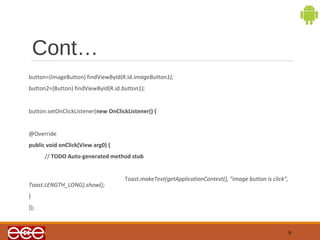
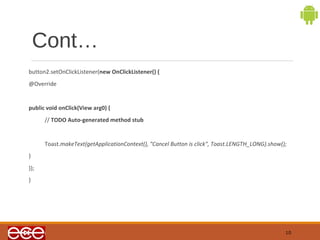
The document discusses buttons in Android applications. It explains that buttons can contain text or images and are defined in XML layout files using <Button> elements. The document also provides an example XML layout file with an ImageButton and Button, and the corresponding Java code to set onclick listeners for the buttons and display Toast messages when each button is clicked.