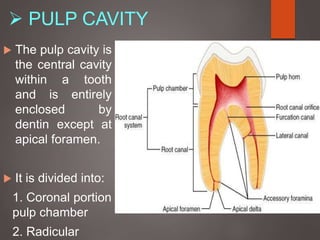
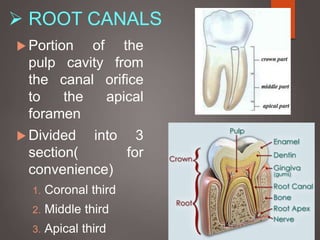
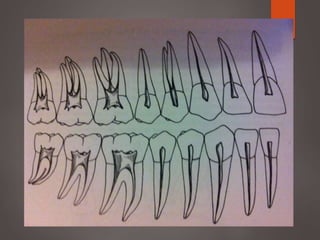
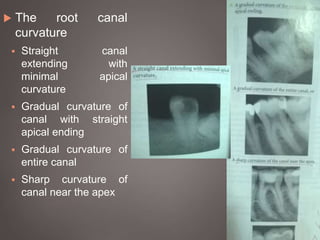
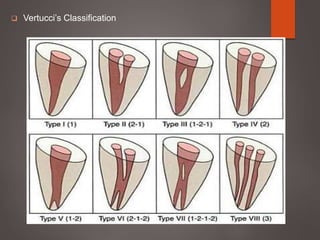
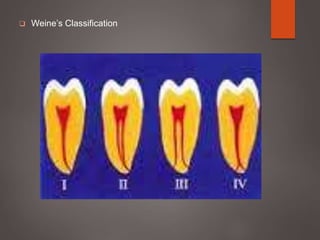
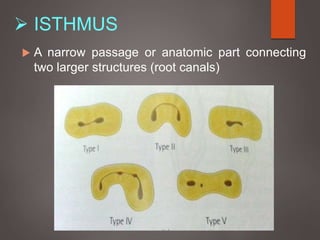
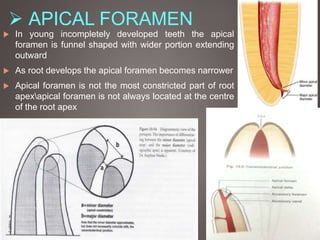
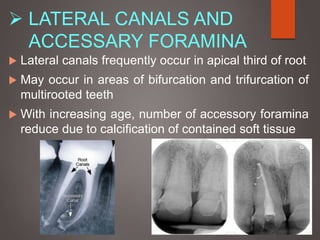
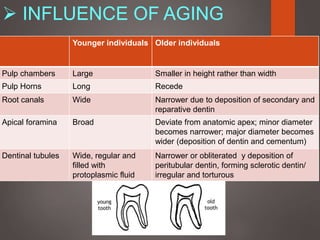
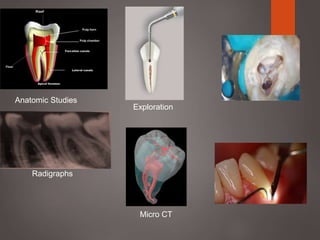
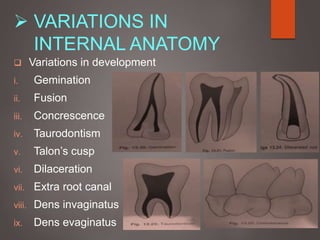
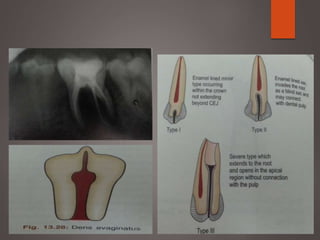
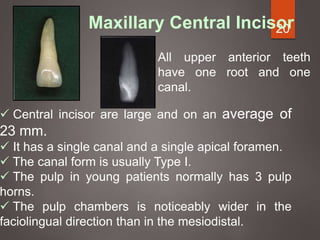
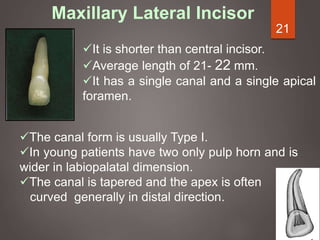
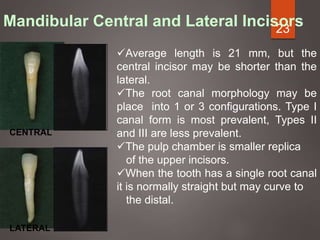
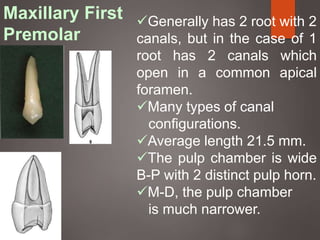
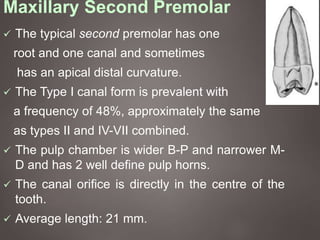
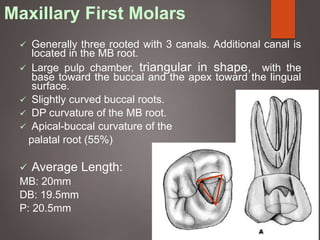
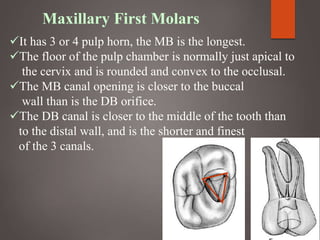
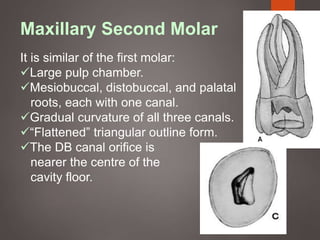
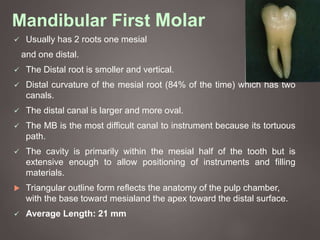
The document provides an in-depth overview of tooth pulp anatomy, including the pulp cavity, pulp chamber, root canals, and variations in dental anatomy. It discusses the structural characteristics of various teeth, their canal configurations, and the impact of aging on pulp anatomy. Additionally, it covers methods for determining pulp anatomy and variations such as gemination and fusion.