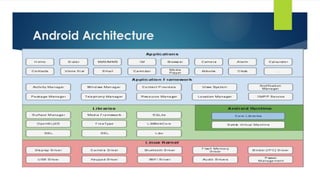
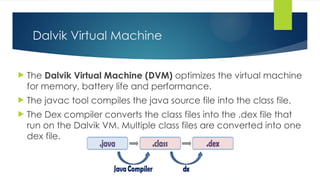
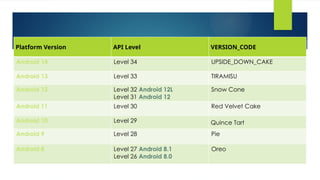
The document provides a comprehensive overview of mobile application development, particularly focusing on the history and evolution of mobile phones and the Android operating system. It discusses the architecture of Android, including its various components such as application framework, runtime, and libraries, along with the significance of the Linux kernel in managing hardware drivers and ensuring security. Additionally, it highlights the tools and technologies used for mobile app development, including SDKs and development frameworks like Java, Kotlin, and Flutter.