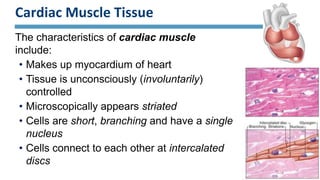
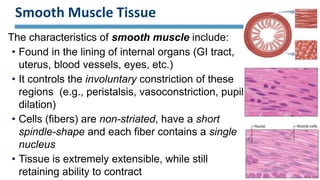
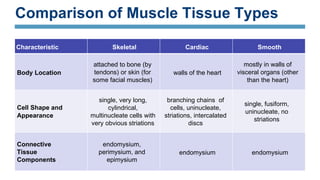
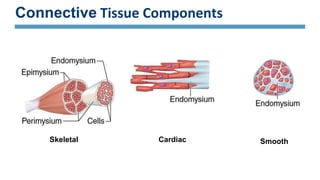
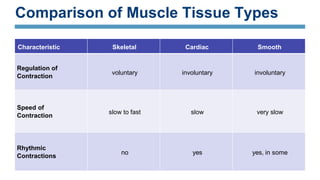
The document discusses the three main types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is voluntarily controlled and attached to bones, cardiac muscle makes up the heart wall and contracts involuntarily, and smooth muscle lines organs and controls involuntary functions like digestion. Each type has distinct characteristics at the cellular level in terms of shape, structure, nucleus number, and speed and control of contraction that relate to their different functions in the body.