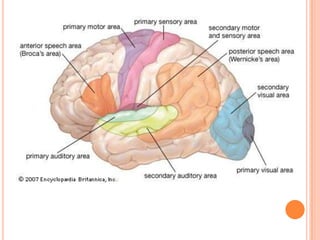
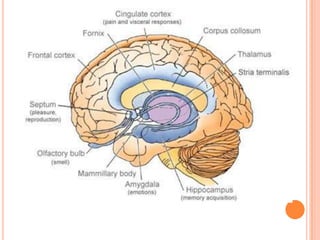
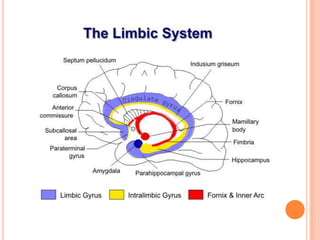
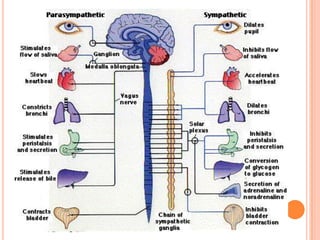
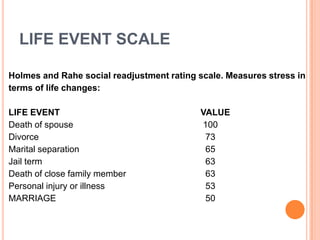
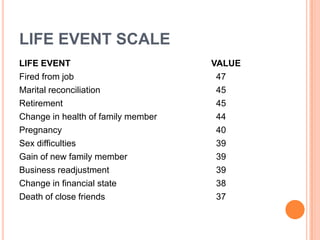
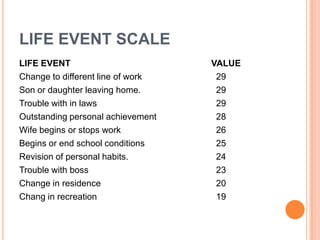
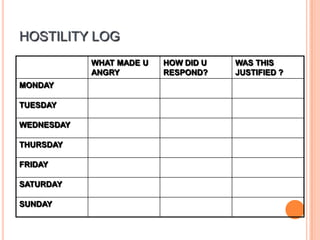
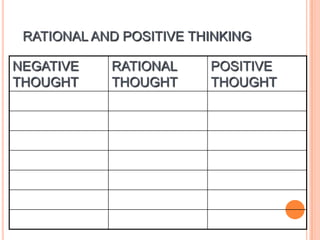
This document provides information on anger management. It discusses understanding stress and its effects, as well as strategies for managing anger. Biological, psychological, and social factors that influence behavior and stress responses are examined. Tools for managing anger include relaxation techniques like deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation. Maintaining an hostility log, using positive thinking, and seeking social support are also presented as anger management strategies.