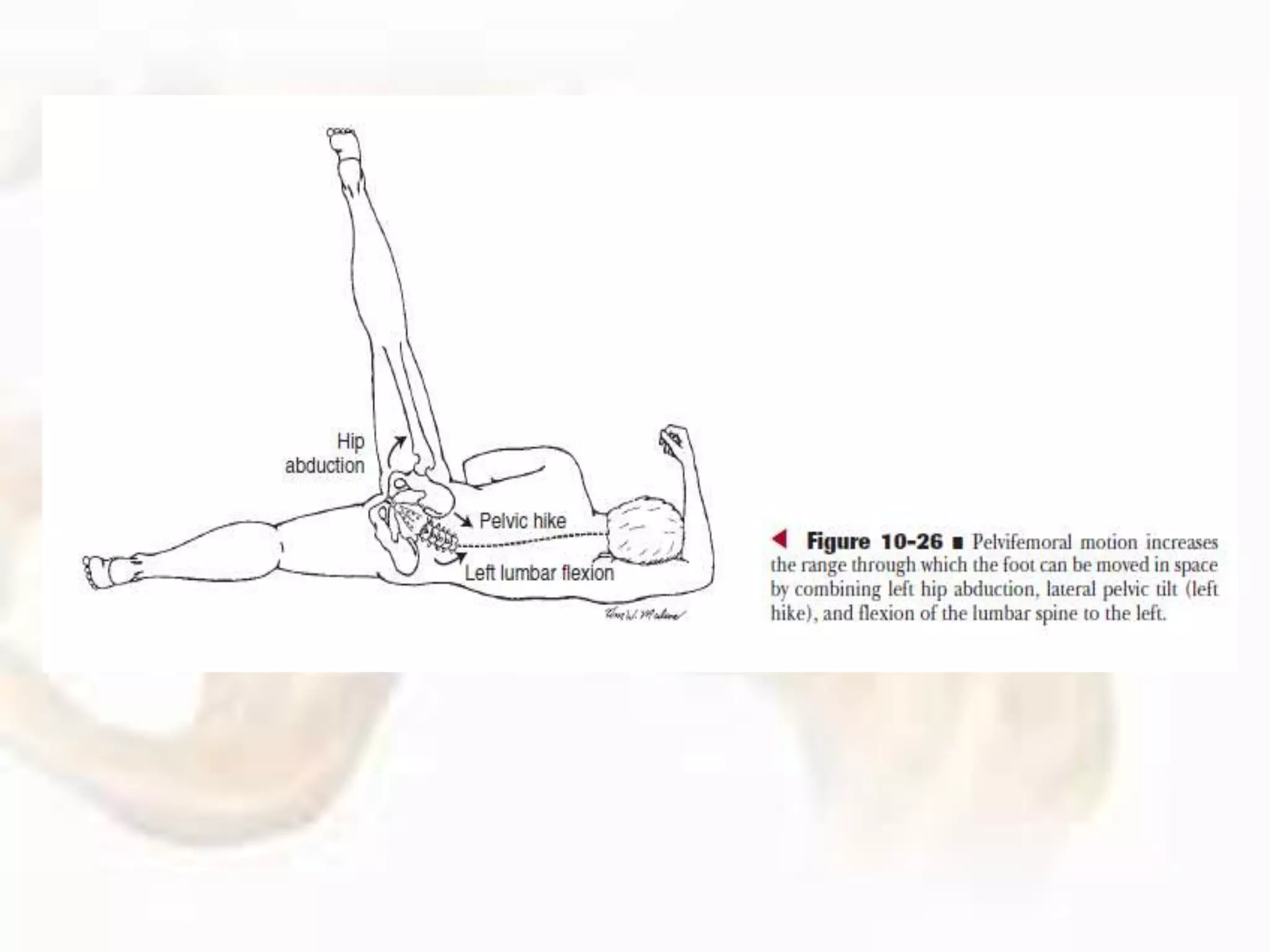
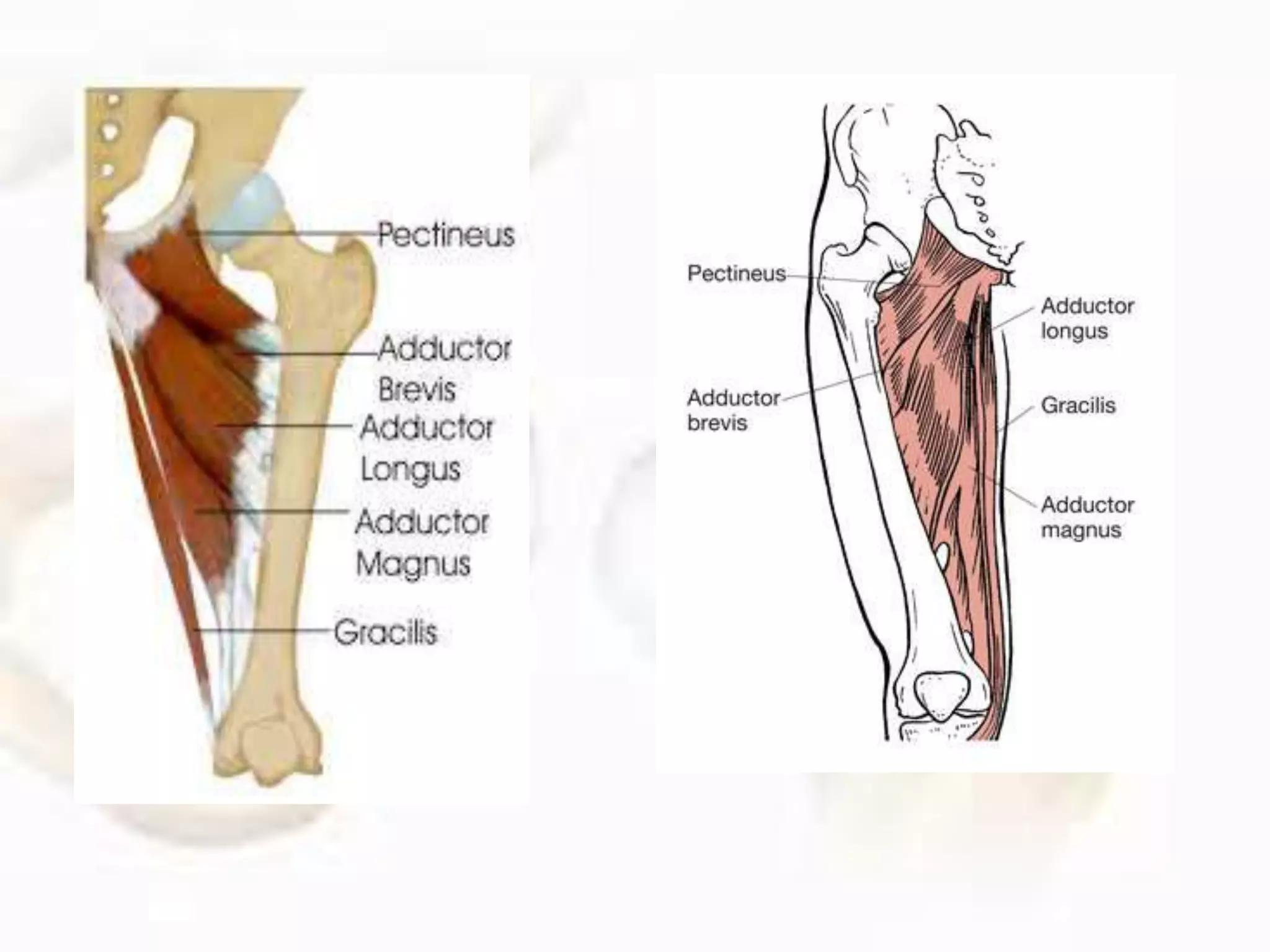
The hip joint, a diarthrodial ball-and-socket joint, supports the weight of the torso and has functions in various dynamic postures. Its anatomy includes the acetabulum formed by three pelvic bones, the femoral head, and surrounding ligaments that enhance stability and lubrication. Structural adaptations in the femur and pelvis allow for effective weight-bearing and resistance to mechanical stress.












































































































































![• The magnitude of body weight (W) compressing the right
hip joint in right unilateral stance, therefore, is:
Right hip joint compression body weight = [2/3*W]+[1/6*W]
Right hip joint compression body weight =5/6*W](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thehipcomplex-170811091823/75/The-hip-complex-172-2048.jpg)