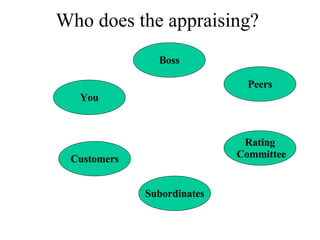
The document discusses performance appraisal, which is a process used to evaluate how well employees perform their jobs compared to set standards. It involves setting standards, assessing performance against those standards, identifying factors influencing performance, and providing feedback. Performance appraisals help with performance management, planning improvements, career development by identifying strengths and weaknesses, and determining salary raises. The objectives, process, methods, raters, and design considerations of an effective performance appraisal system are also outlined.