This document provides information on various pharmaceutical dosage forms and excipients. It discusses:
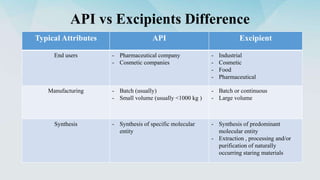
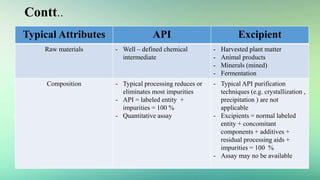
1) The difference between active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients, and typical attributes of each.
2) The process for tablet manufacturing including granulation and coating steps.
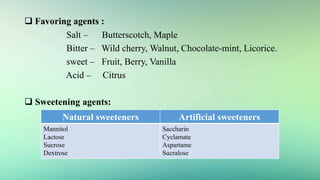
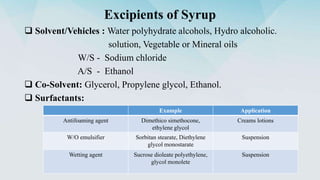
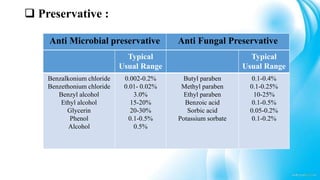
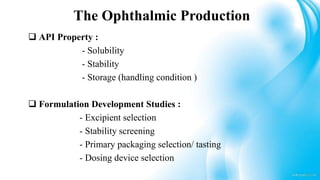
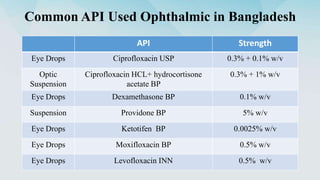
3) Common excipients used in tablets, syrups, and ophthalmic products and their functions.
4) Processes for preparing syrups and coating tablets.
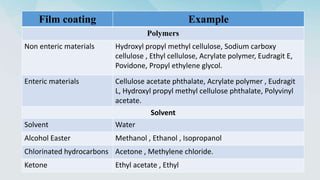
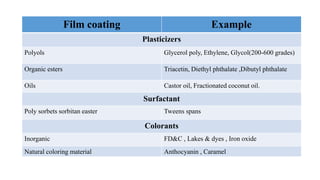
5) Polymers and other materials used for different types of tablet coatings including film coatings, enteric coatings and controlled release coatings.