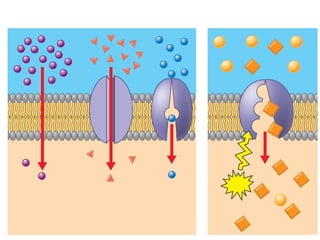
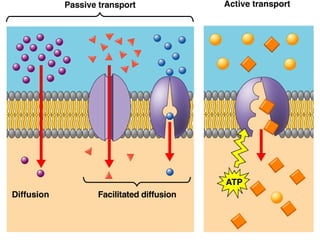
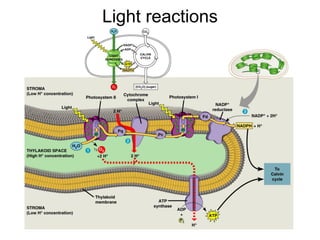
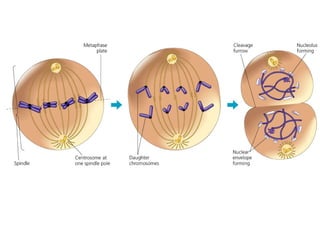
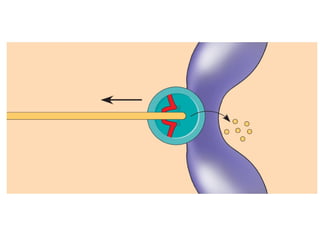
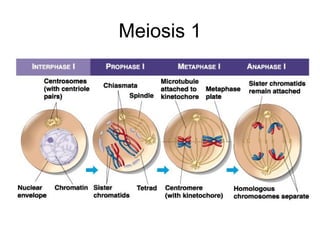
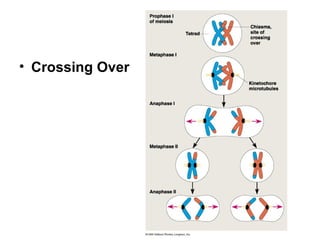
The document discusses various topics related to metabolism and cells, including:
- ATP provides a replenishable form of energy through its phosphate groups.
- Organic compounds contain carbon atoms covalently bonded to each other, which is not found in inorganic compounds.
- The inner and outer mitochondrial membranes are analogous structures.
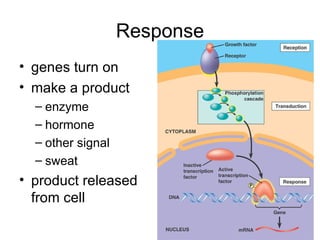
- Protein synthesis (mRNA translation) is an example of anabolism.
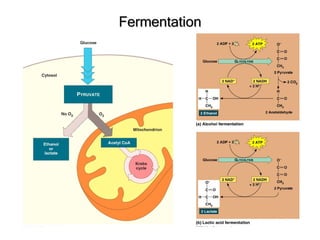
- Fermentation directly produces alcohol or lactic acid.