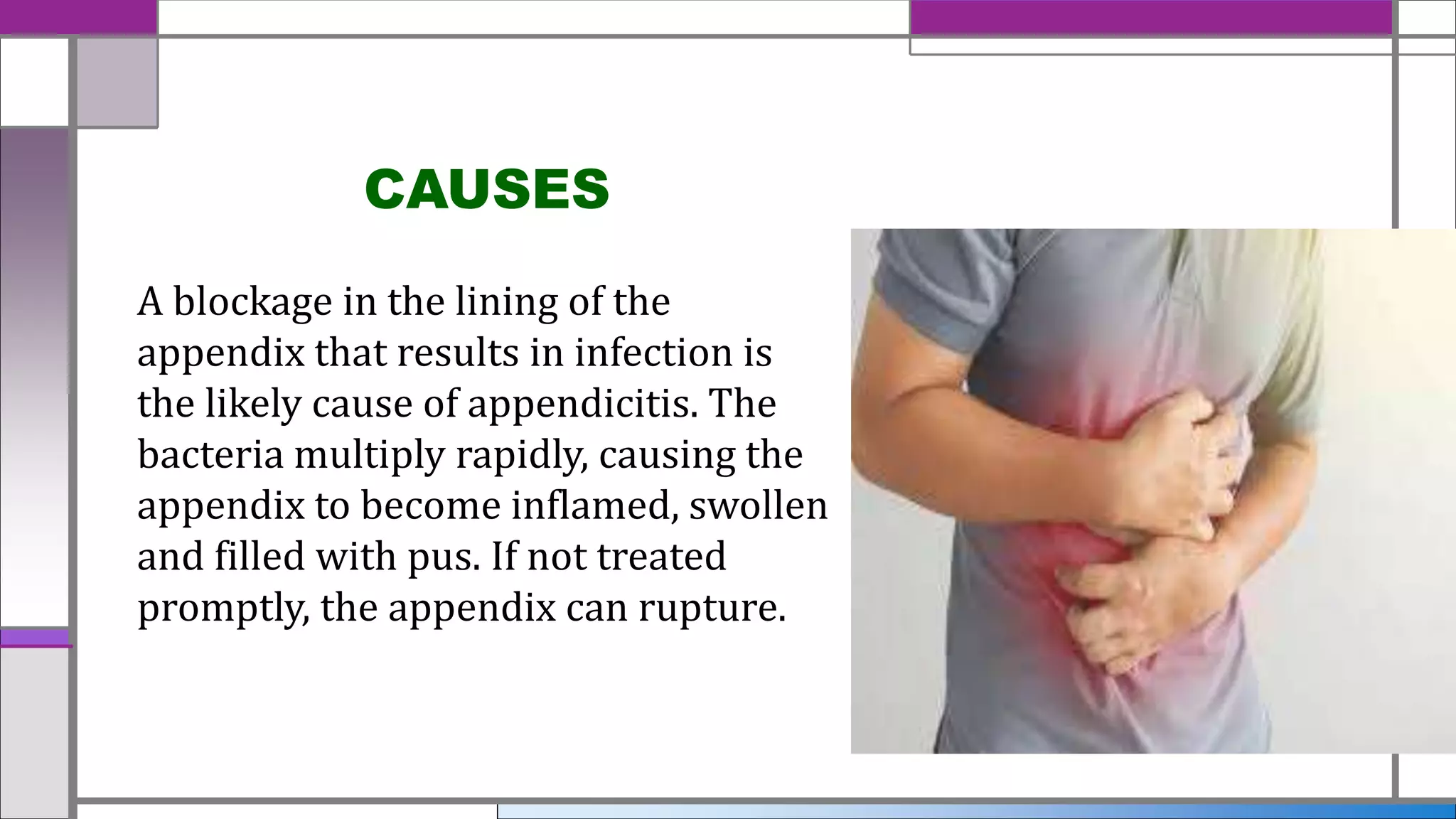
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix often causing severe pain in the lower right abdomen, with symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and fever. The standard treatment involves surgical removal of the appendix, typically conducted as an open or laparoscopic procedure, often preceded by antibiotics. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent complications such as rupture and infection spread.