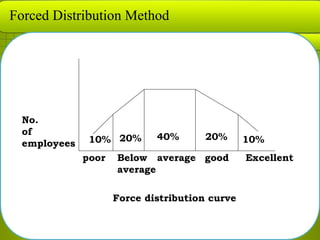
Performance appraisal methods can be categorized as traditional or modern. Traditional methods include graphic rating scales, forced choice descriptions, forced distribution, checklists, and critical incidents. These methods have advantages like low cost and ease of use but also have disadvantages like rater bias. Modern methods include management by objectives (appraising results), behaviorally anchored rating scales, and 360 degree feedback. The 360 degree feedback involves collecting performance data from supervisors, peers, customers, and the individual to evaluate interpersonal skills and customer satisfaction. Overall, performance appraisal aims to provide feedback to employees on their strengths and weaknesses to help them improve and support organizational goals.