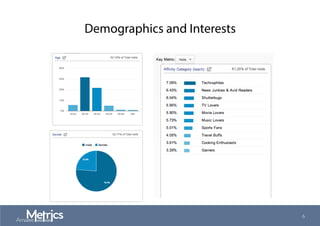
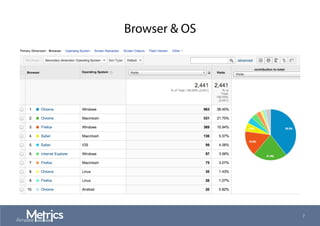
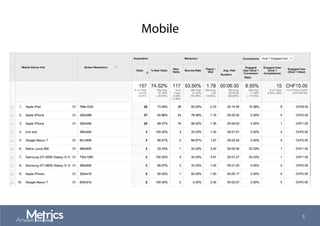
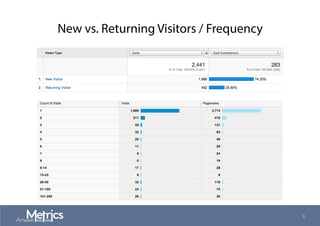
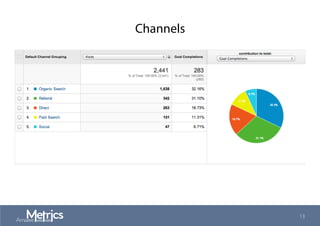
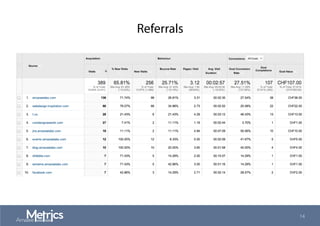
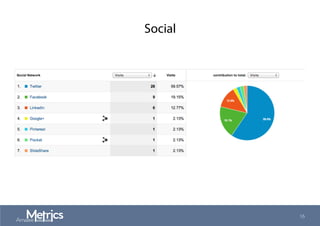
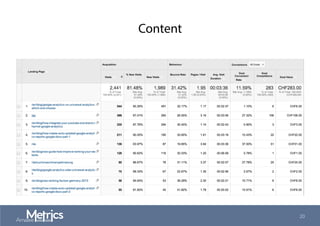
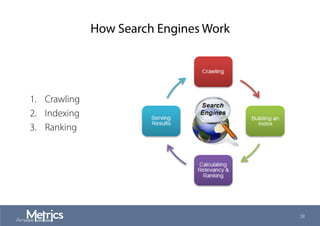
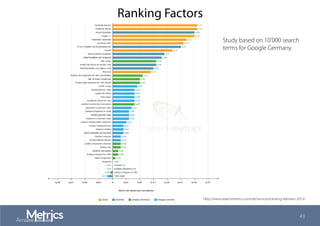
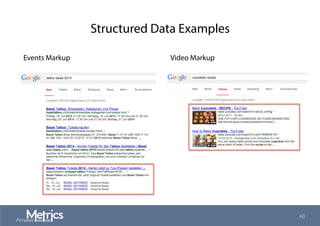
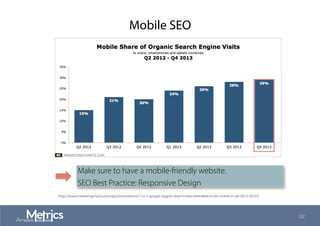
This document provides an overview of web analytics and search engine optimization (SEO) strategies for startups. It discusses using web analytics to understand website audiences, how visitors find and use the site, and measuring key metrics. For SEO, it outlines technical optimization strategies like keyword research, on-page elements, internal linking, and site speed. The goal is to help startups make data-driven decisions to improve performance.