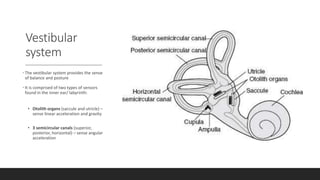
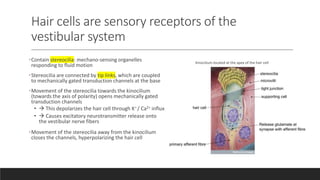
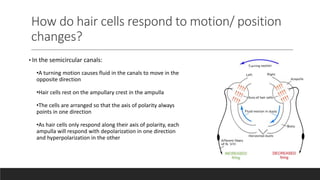
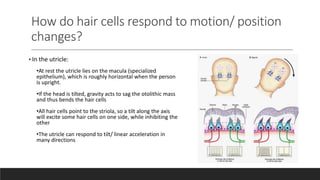
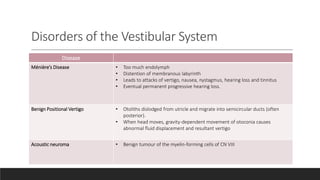
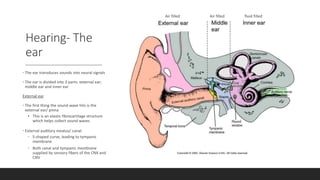
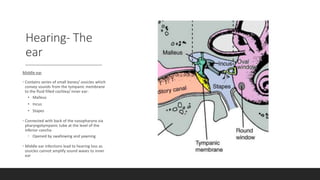
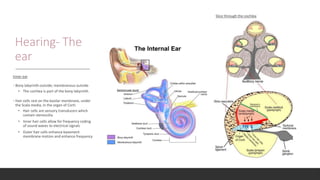
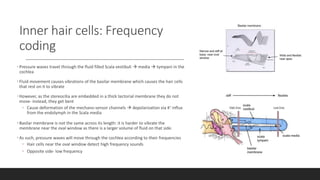
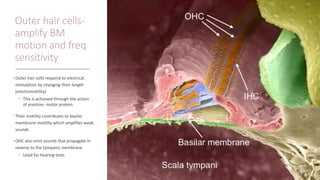
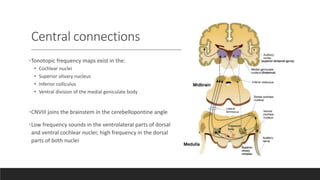
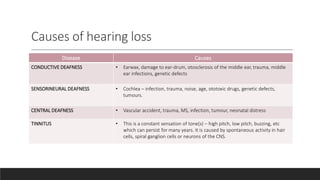
The vestibular system senses balance and head position using hair cells in the inner ear that detect linear and angular acceleration. Hair cells contain stereocilia that open ion channels when bent, triggering neurotransmitter release. Semicircular canals detect turning while otolith organs sense gravity. Disorders include Ménière's disease and benign positional vertigo. The ear transduces sound into neural signals. Sound waves hit the tympanic membrane and ossicles, vibrating the cochlea's basilar membrane. Hair cells along it fire at different frequencies. Inner hair cells transmit signals while outer hair cells amplify vibrations. Hearing loss can be conductive, sensorineural, or central.