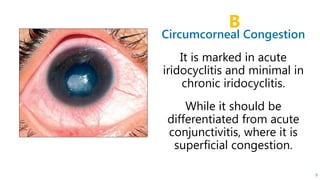
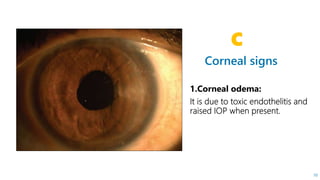
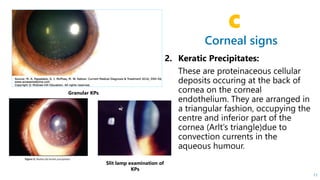
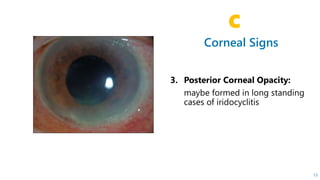
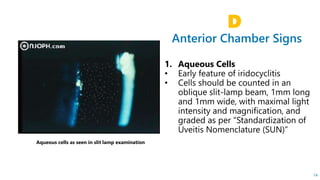
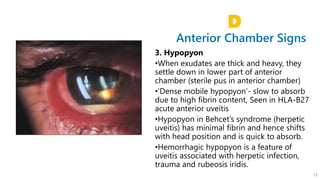
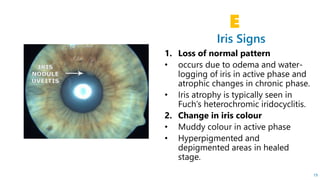
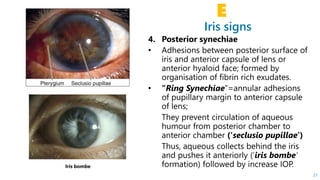
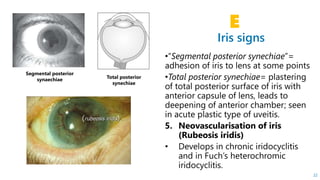
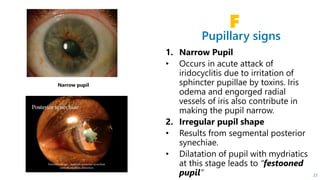
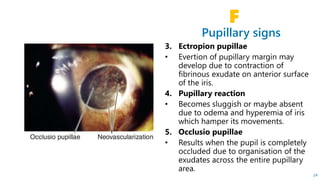
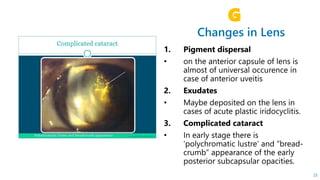
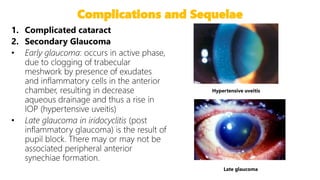
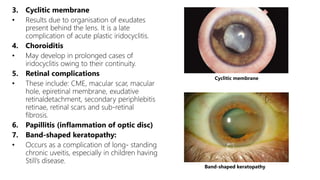
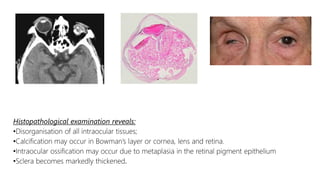
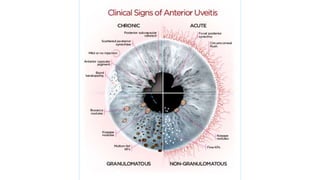
This document describes the symptoms, signs, and differential diagnosis of uveitis. The key symptoms are dull aching and throbbing pain that is worse at night and referred to the forehead and scalp. Examination findings include lid edema, keratic precipitates, aqueous cells and flare, iris nodules and posterior synechiae, changes to the lens and intraocular pressure, and complications such as glaucoma. Granulomatous and non-granulomatous uveitis can be differentiated based on features such as onset, pain, photophobia, ciliary congestion, and characteristics of keratic precipitates, aqueous flare, iris involvement, and posterior synechiae. Careful slit lamp