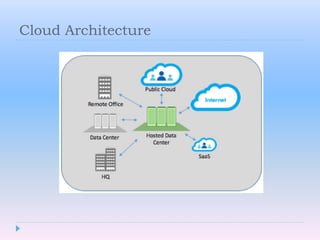
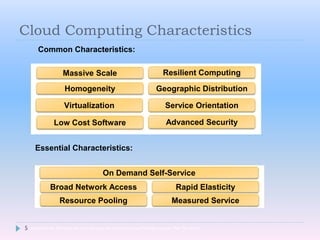
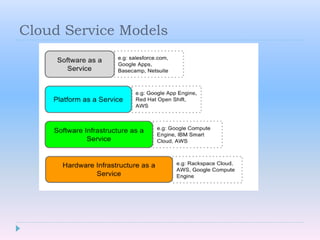
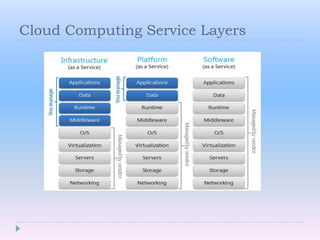
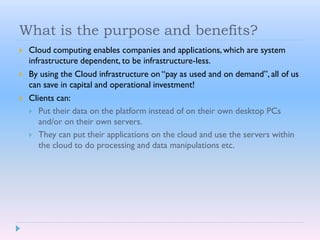
Cloud computing allows users to access software, storage, and services over the Internet. It provides on-demand access to shared computing resources that can be accessed from anywhere, scales up or down depending on usage, and users only pay for the resources they use. Key characteristics include hosting services remotely over the Internet, ubiquitous access from any device, and paying for what you use similar to a utility.