This document discusses psychotic disorders including schizophrenia. It provides details on:
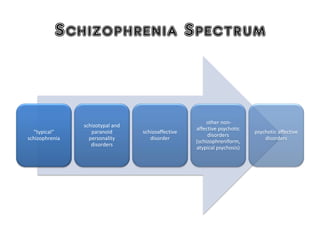
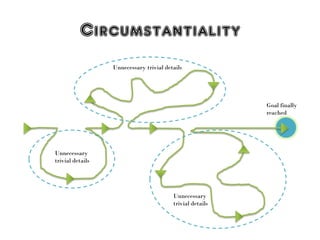
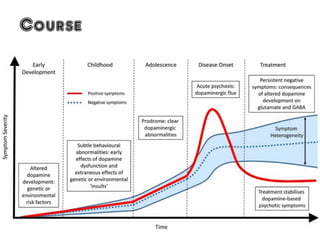
1) The diagnostic criteria and characteristics of schizophrenia according to the DSM-5 including symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized speech.
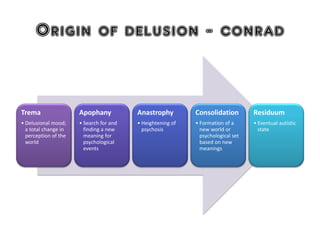
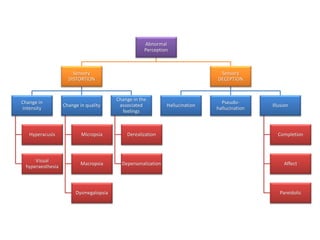
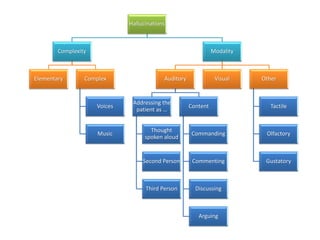
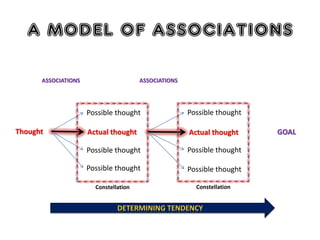
2) The origins and models of delusions and hallucinations, which are common symptoms of schizophrenia. It describes different types of hallucinations and models of thought organization.
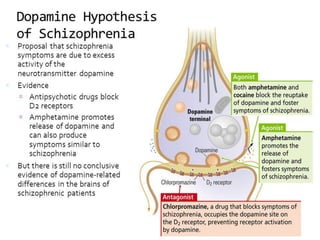
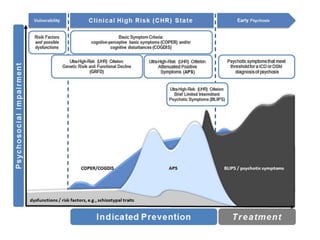
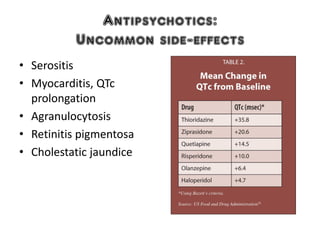
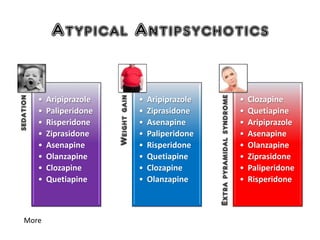
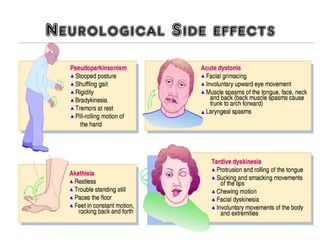
3) Treatment options for schizophrenia including antipsychotic medications and psychosocial interventions. Common atypical antipsychotics are listed and their side effect profiles described.