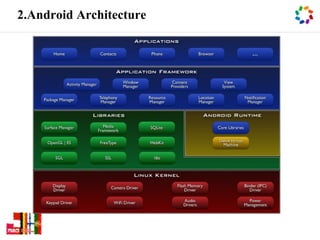
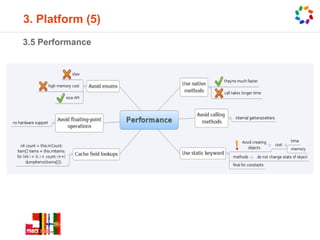
Android is the world's most popular mobile platform, allowing users to use Google apps and access over 600,000 third-party apps and games from Google Play. It powers hundreds of millions of devices globally across 190+ countries. Android devices offer new features not found on other platforms and put users in control of their mobile experience.