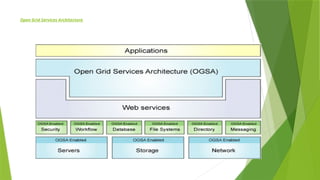
The document explains the Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA), a framework for connecting and managing various computer resources over a network, allowing efficient sharing of computing power and data for complex problem-solving. It breaks down the components of OGSA into layers: applications, management (OGSA), communication (web services), specialized services, and infrastructure, each serving a specific role in ensuring seamless integration and functionality. Additionally, it highlights the Open Grid Services Infrastructure (OGSI) that facilitates collaboration among multiple computers, sharing resources, managing tasks, and providing security for efficient grid computing.