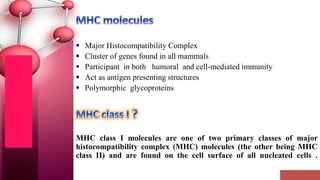
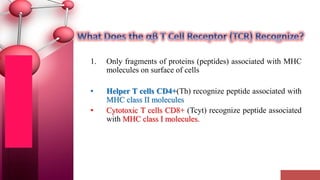
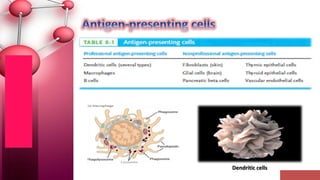
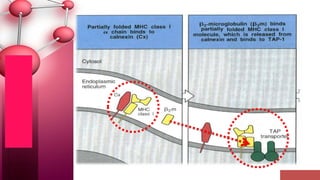
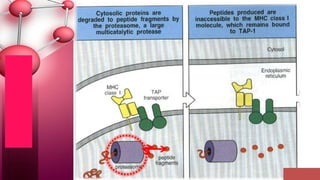
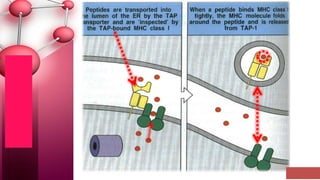
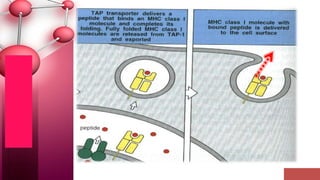
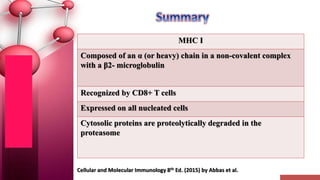
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules are crucial for immune response, presenting peptide fragments of non-self proteins to cytotoxic T cells. They consist of an α-chain and β2-microglobulin, with recognition requiring cell contact and specific peptide-MHC association. If the MHC I molecules are absent, natural killer (NK) cells respond to potentially infected cells, indicating their role in cellular immunity.