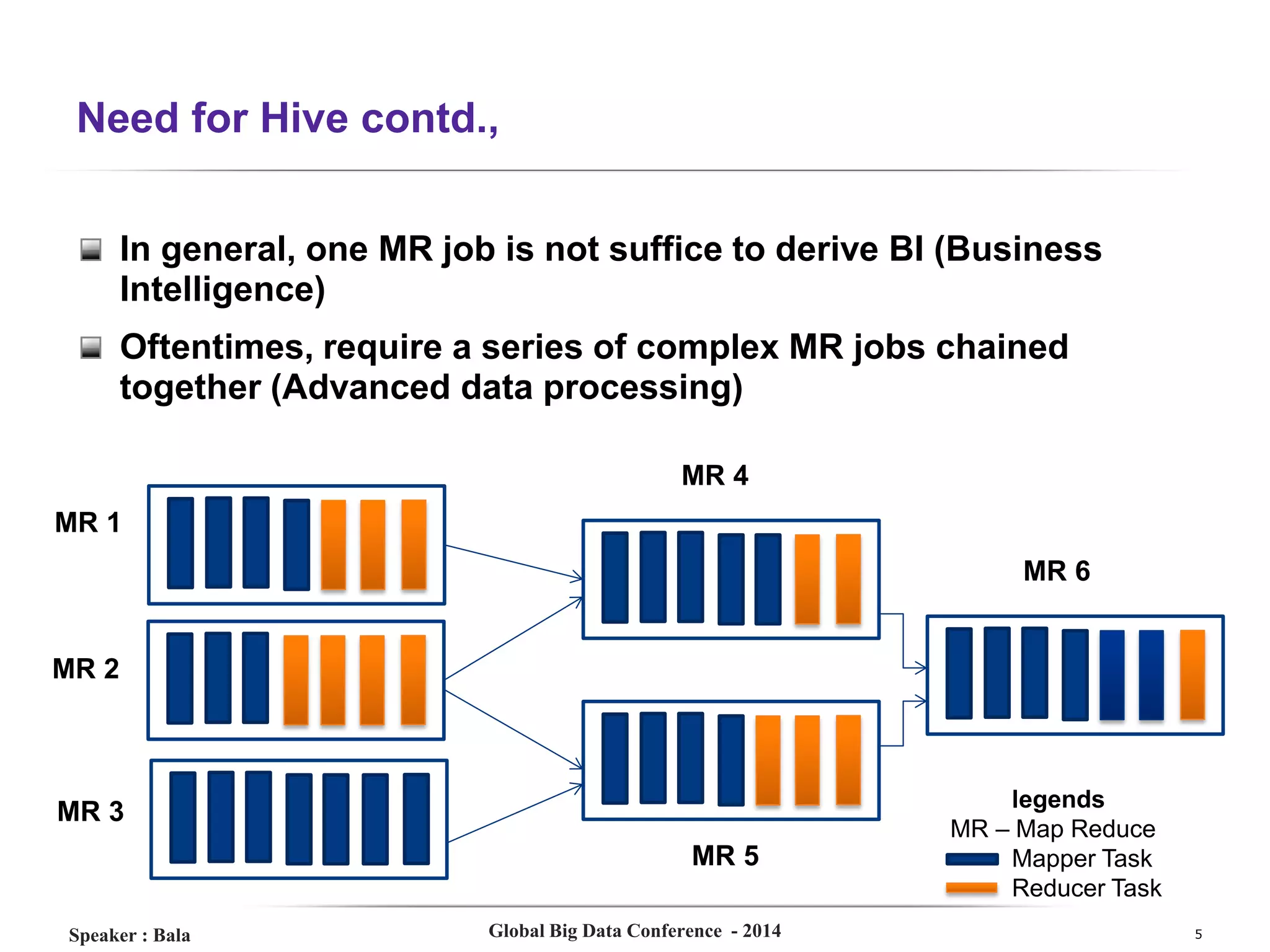
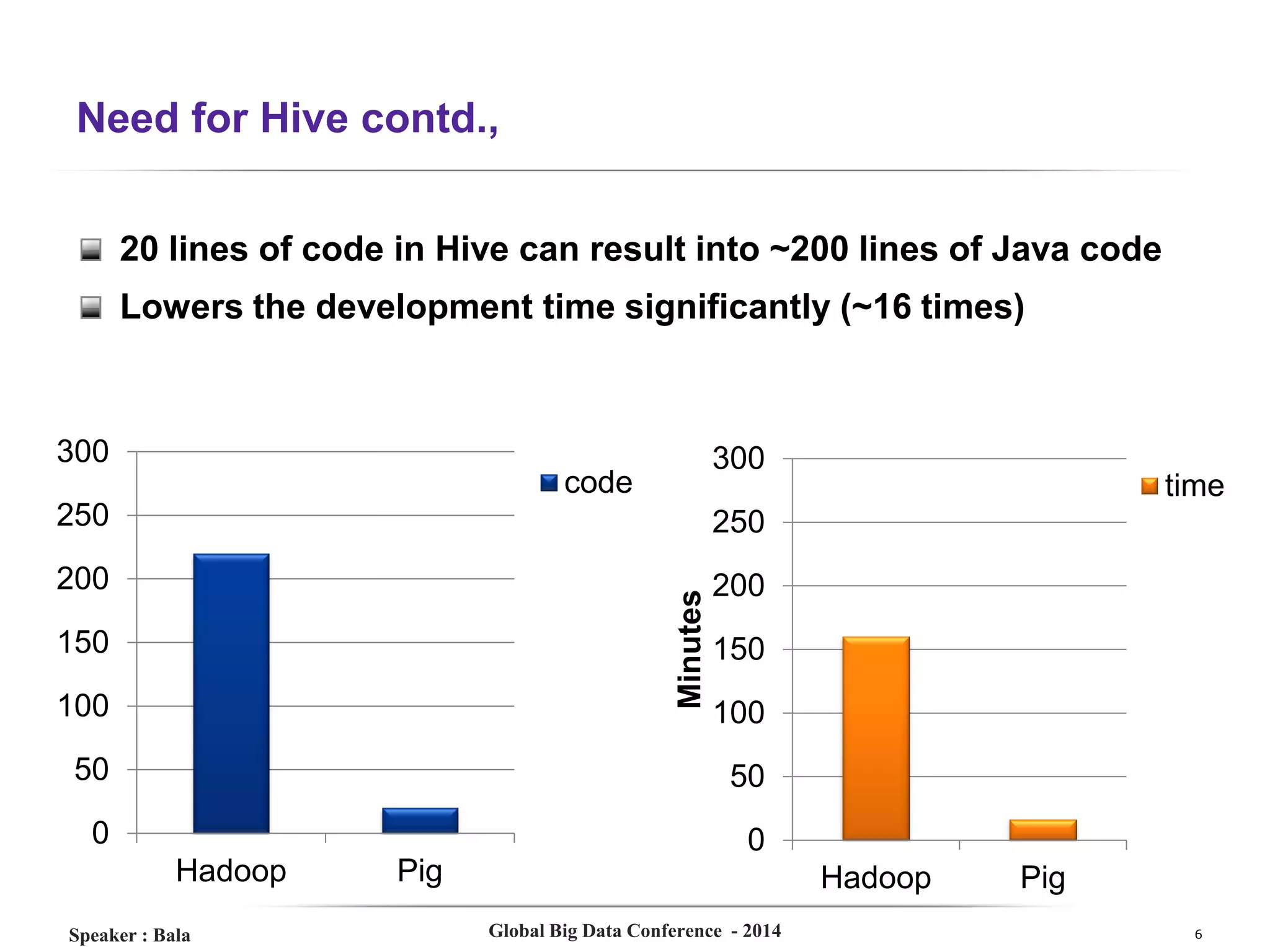
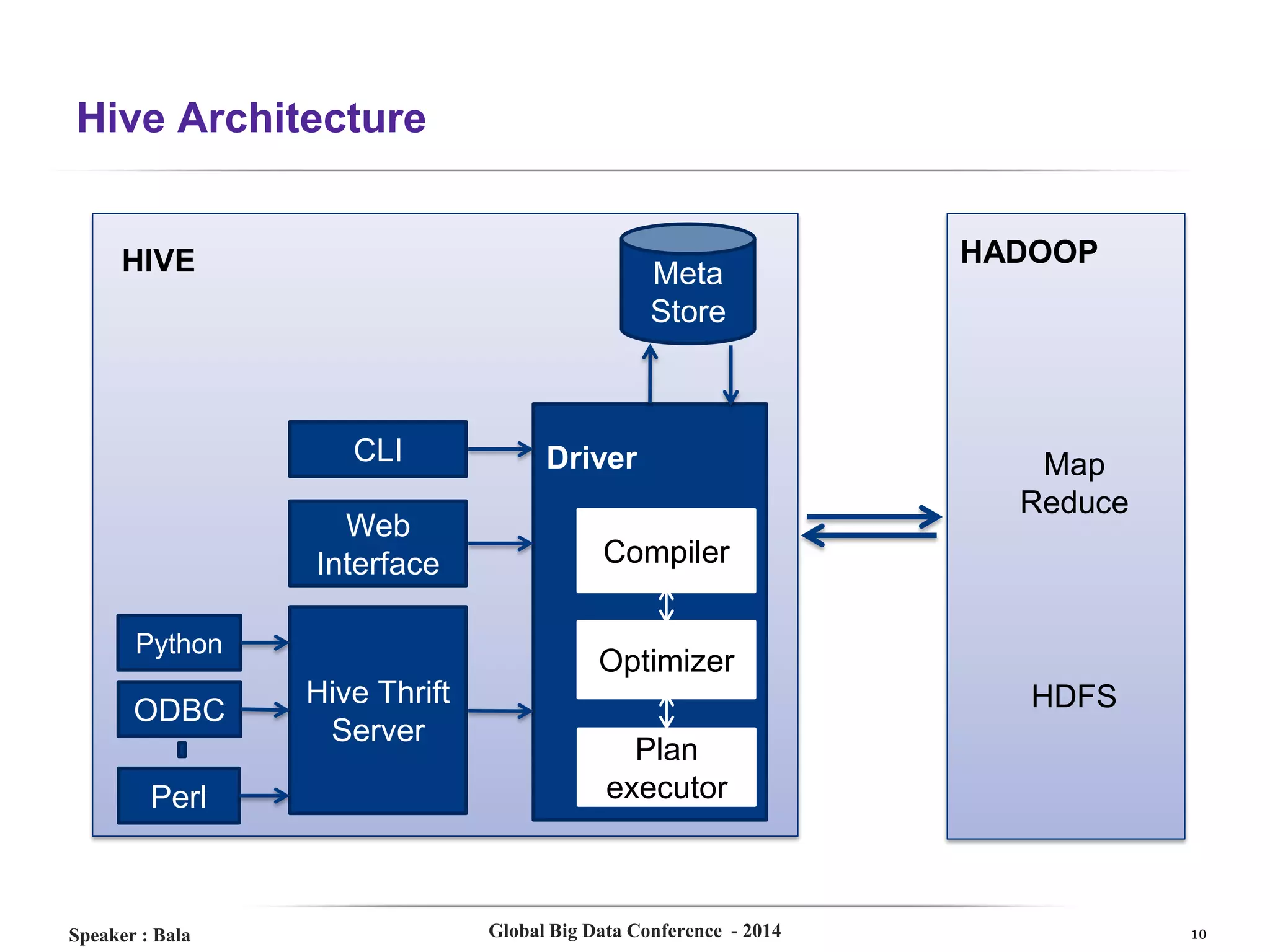
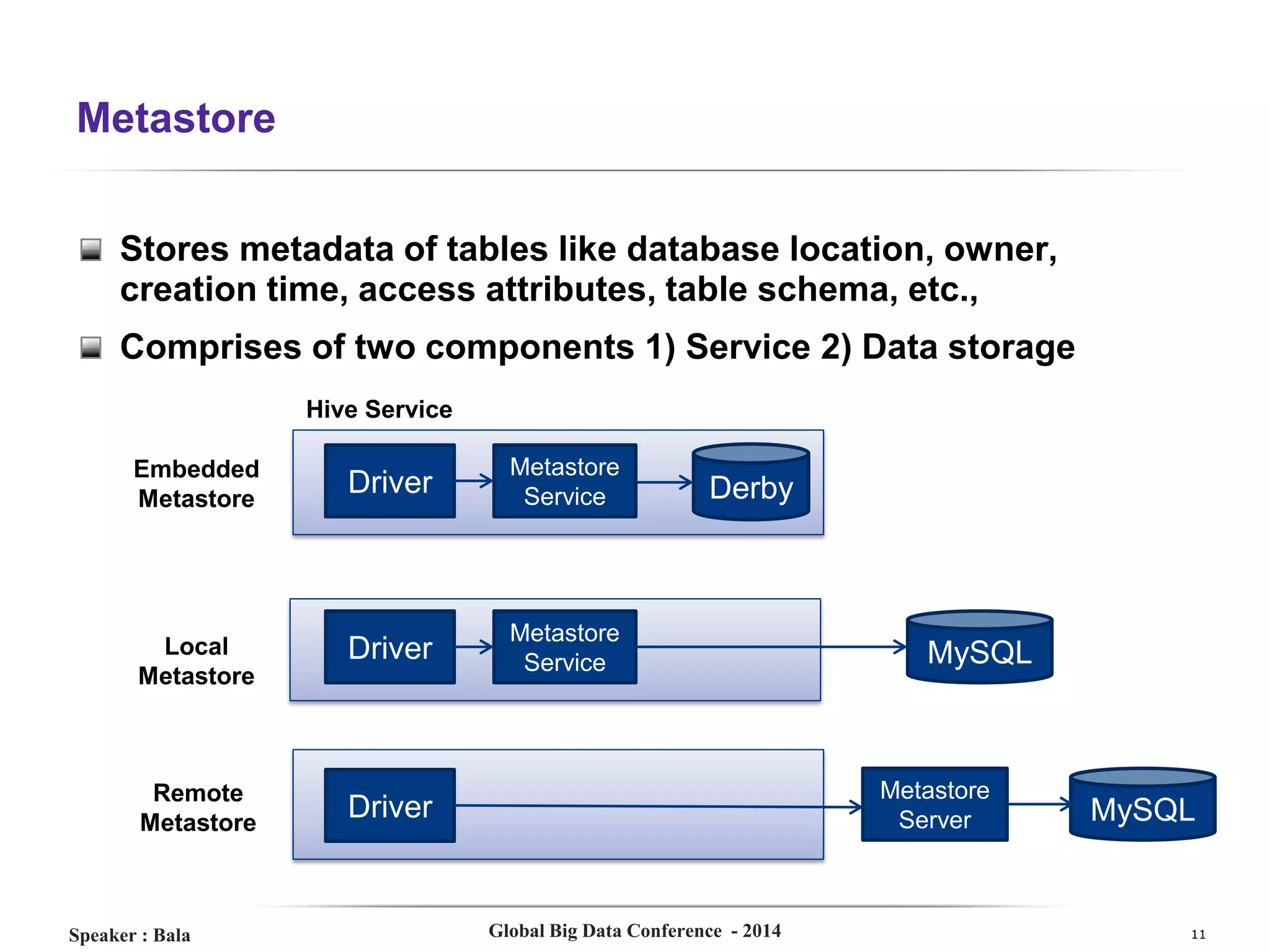
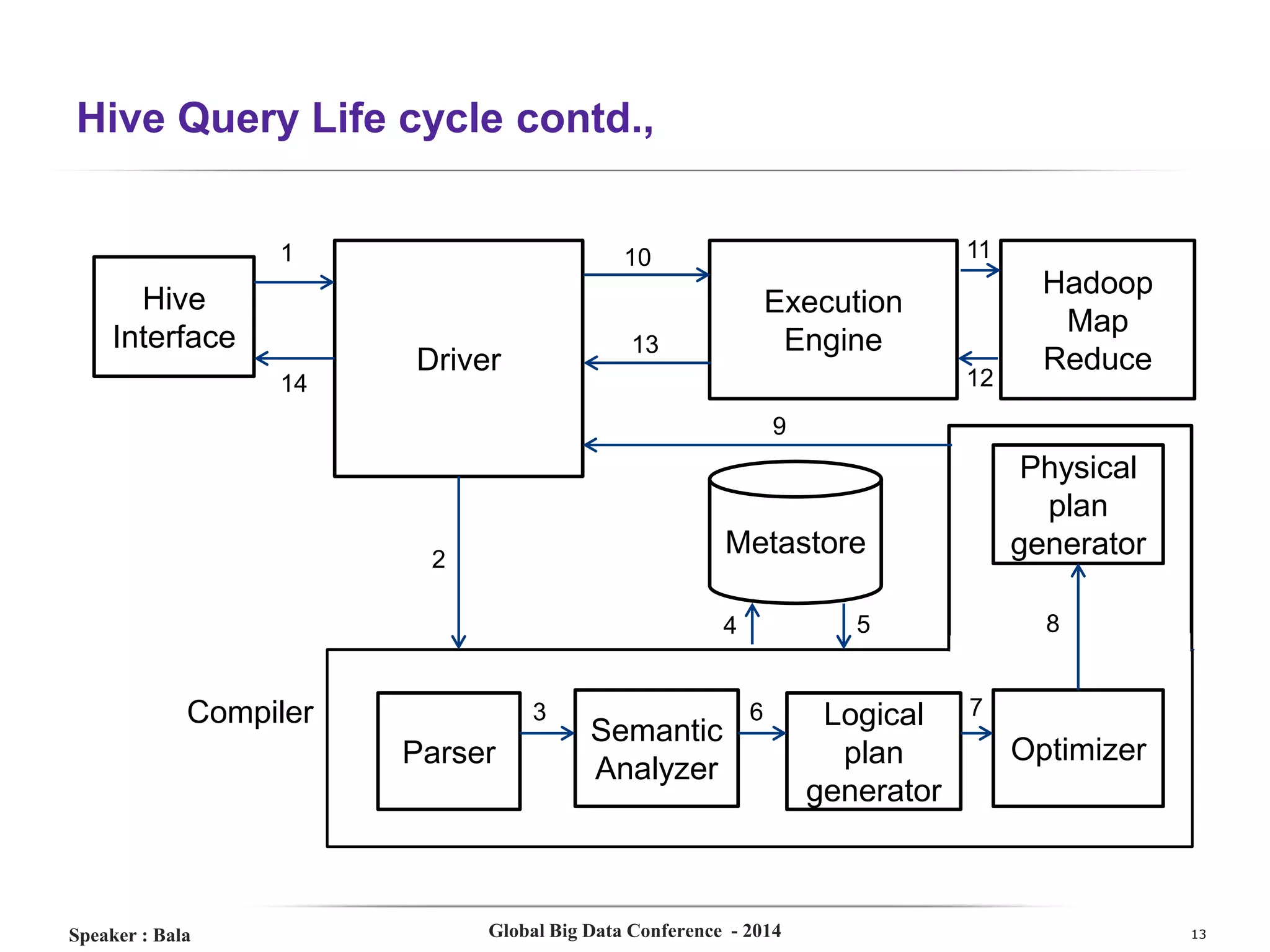
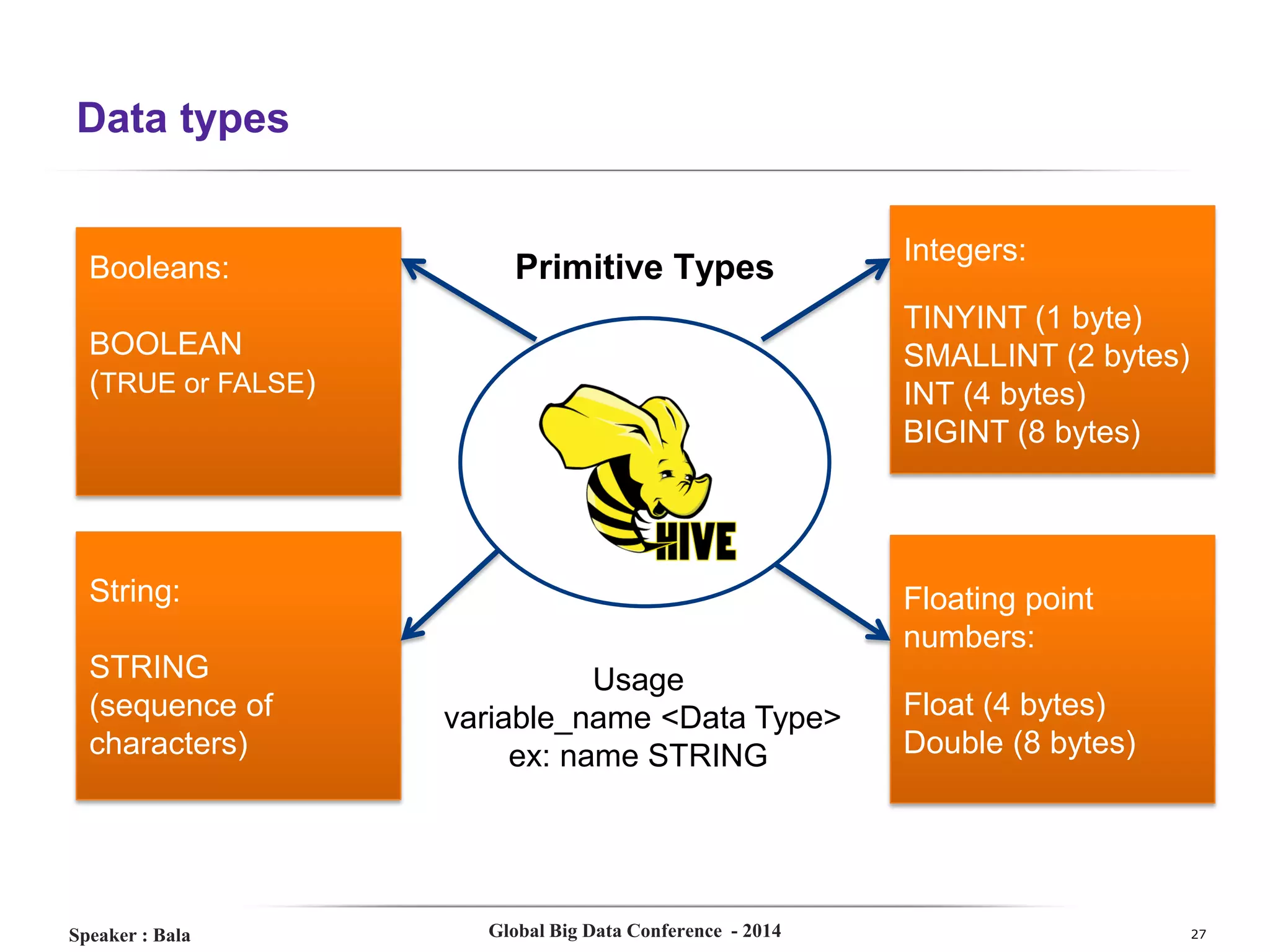
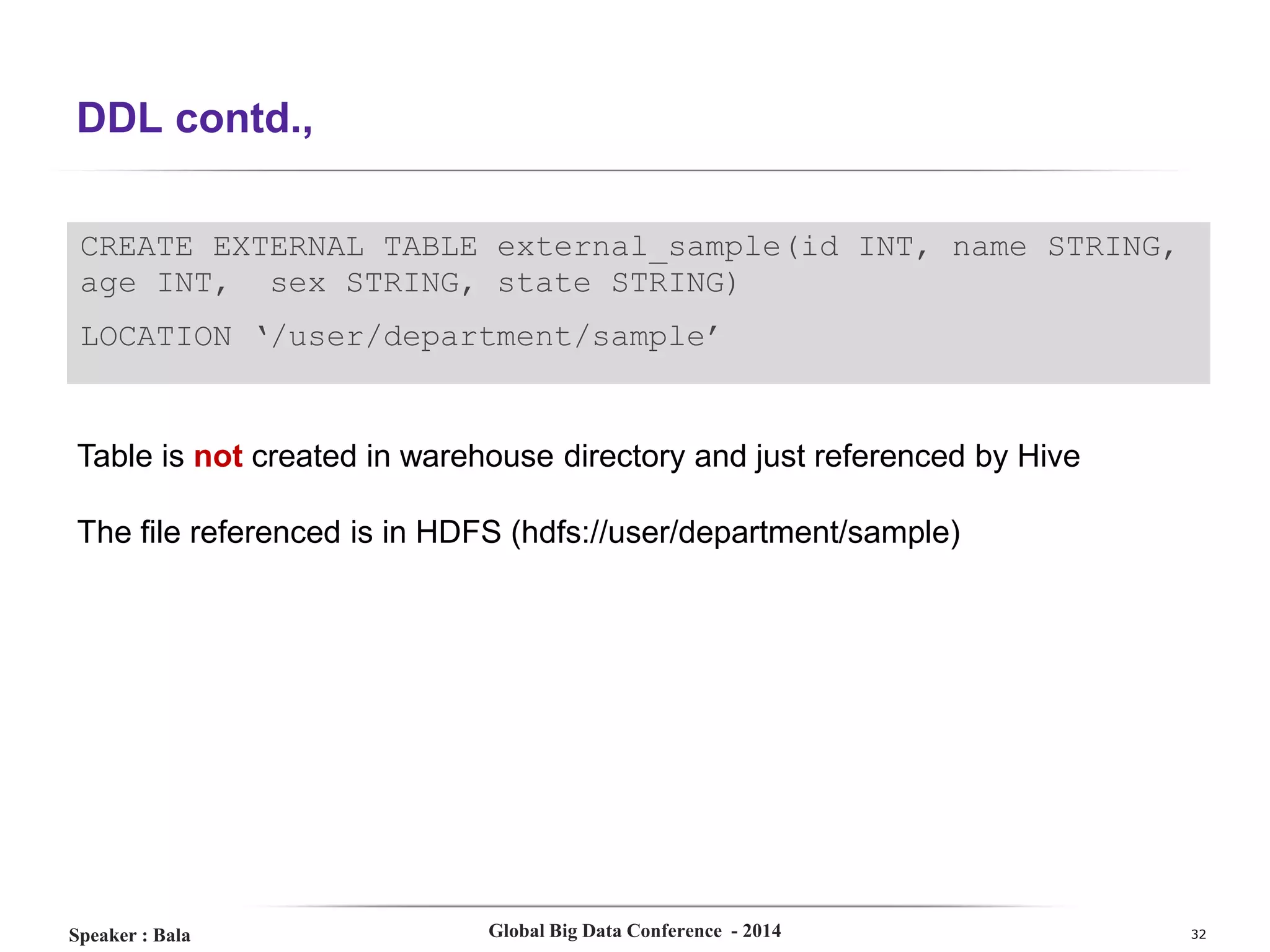
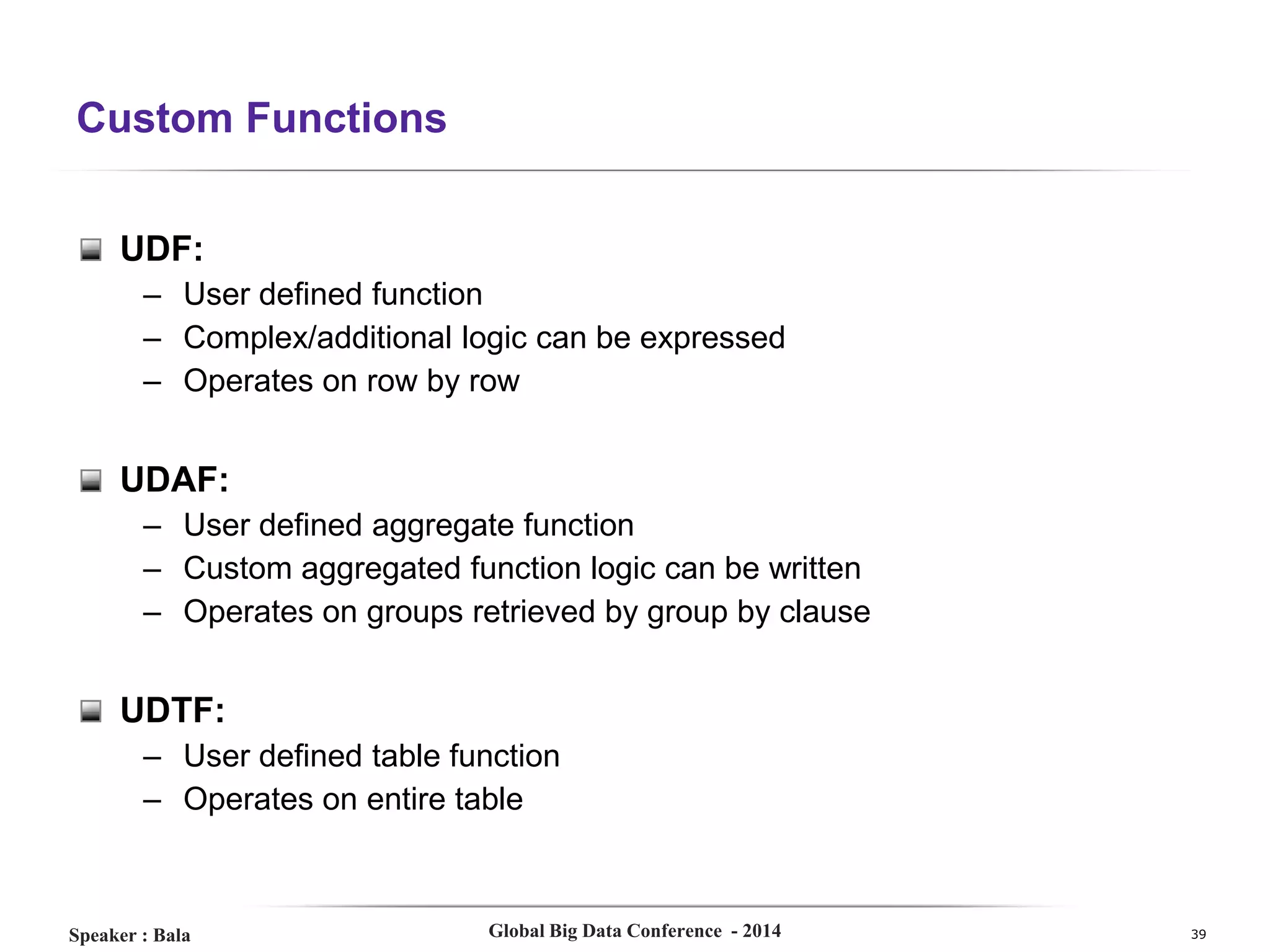
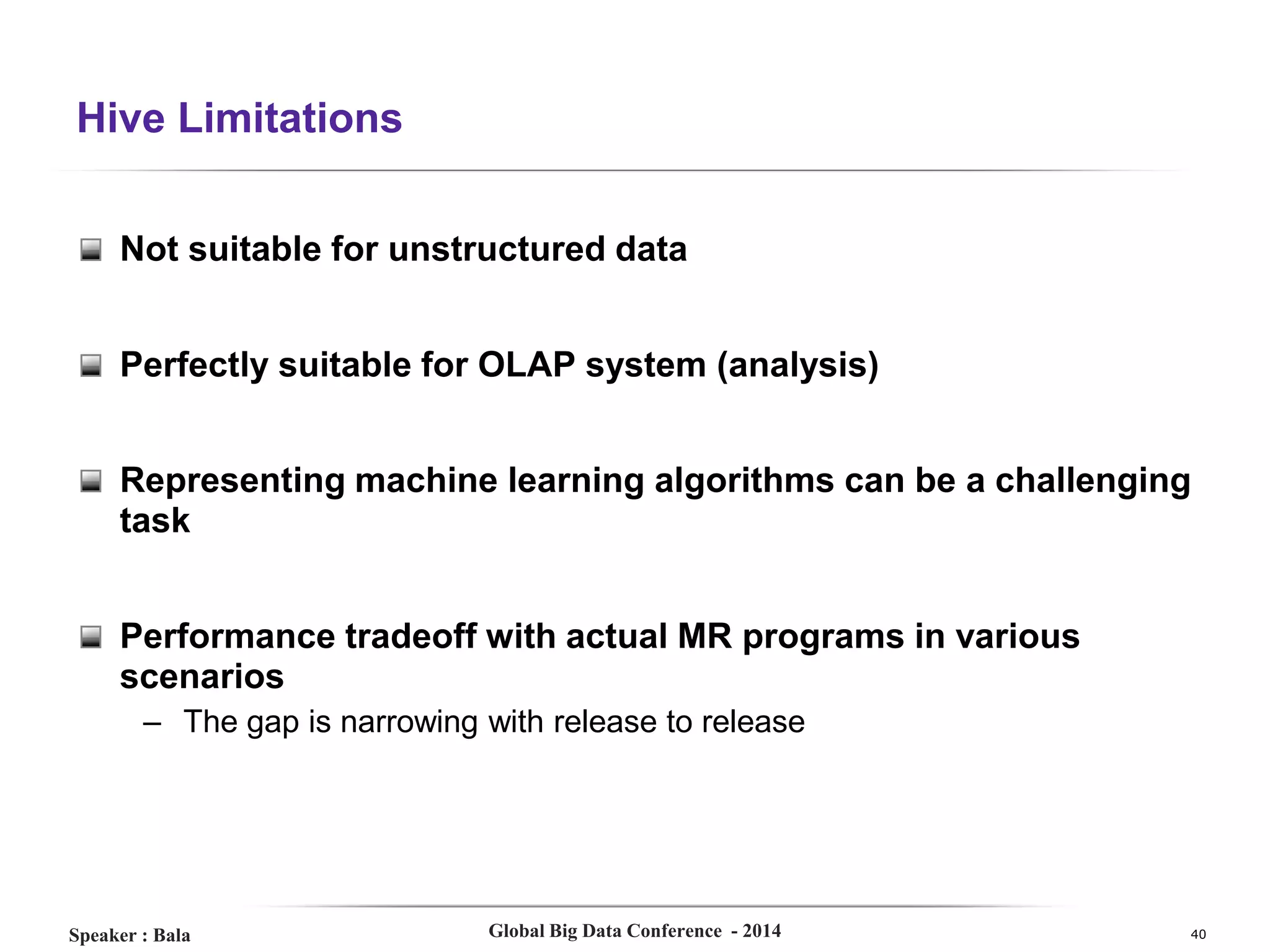
The document presents a detailed overview of Hive, a data warehouse solution built on Hadoop, discussing its purpose, architecture, and functionalities. It covers the Hive query lifecycle, data modeling techniques, and the advantages of using Hive over traditional Java-based processing, emphasizing its effectiveness in handling structured data. Additional sections include practical tips, limitations, and data loading techniques, as well as examples of Hive query language and definitions of key terms.











![Data types contd.,
Key must be a primitive in MAP
Referencing complex types
Previous example:
– marks ARRAY<INT>
– record STRUCT <name STRING, id INT, marks ARRAY<INT>>
– score MAP<STRING, INT>
SELECT marks[0], record.name, score[‘joe’]
Complex type inside a complex type is allowed
– array inside a struct (as seen before)
Speaker : Bala
Global Big Data Conference - 2014
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hive-140131182741-phpapp01/75/Hive-29-2048.jpg)













![Schema on Read (?)
[To do] where to put this slide?
Explain what is schema on read
Explain what is schema on write
Advantages of using schema on read
– Faster load time
– Impacts query time
Speaker : Bala
Global Big Data Conference - 2014
46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hive-140131182741-phpapp01/75/Hive-46-2048.jpg)