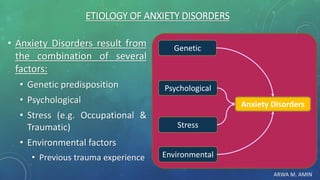
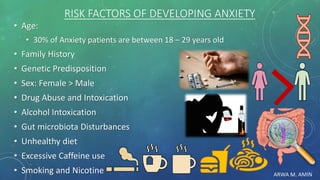
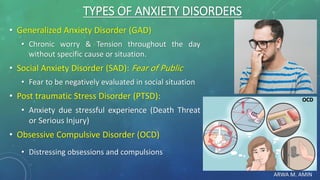
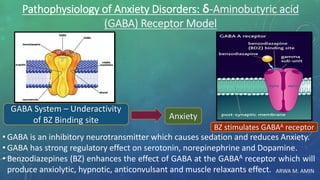
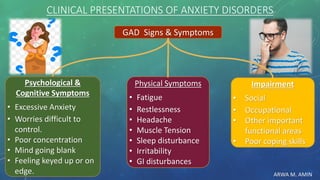
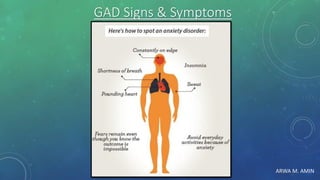
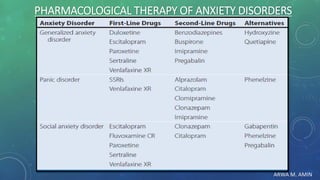
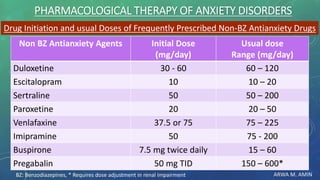
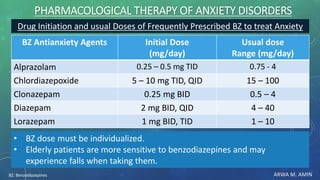
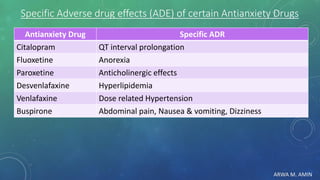
The document discusses anxiety and anxiety disorders, outlining their prevalence, etiology, risk factors, types, and pathophysiology. It emphasizes the diagnostic criteria for Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) according to DSM-5 standards, alongside treatment options including both non-pharmacological methods like cognitive behavioral therapy and pharmacological interventions. A case discussion illustrates these concepts with a specific patient, highlighting her symptoms, pertinent history, and potential treatment strategies.