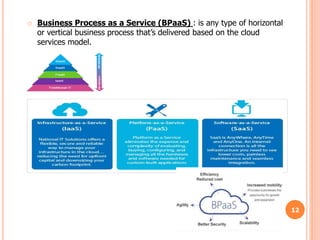
Cloud computing refers to a network-based computing model that provides on-demand services over the internet, allowing businesses to save on capital and operational investments. The document outlines its history, types (public, private, hybrid), advantages like flexibility and cost savings, and disadvantages such as dependency and security concerns. Overall, cloud computing is characterized by its ability to make resources accessible anywhere, while also posing challenges in terms of data security and provider dependency.