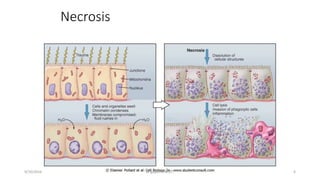
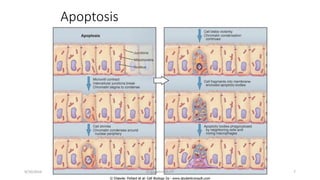
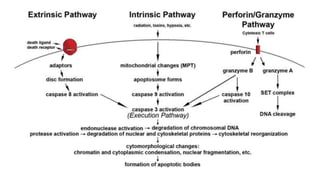
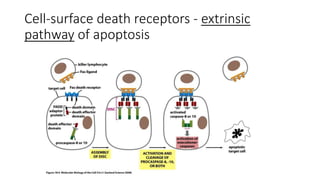
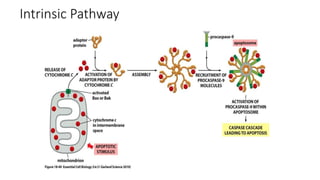
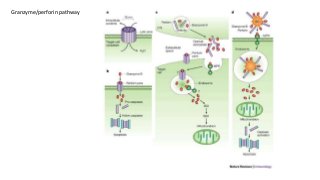
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a vital process in the body that occurs through development, aging, and when cells are damaged. It is characterized by distinct morphological changes and biochemical mechanisms. The process involves caspase activation and a complex cascade of events. There are three main pathways that trigger apoptosis - the intrinsic pathway which involves mitochondria, the extrinsic or death receptor pathway activated by extracellular signals, and the perforin/granzyme pathway used by cytotoxic T cells. All pathways ultimately activate executioner caspases like caspase-3 to carry out the final stages of apoptosis.