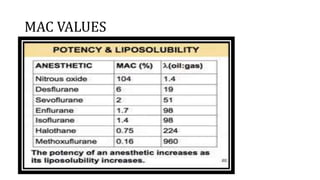
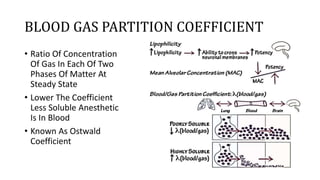
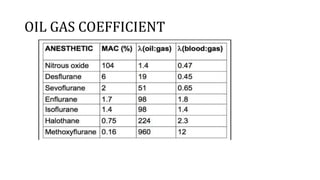
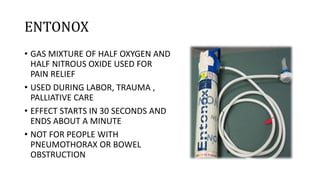
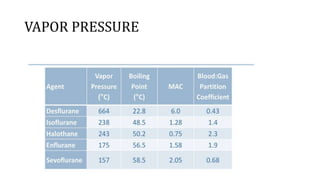
This document discusses inhalational anesthetics, including their properties, mechanisms of action, examples of agents, and factors that influence their potency and effects. It defines minimum alveolar concentration as the concentration needed to prevent movement in 50% of subjects in response to pain. Several volatile anesthetic agents are mentioned, such as halothane, isoflurane, desflurane, and sevoflurane, along with their characteristics and side effect profiles. Nitrous oxide is discussed as a gaseous anesthetic often used in combination with other agents.