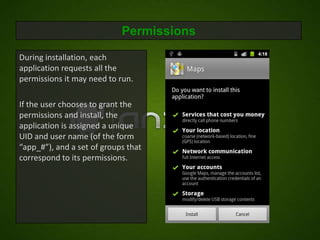
This document discusses Android security and outlines some of its key features and challenges. It describes how Android extends traditional UNIX security models through permissions and how permissions are enforced at different levels of the software stack, from installation to system calls to services. However, it notes some problems with Android's permission approach including coarse-grained permissions and difficulty updating devices. It proposes possible improvements such as better permission documentation and expanding security scanning.



![How Zygote Sets UIDS and GIDS:
[android/platform/dalvik.git]/vm/native/dalvik_system_Zygote.cpp
Set by Zygote. How?
static pid_t forkAndSpecializeCommon(const u4* args, bool
isSystemServer)
Before the application is {
run, the spawning process, pid_t pid;
uid_t uid = (uid_t) args[0];
zygote, uses standard UNIX gid_t gid = (gid_t) args[1];
system calls to set its UID ArrayObject* gids = (ArrayObject *)args[2];
……
and GIDs. pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
/* The child process */
……
err = setgroupsIntarray(gids);
……
err = setgid(gid);
……
err = setuid(uid);
……](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidsecuritymodel-120416034759-phpapp02/85/Android-security-model-5-320.jpg)
![How Permissions are Enforced – In the Kernel:
Example: socket()
[android/platform/system/core.git]/include/private/android_filesystem_config.h
Enforced by kernel. How?
/* The 3000 series are intended for use as supplemental group id's
only. */
/* They indicate special Android capabilities that the kernel is aware
On application install, of. */
AID_NET_BT_ADMIN 3001 /* bluetooth: create any socket */
some system permissions AID_NET_BT 3002 /* bluetooth: create sco, rfcomm or l2cap
are mapped to UNIX sockets */
AID_INET 3003 /* can create AF_INET and AF_INET6 sockets */
groups with standardized AID_NET_RAW 3004 /* can create raw INET sockets */
gids.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidsecuritymodel-120416034759-phpapp02/85/Android-security-model-6-320.jpg)