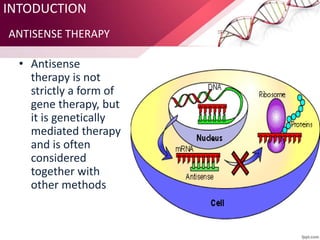
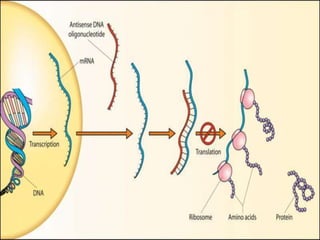
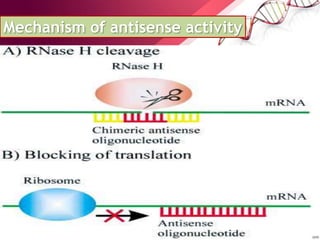
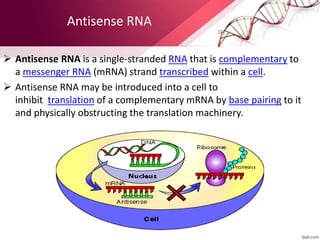
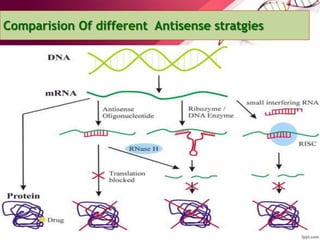
Antisense therapy is a form of genetic treatment that uses artificially synthesized nucleic acid sequences to bind to messenger RNA (mRNA) produced by a disease-causing gene, inactivating it and effectively turning the gene "off". This approach is being researched as a treatment for various diseases including cancers, diabetes, ALS, and muscular dystrophy. Antisense drugs work by forming DNA/RNA hybrids that are degraded by the RNase H enzyme, preventing translation of the mRNA into protein.