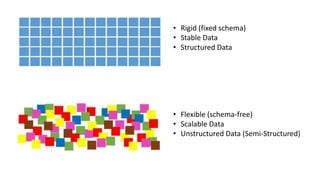
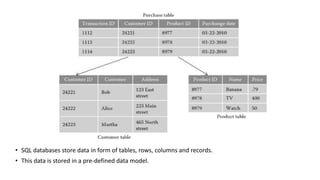
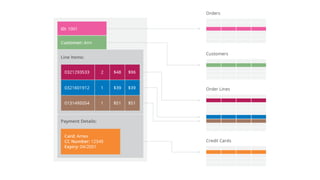
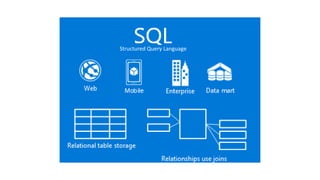
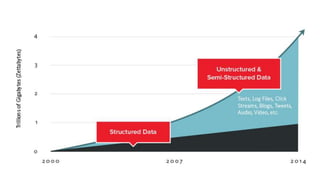
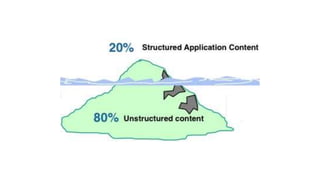
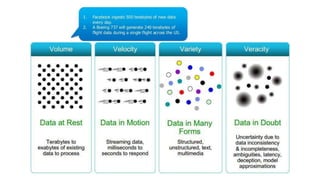
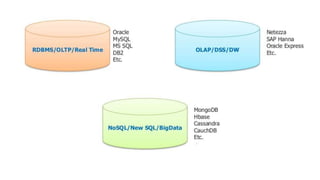
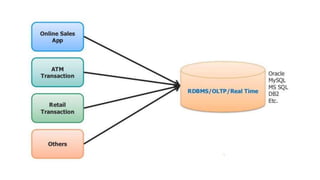
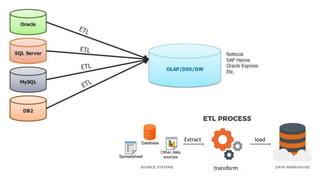
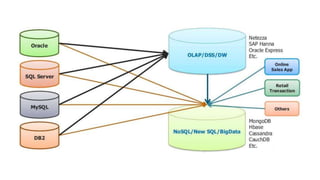
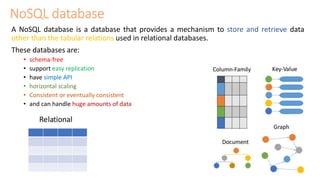
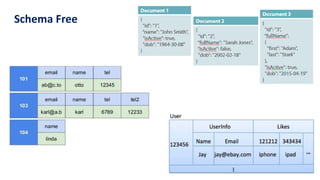
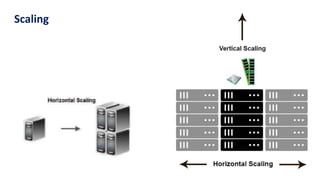
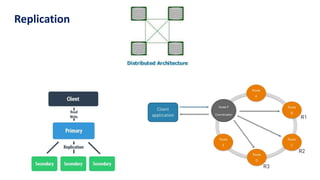
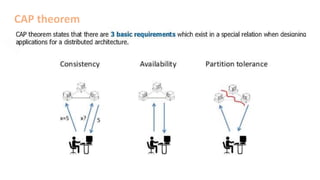
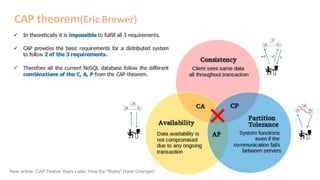
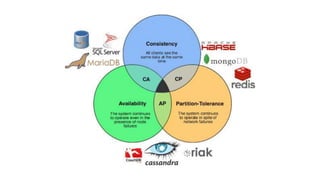
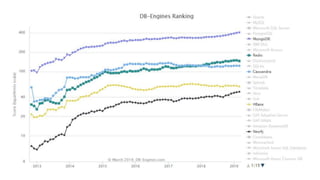
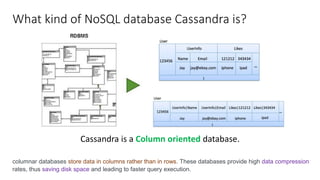
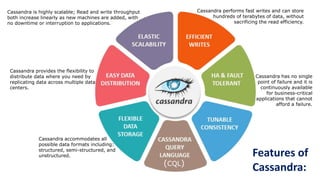
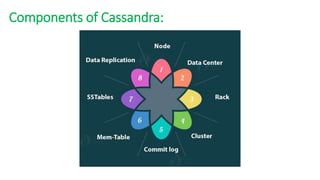
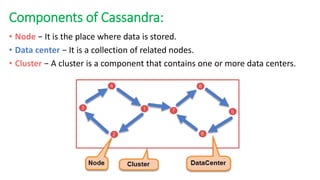
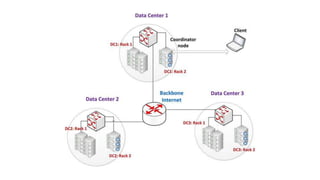
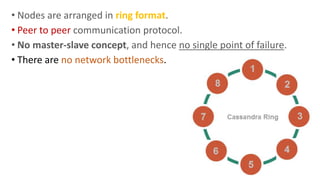
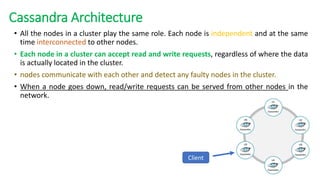
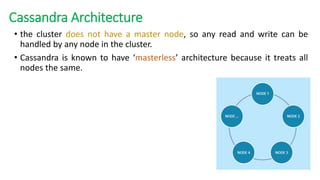
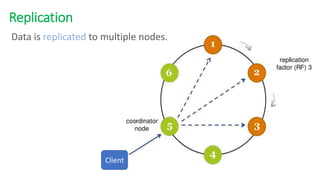
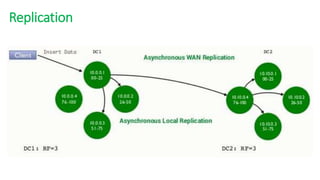
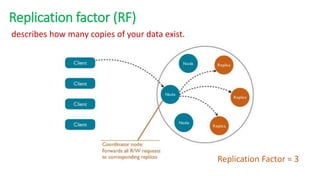
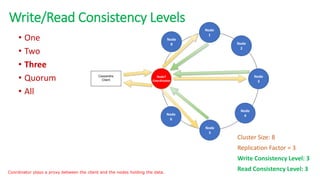
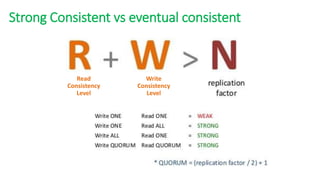
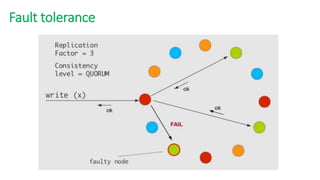
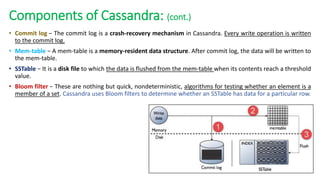
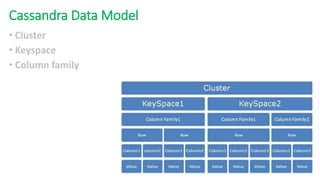
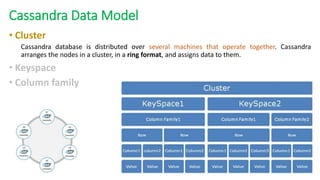
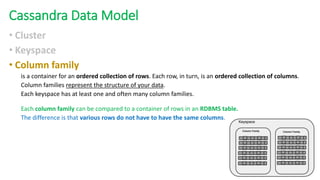
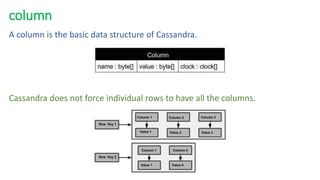
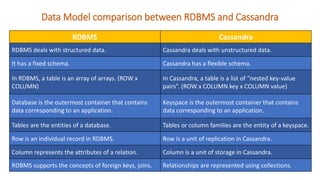
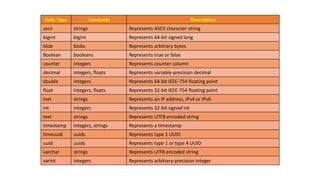
The document provides an overview of NoSQL databases, emphasizing the characteristics of Cassandra as a column-oriented, highly scalable NoSQL database designed for managing vast amounts of data. Cassandra's architecture features a masterless design with fault tolerance, supporting a variety of data formats and allowing for seamless distribution and replication across multiple nodes. Key components and operations, along with comparisons to RDBMS, are also discussed, highlighting Cassandra's flexibility and performance advantages.