Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


![DOC ID
Paper Lead Acid System Technology
[1] Electric Vehicle (Mobile)
GPRS
[2] Stationary (Fixed)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kicsokapresentationfall2014-150216072511-conversion-gate01/85/Network-based-Wireless-for-Remote-Monitoring-Lead-Acid-Battery-4-320.jpg)
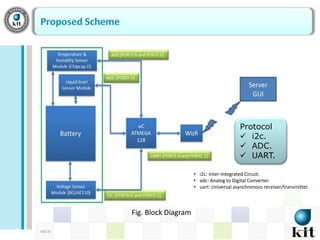
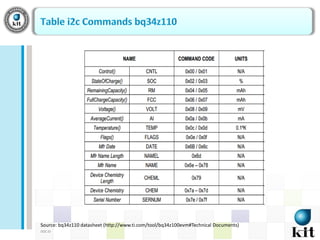
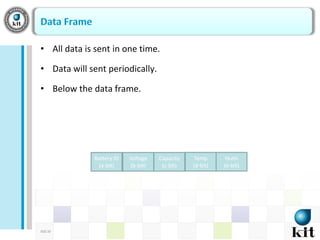
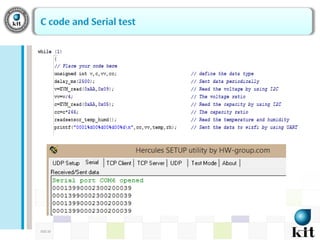
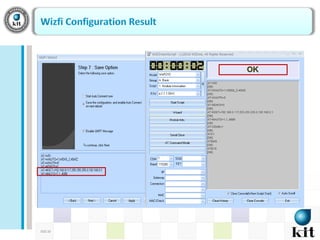
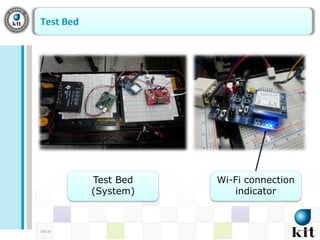
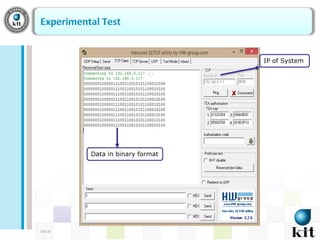
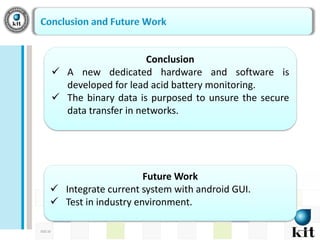



This document presents a network-based wireless system for remotely monitoring lead acid batteries. It introduces the proposed scheme which uses IP networks to monitor batteries in real-time and securely from mobile or fixed systems. The system collects data from batteries using I2C, ADC and UART protocols, frames it for transmission, and sends it periodically over Wi-Fi networks. Experimental results demonstrate proof-of-concept and the authors conclude it is a new dedicated monitoring system, while future work involves integrating an Android GUI and industry testing.



![DOC ID
Paper Lead Acid System Technology
[1] Electric Vehicle (Mobile)
GPRS
[2] Stationary (Fixed)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kicsokapresentationfall2014-150216072511-conversion-gate01/85/Network-based-Wireless-for-Remote-Monitoring-Lead-Acid-Battery-4-320.jpg)










