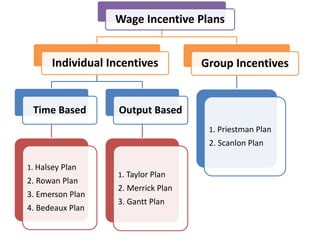
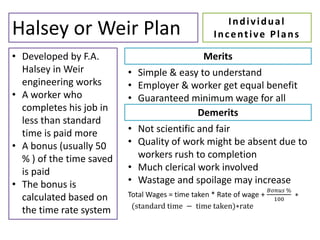
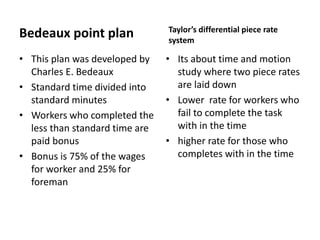
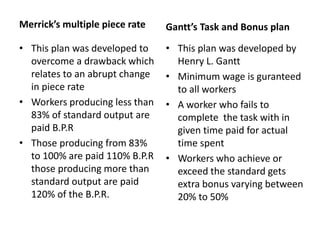
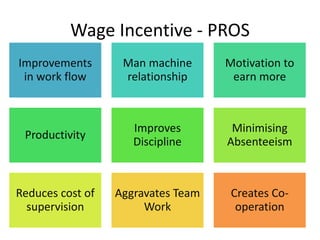
This document discusses wage incentives and fringe benefits. It defines wage incentives as extra financial motivations designed to stimulate effort and reward performance. It then describes various types of individual and group incentive plans such as Halsey, Rowan, Emerson, and Scanlon plans. The pros of incentives include improved productivity and motivation, while the cons include risks to health from overwork. Fringe benefits are described as supplementary compensation provided in addition to wages, such as paid time off, health benefits, and retirement plans, with the objectives of improving industrial relations and employee welfare.