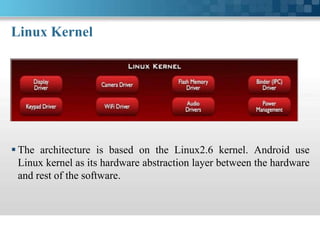
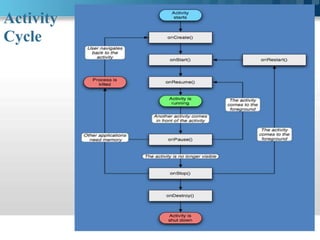
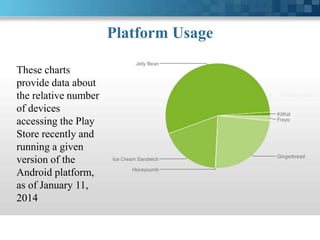
This document presents information about Android. It discusses what Android is, its history and architecture. The architecture includes layers such as the Linux kernel, native libraries, Android runtime and application framework. It also discusses Android's application lifecycle, development tools used, programming languages, advantages like being open source, and limitations like battery life. Future possibilities for Android discussed include lock screens with shortcuts, better notifications, always-listening voice control and multi-touch swipe controls. The document concludes with a bibliography citing sources of information about Android.