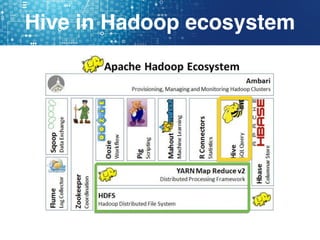
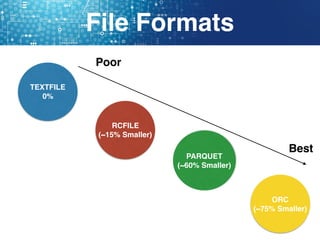
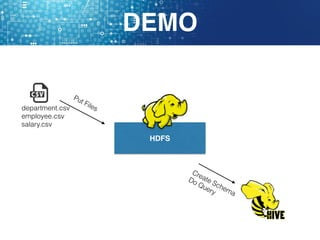
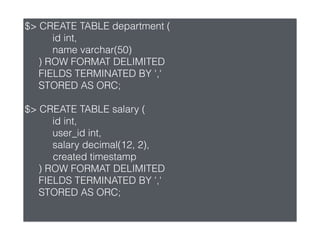
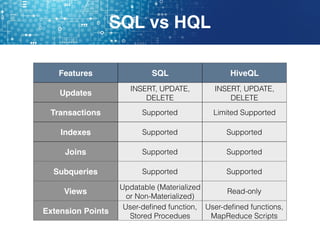
Hive is a data warehouse software that allows users to query and manage large datasets stored in Hadoop using SQL-like language called HiveQL. It facilitates reading, writing, and managing large datasets in distributed storage. Hive is best used for batch processing jobs rather than online transactions due to limitations in updating and deleting data. Common file formats used in Hive include textfiles, RCFiles, Parquet and ORC, with Parquet and ORC being preferred due to smaller file sizes.