This document provides an analysis of Apple in 2010, including:
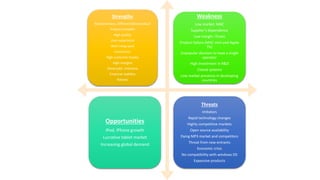
1. It identifies Apple's competitive advantages such as innovative, differentiated products and high customer loyalty, but also weaknesses like low market share for Mac and dependence on suppliers.
2. It performs a Porter's Five Forces analysis of threats from imitators, technology changes, and competitive markets facing Apple.
3. It considers alternatives for Apple such as expanding to developing markets, continuing product differentiation, and using the iPad to target mobile computing.