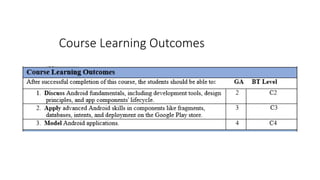
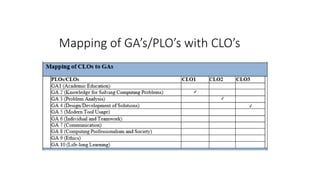
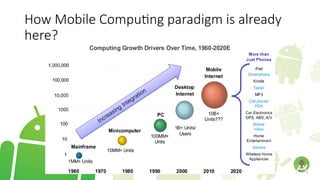
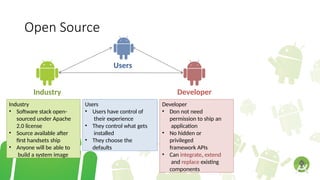
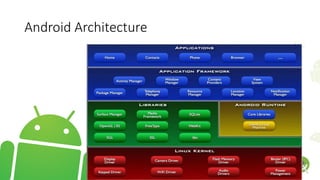
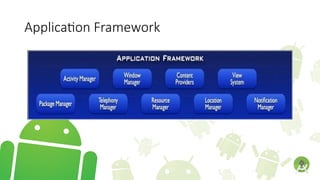
The document outlines the introduction to a mobile application development course focused on Android, detailing course objectives, assessments, attendance policies, and required materials. It covers the history of Android, its architecture, and the tools necessary for development, such as Android Studio and the Android SDK. Key topics include the Android ecosystem, the evolution of Android versions, and guidelines for effective participation and submissions in the course.