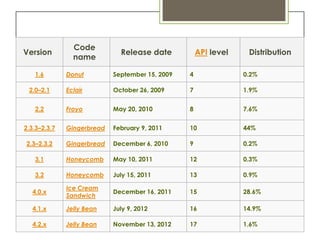
The document discusses a seminar on Android technology, detailing its introduction, platform, development tools, various versions, and overall evaluation. It outlines the operating system's features, security mechanisms, the evolution through different versions from Cupcake to Jelly Bean, and highlights advantages, limitations, and future possibilities for the Android platform. The conclusion expresses hope for future versions to address existing limitations and actualize potential.