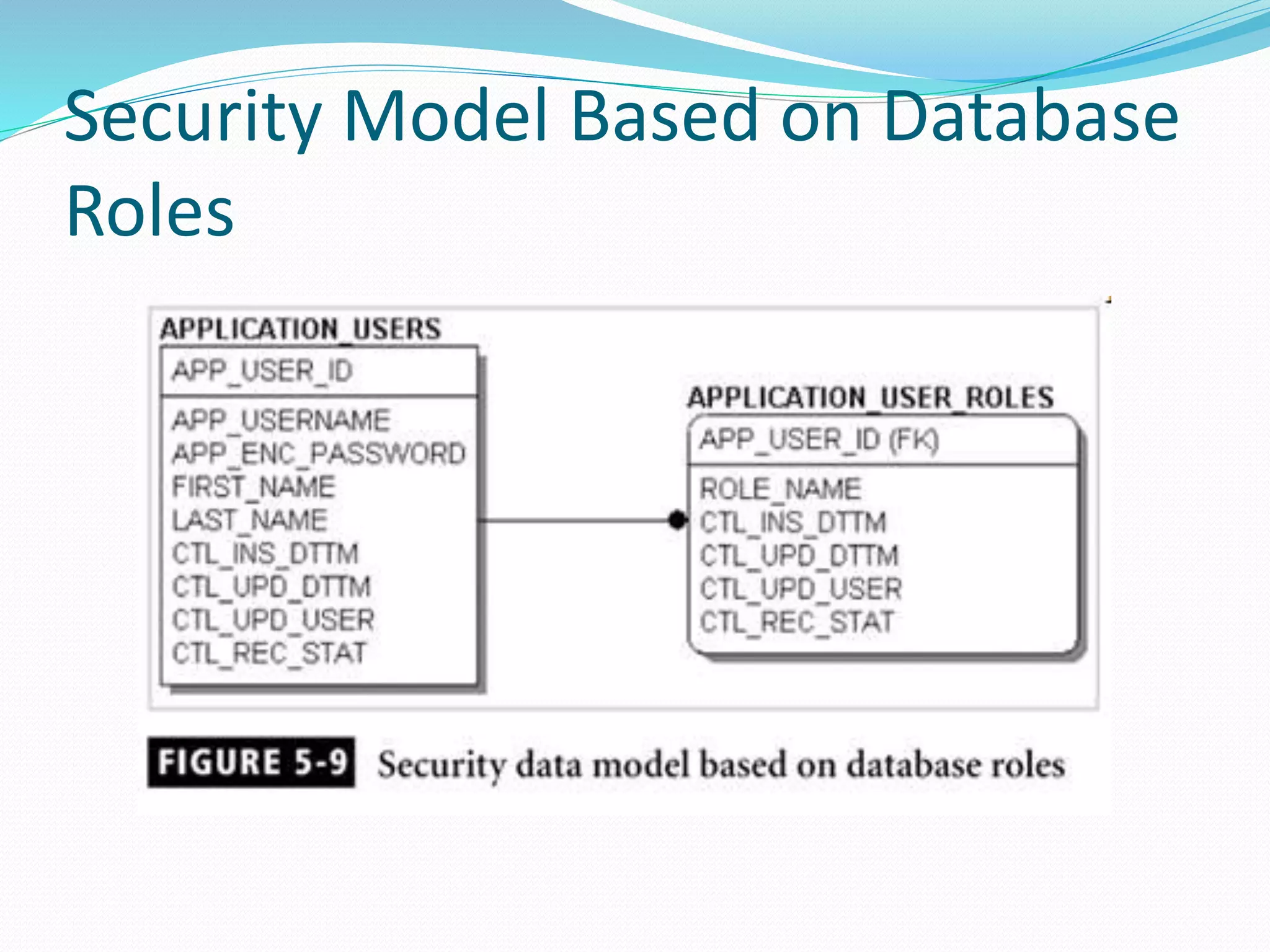
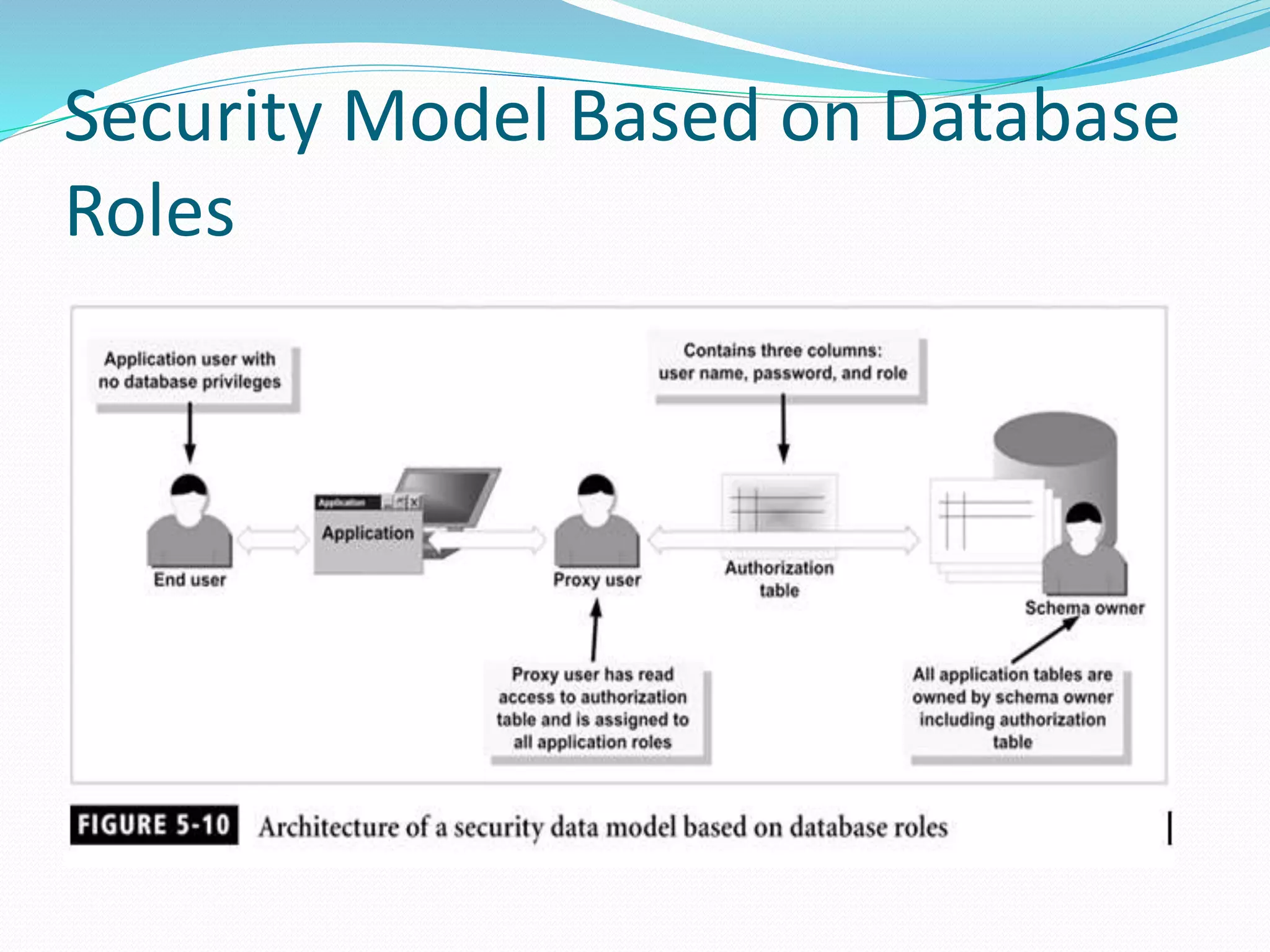
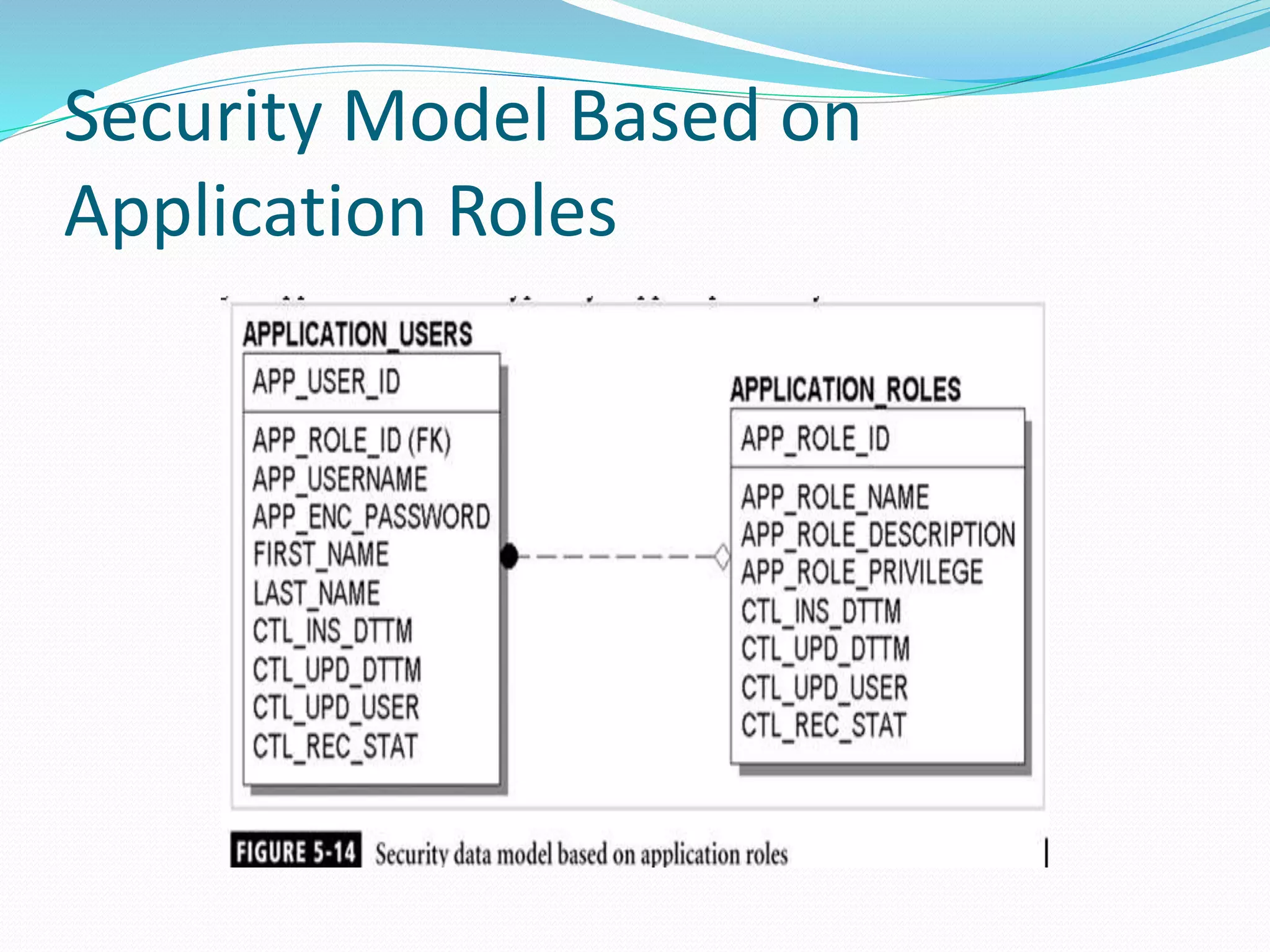
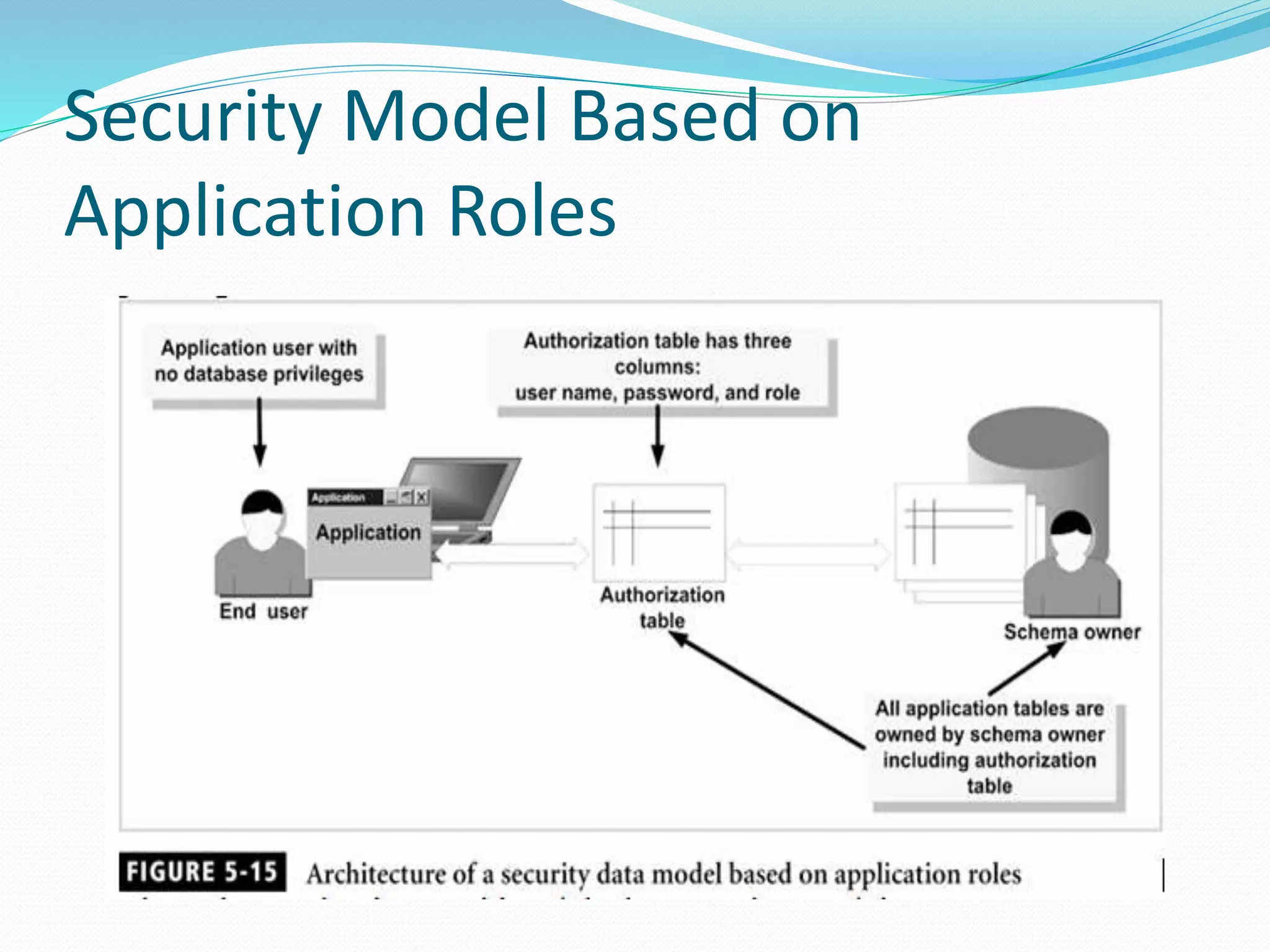
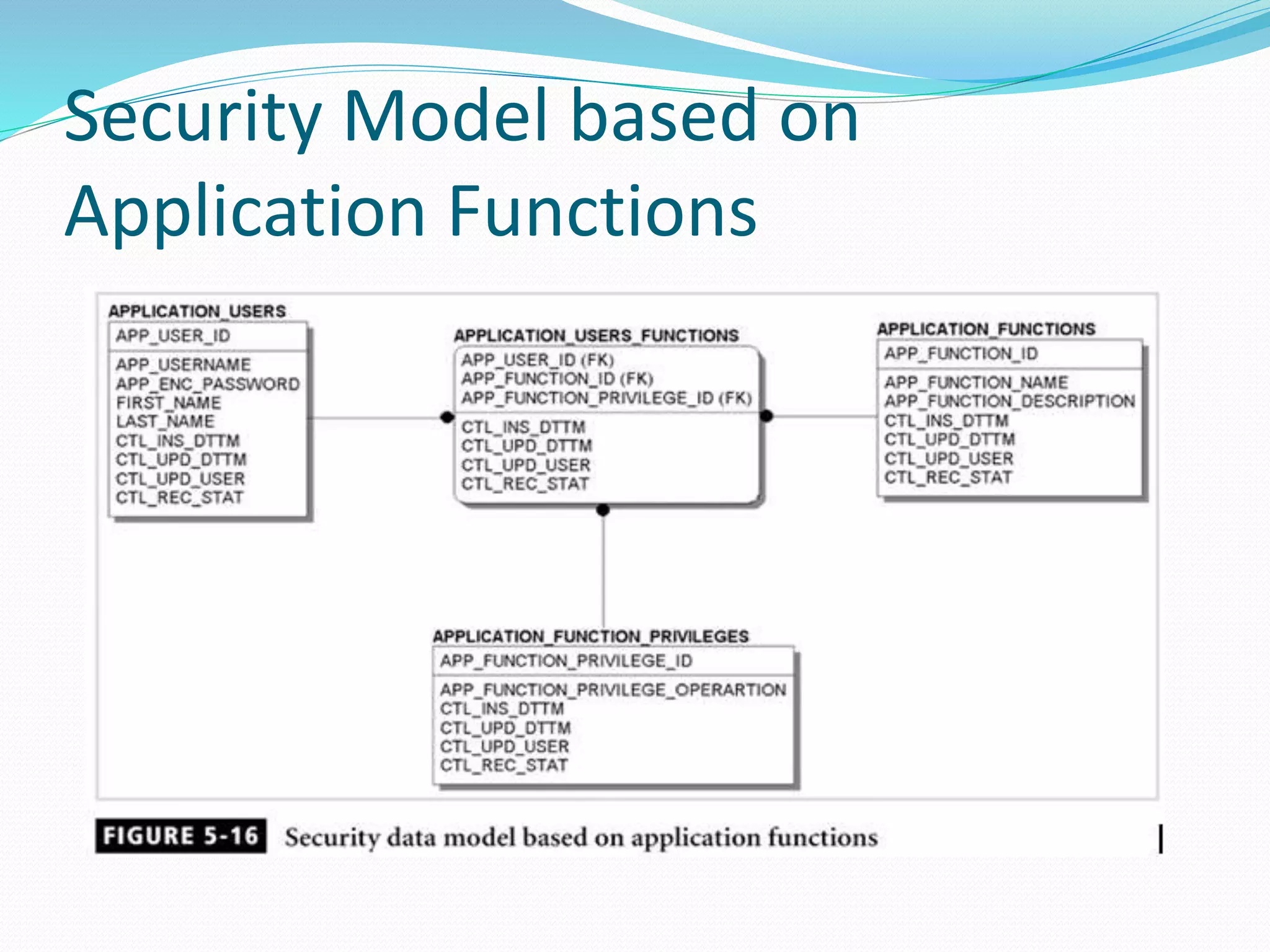
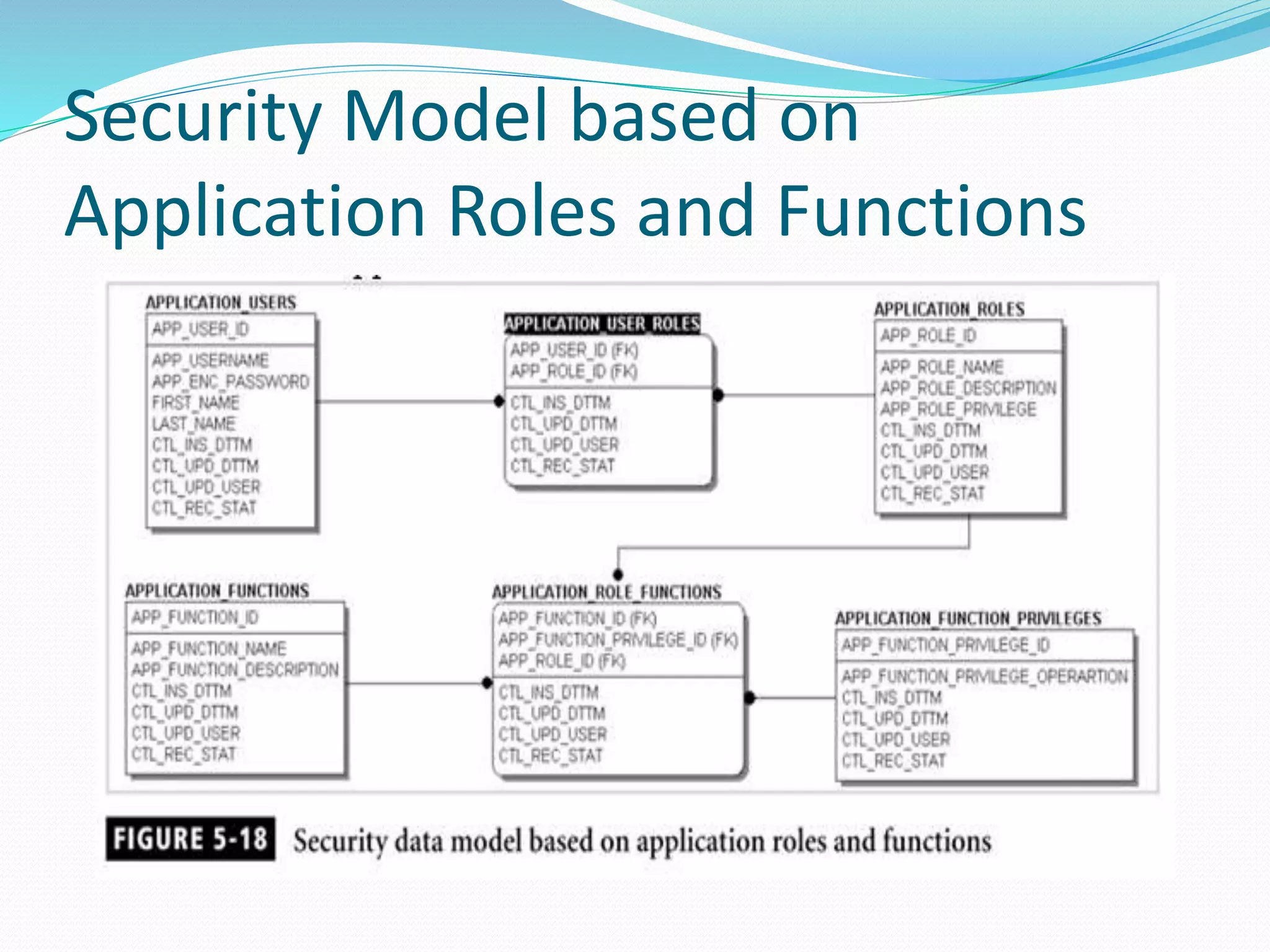
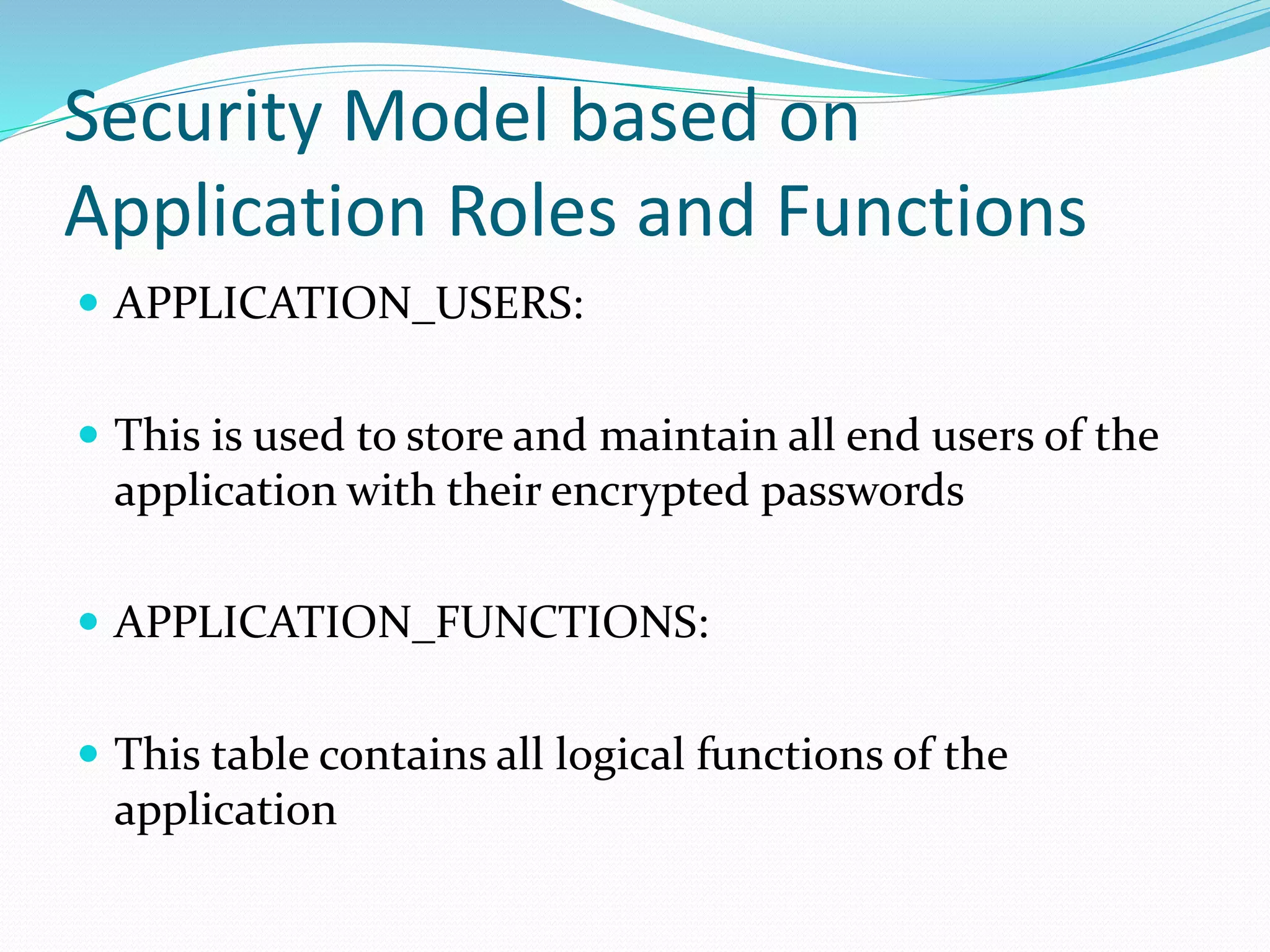
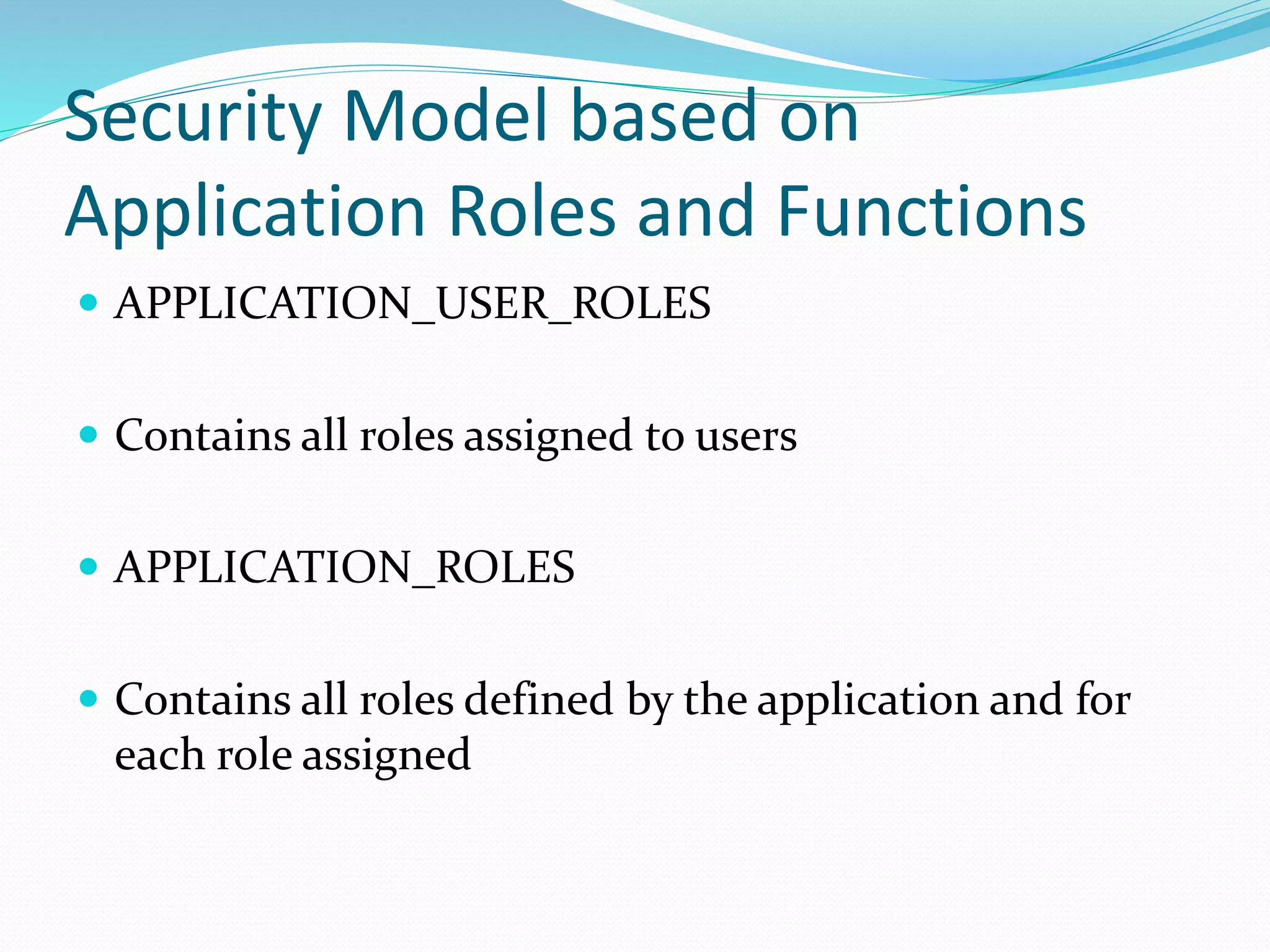
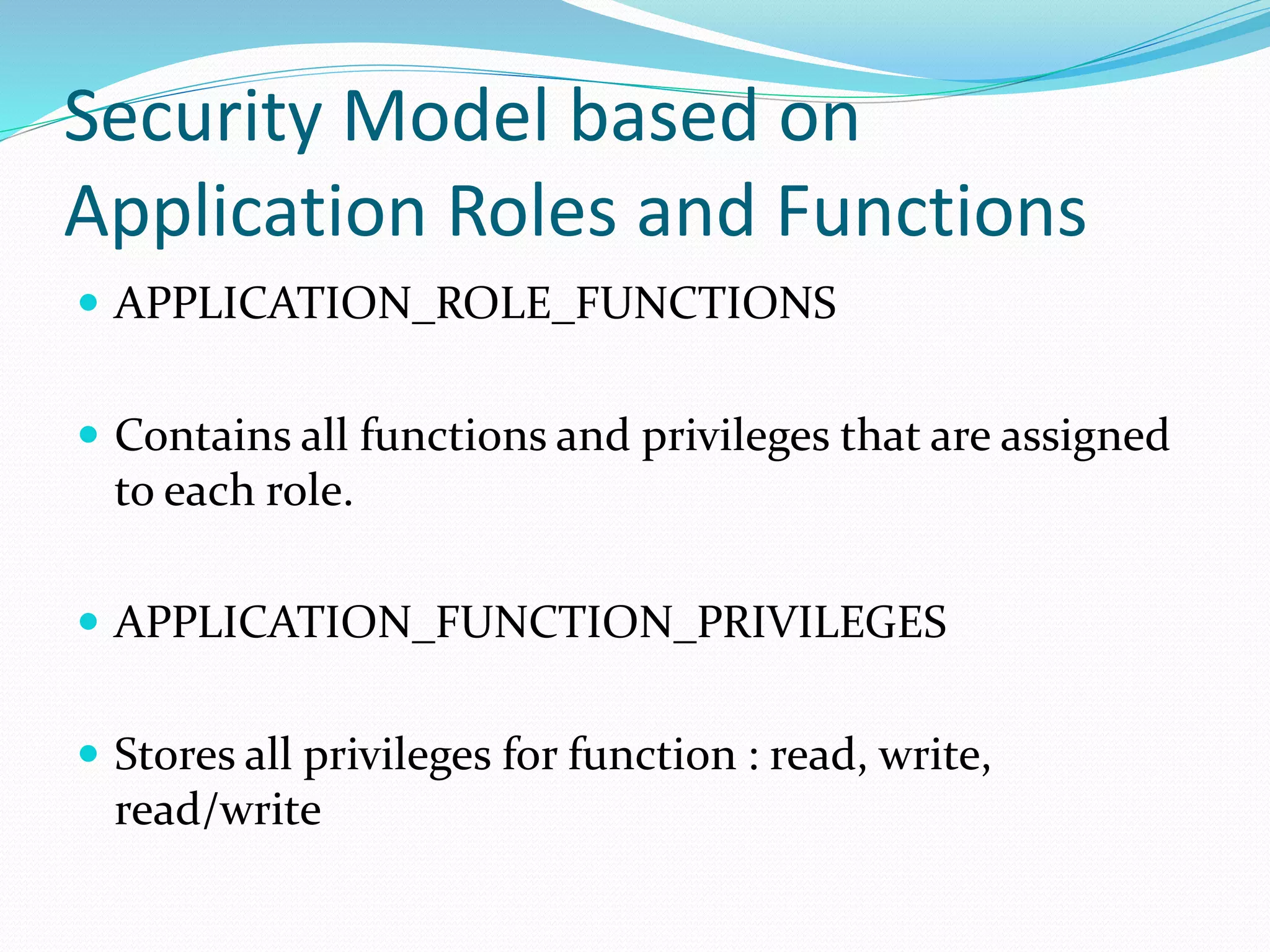
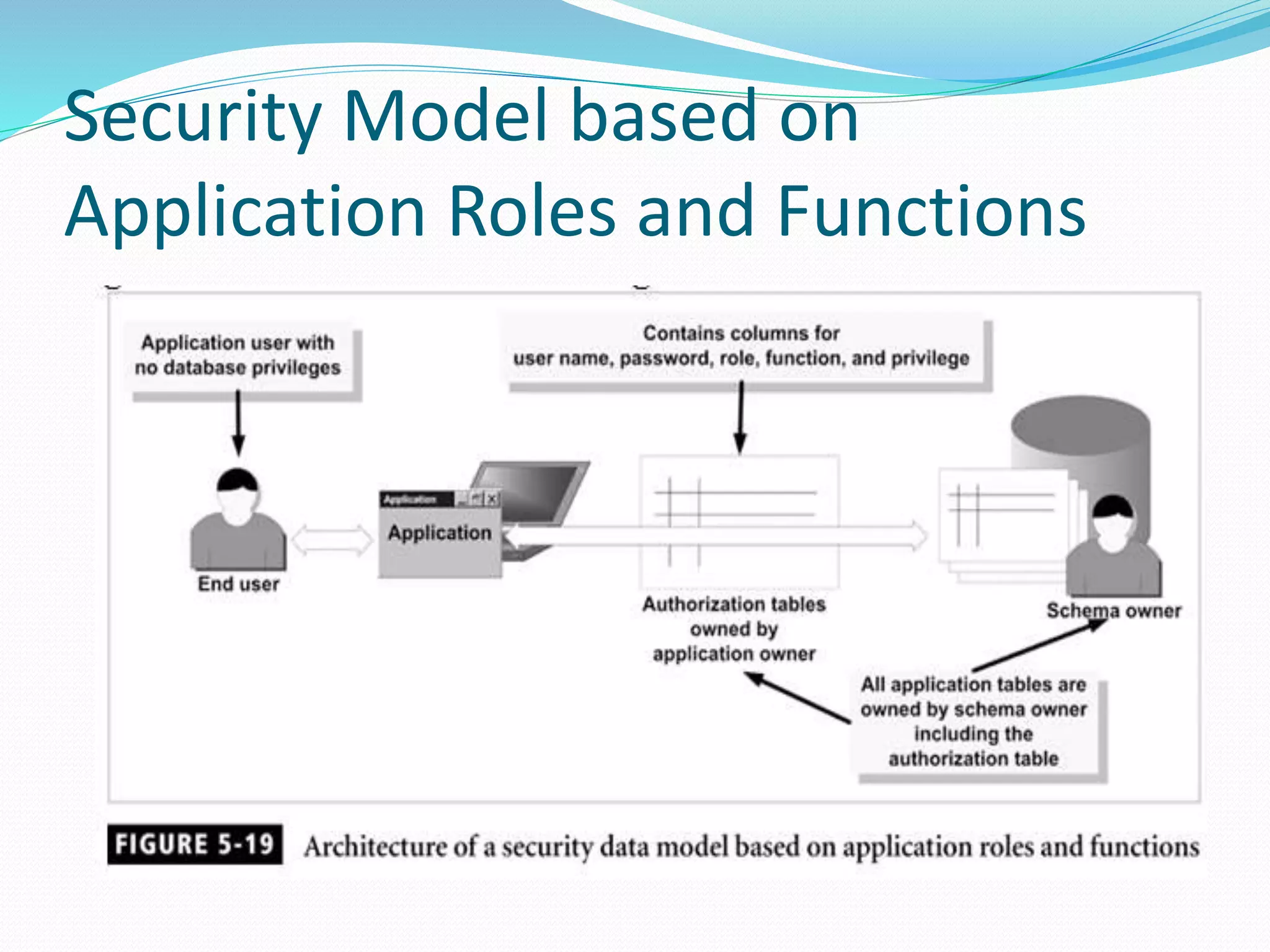
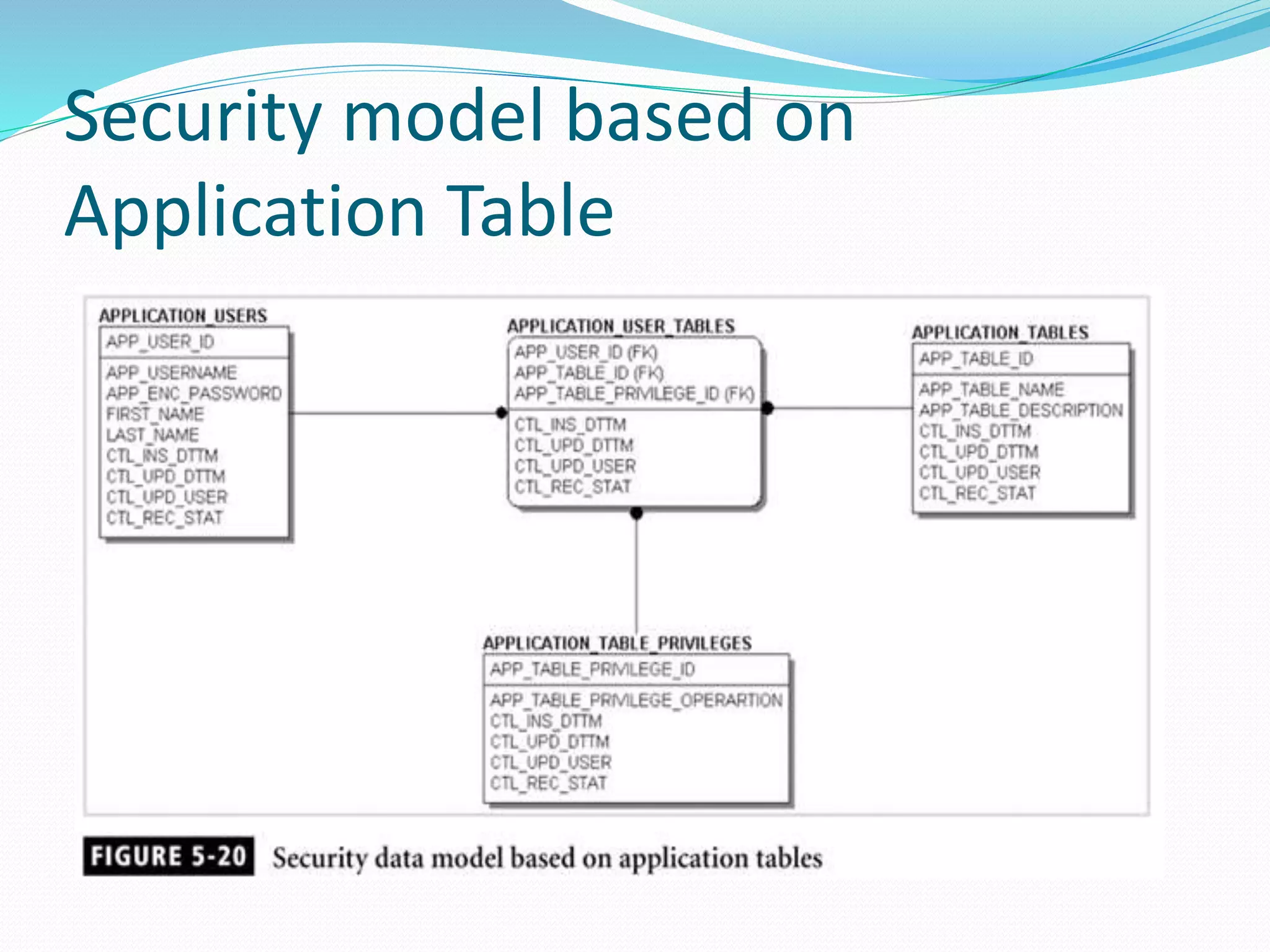
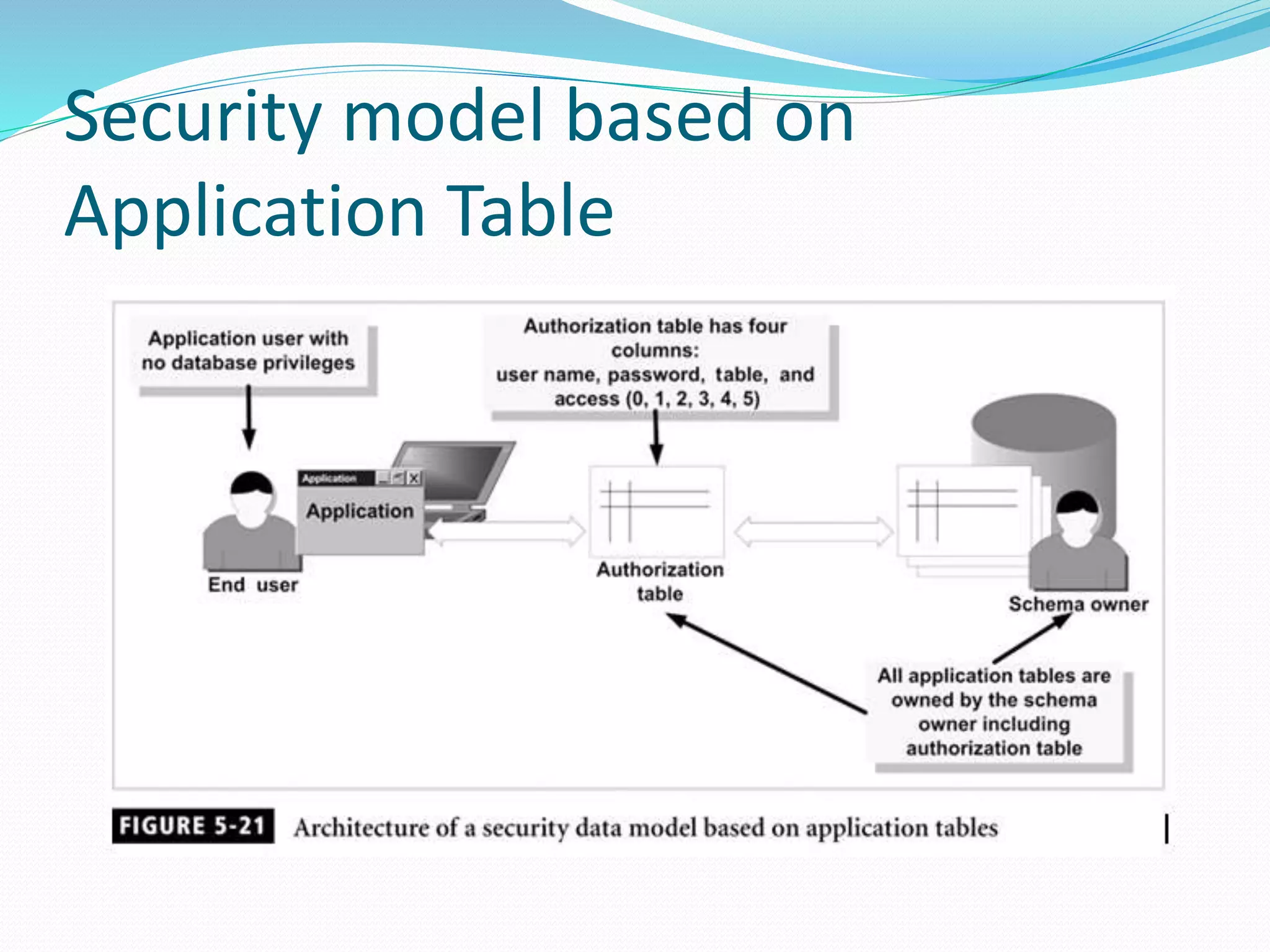
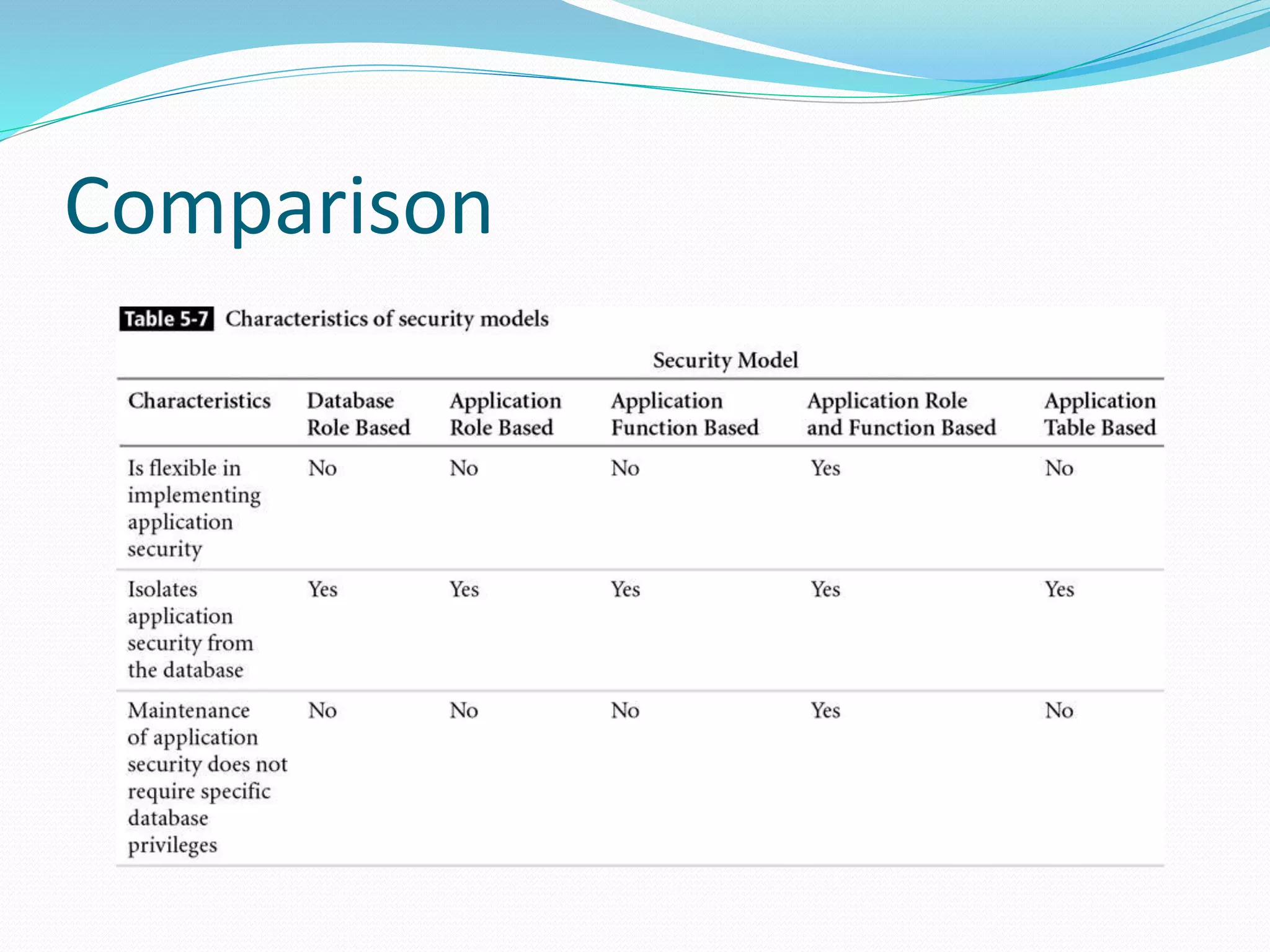
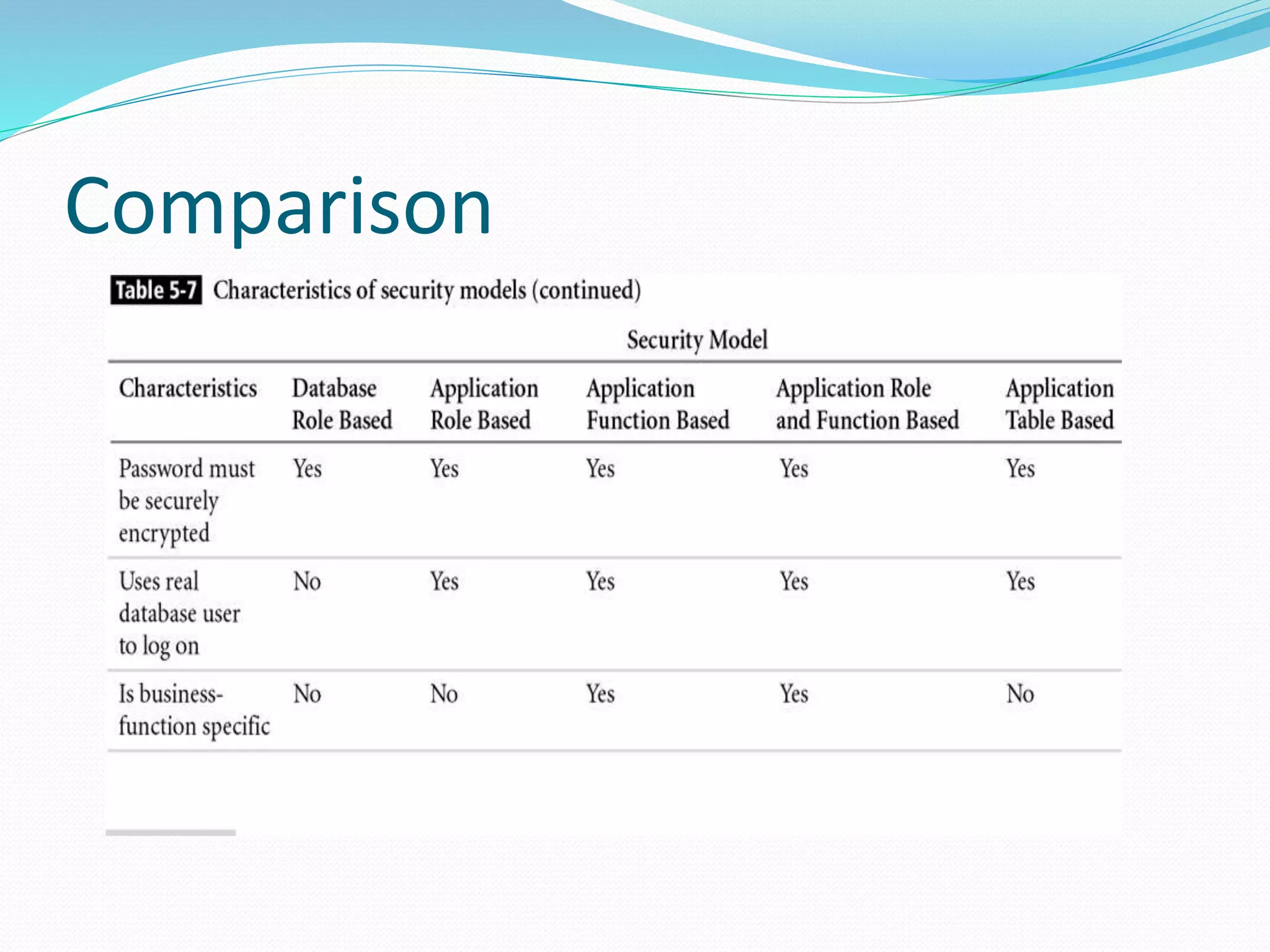
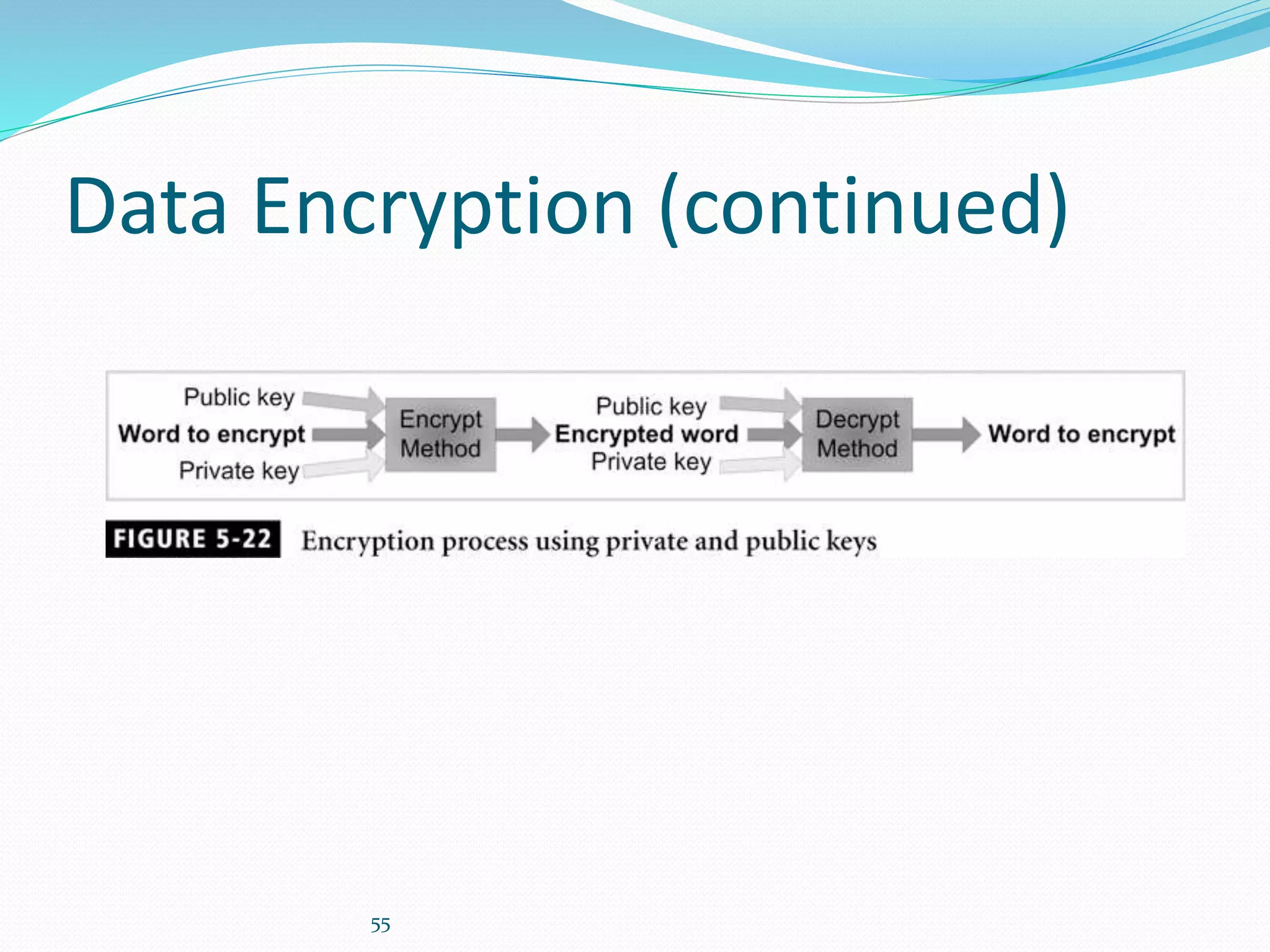
This document discusses 5 different application security models: database role based, application role based, application function based, application role and function based, and application table based. For each model, it describes the key tables used to implement the model, how privileges are assigned, and some characteristics of the model. The models aim to provide data security and access protection at the table level through different approaches to assigning privileges to users.