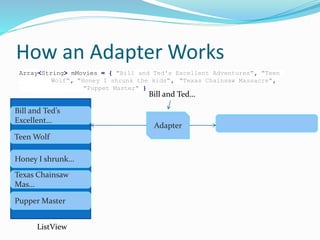
The document discusses the key components of a ListView in Android, including the ListView itself, list items, and data for each item. It explains that list items can contain simple or complex layouts. The data comes from adapters that act as intermediaries between the data source and ListView. Adapters fetch data, create layouts for each item, and return items to the ListView. Common data sources are arrays, content providers, and database cursors. The main adapter types are ArrayAdapter for arrays and SimpleCursorAdapter for content providers and cursors.