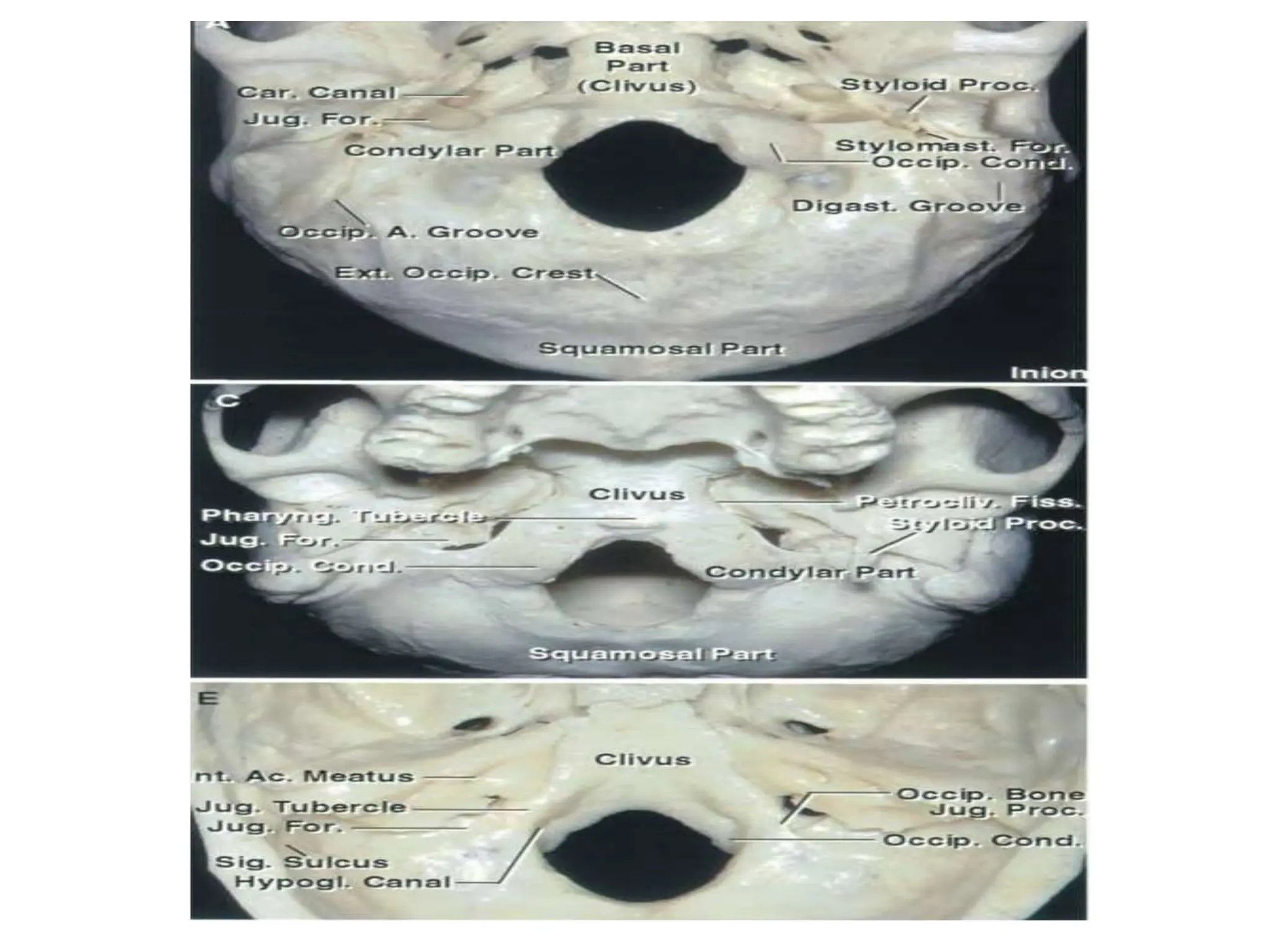
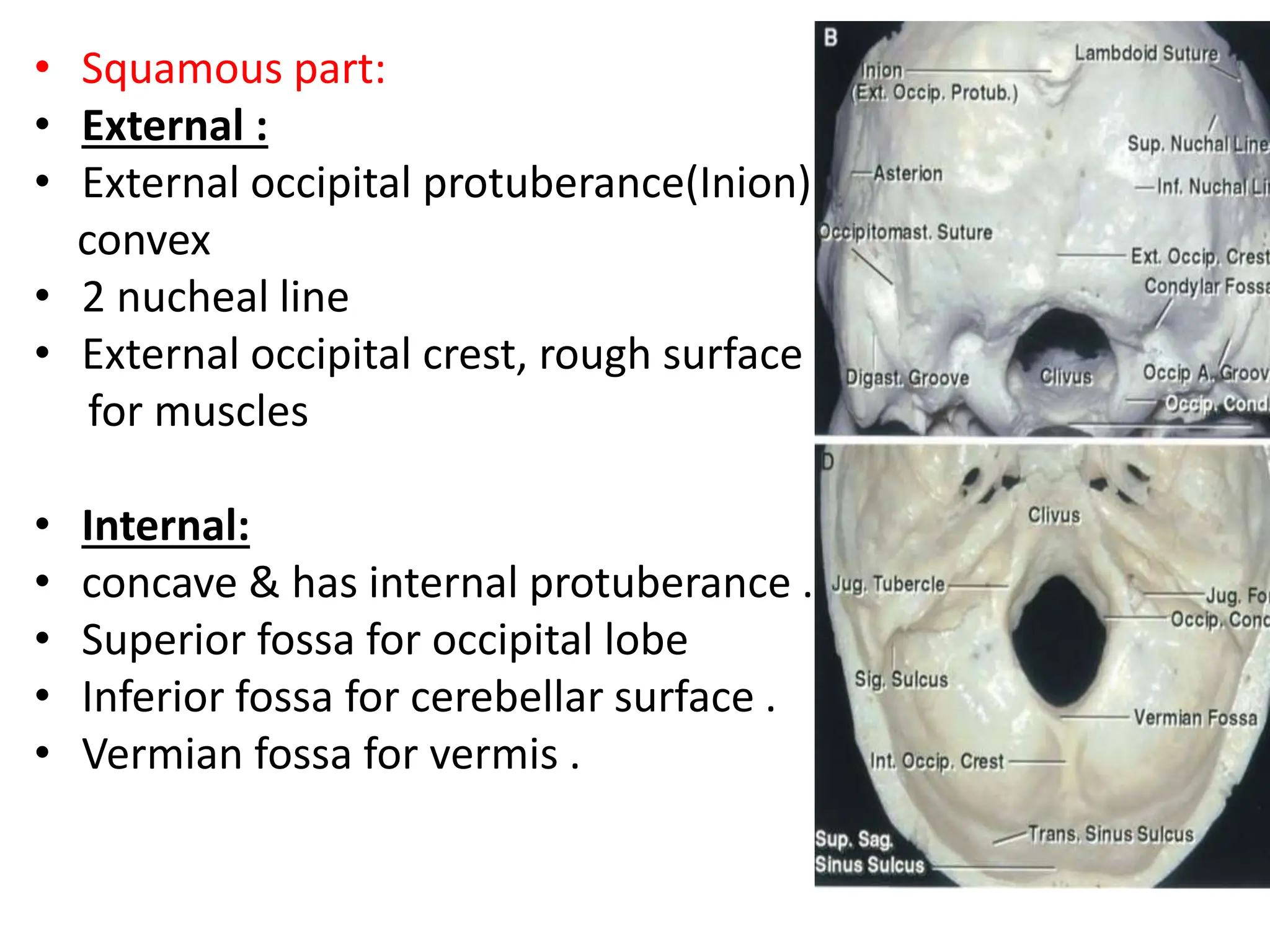
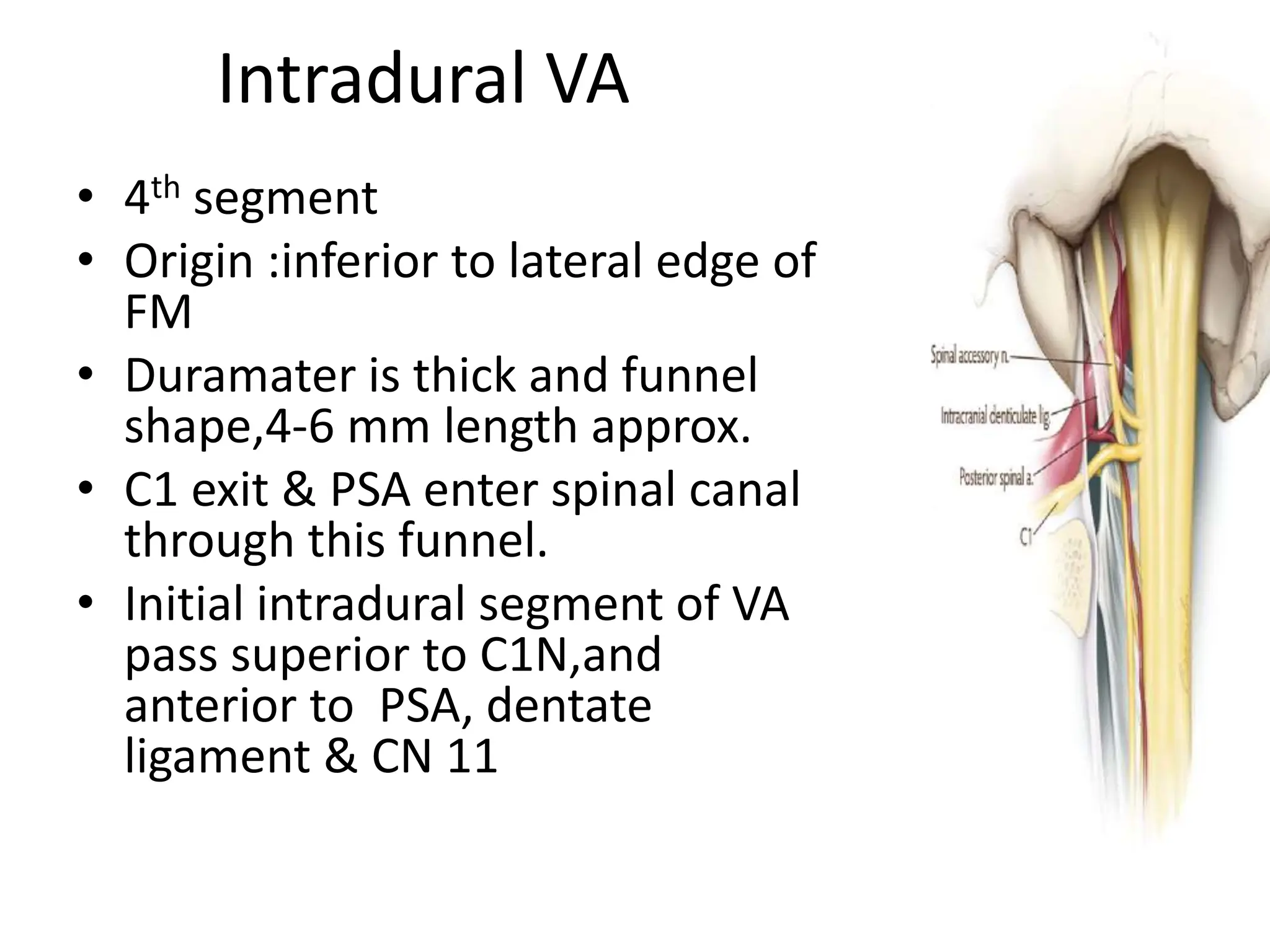
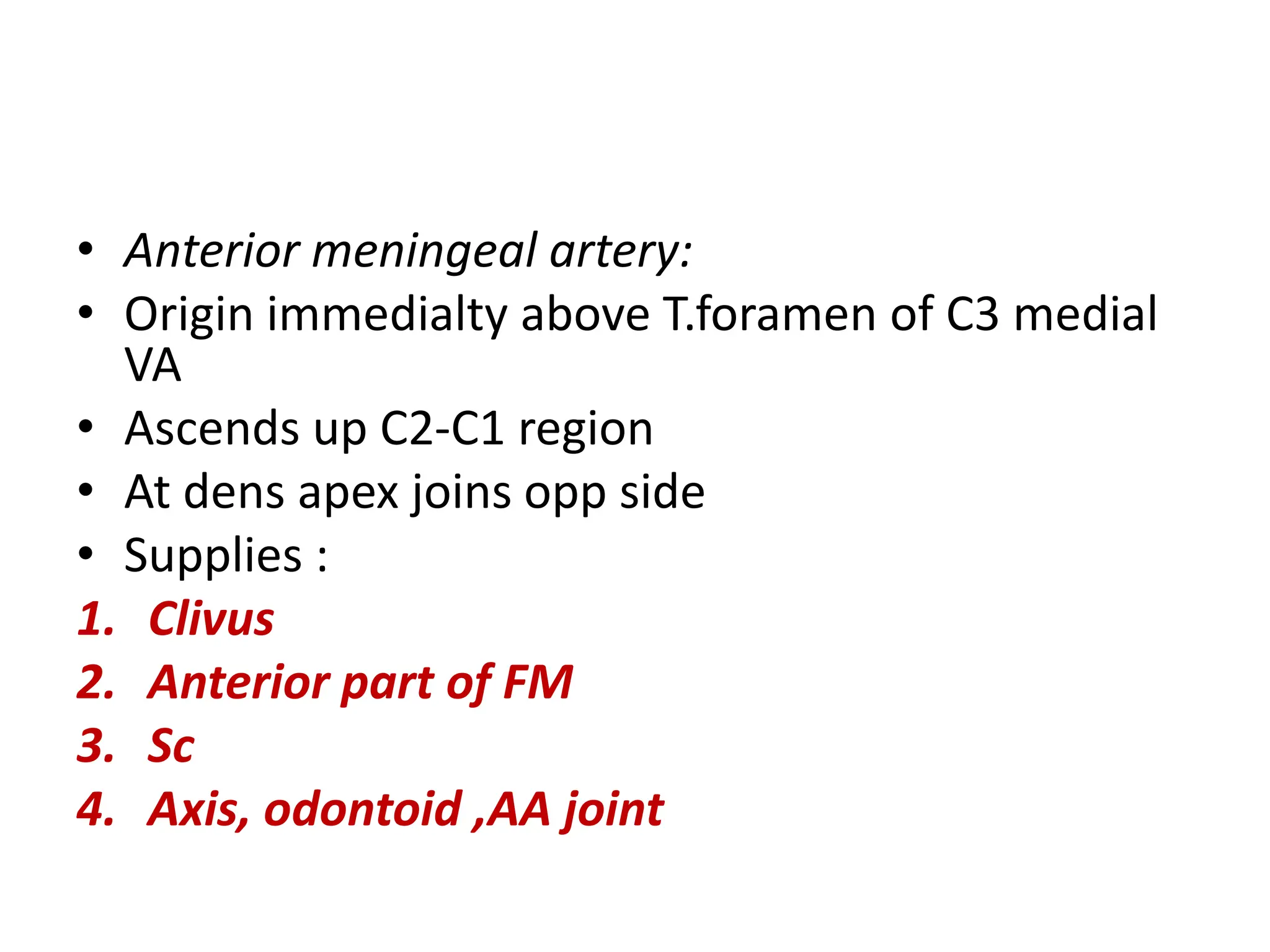
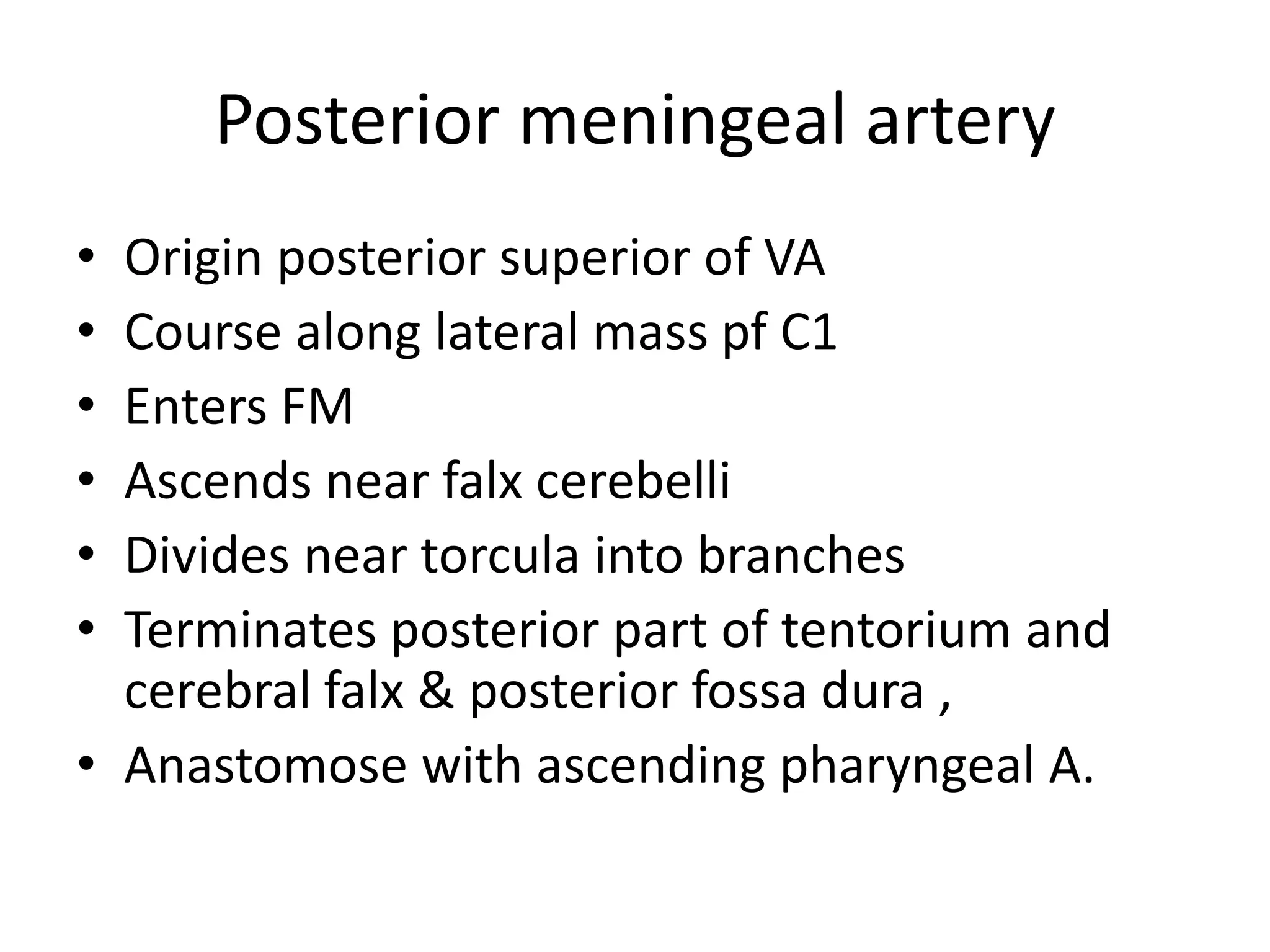
The document provides a detailed overview of the anatomy of the foramen magnum, including its location, components, and relationships with surrounding structures such as the occipital bone, vertebrae, and cranial nerves. It describes the bony, muscular, neural, and vascular relations associated with the foramen magnum, including ligaments and arteries, and highlights the significance of the area in neurosurgery. Additionally, it outlines the connections and pathways of cranial and cervical nerves in relation to the foramen magnum.