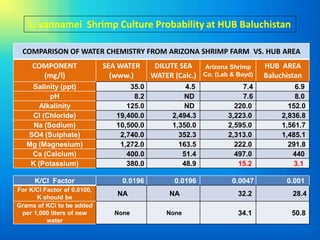
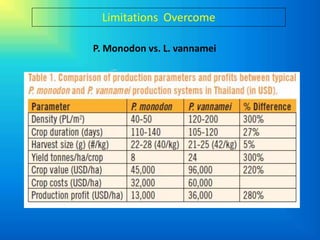
This document provides information about aquaculture consulting services for freshwater, brackishwater, and marine farming. It discusses sustainable shrimp and finfish farming techniques like coastal shrimp culture, coastal land-based and cage finfish culture, and inland low salinity shrimp and finfish culture. Specific techniques covered include conventional marine shrimp culture, marine finfish cage culture, and biofloc technology. Several cultured and experimental species are listed. Benefits of biofloc culture systems are outlined. Information is also provided about inland low salinity groundwater aquaculture and the potential for L. vannamei shrimp culture in Baluchistan based on a comparison of water chemistry. Limitations to aquaculture in the region are discussed