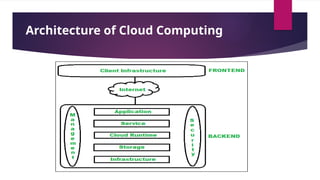
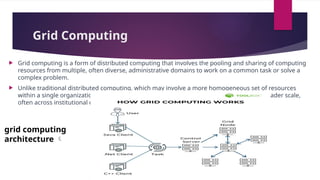
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, highlighting its definition, real-life applications, and architecture, including frontend and backend components. It outlines the advantages such as cost efficiency and scalability, along with disadvantages including security concerns and vendor lock-in. Additionally, it discusses cluster and grid computing, their architectures, benefits, and challenges, emphasizing their role in enhancing computational power and resource sharing.