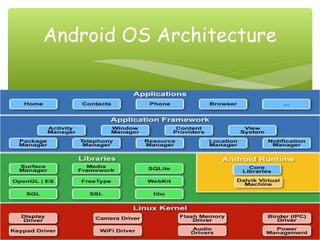
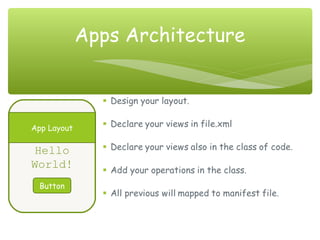
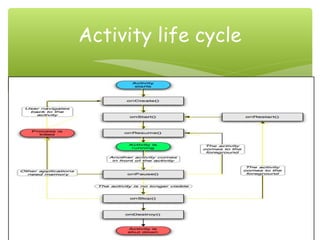
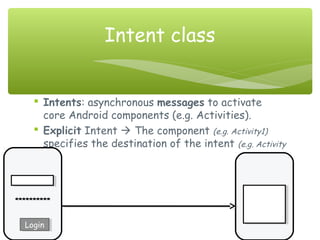
This document provides an overview of the Android operating system, including its history, architecture, apps, and development challenges. It discusses that Android was founded in 2003 by Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Nick Sears and Chris White. In 2007, the Open Handset Alliance was formed between Google, device manufacturers, wireless carriers and chipset makers to develop Android. It then covers the main Android versions from 2008 to present, the architecture including activities and intents, and challenges such as fragmentation and screen sizes.