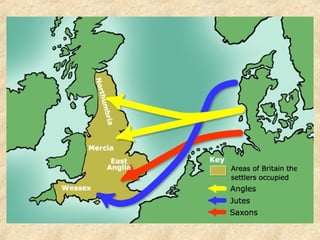
The document provides background information on the Anglo-Saxons who invaded Britain around 450 CE and conquered much of the territory by 800 CE. It describes their warrior culture, which centered around kinship, lordship, and concepts like weregild, lof, and wyrd. It also discusses the oral tradition of epic poems like Beowulf, noting they were sung by bards and provided insights into the culture. The language of Beowulf, Old English, is examined as well, noting it uses unfamiliar letters but sounds similar to modern English once the letter sounds are known.